SNVSA56B May 2015 – February 2017 LM2776
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.2.2 Detailed Design Requirements
The main application of LM2776 is to generate a negative supply voltage. The voltage inverter circuit uses only three external capacitors with an range of the input supply voltage from 2.7 V to 5.5 V.
The LM2776 contains four large CMOS switches which are switched in a sequence to invert the input supply voltage. Energy transfer and storage are provided by external capacitors. Figure 19 shows the voltage conversion scheme. When S1 and S3 are closed, C1 charges to the supply voltage VIN. During this time interval, switches S2 and S4 are open. In the second time interval, S1 and S3 are open; at the same time, S2 and S4 are closed, C1 is charging C2. After a number of cycles, the voltage across C2 is pumped to VIN. Because the anode of C2 is connected to ground, the output at the cathode of C2 equals −(VIN) when there is no load current. The output voltage drop when a load is added is determined by the parasitic resistance (Rds(on) of the MOSFET switches and the equivalent series resistance (ESR) of the capacitors) and the charge transfer loss between capacitors.
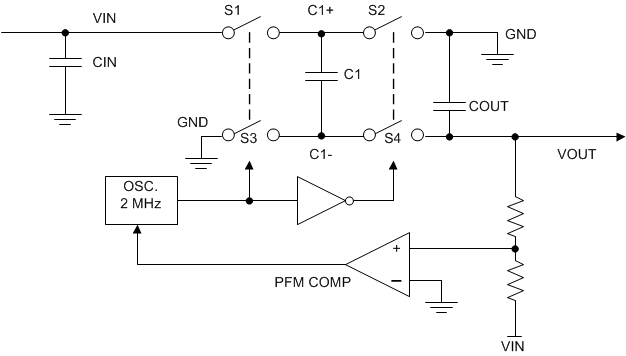 Figure 19. Voltage Inverting Principle
Figure 19. Voltage Inverting Principle The output characteristics of this circuit can be approximated by an ideal voltage source in series with a resistance. The voltage source equals − (VIN). The output resistance ROUT is a function of the ON resistance of the internal MOSFET switches, the oscillator frequency, the capacitance and ESR of C1 and C2. Because the switching current charging and discharging C1 is approximately twice as the output current, the effect of the ESR of the pumping capacitor C1 is multiplied by four in the output resistance. The output capacitor C2 is charging and discharging at a current approximately equal to the output current, therefore, its ESR only counts once in the output resistance. A good approximation of ROUT is:
where
- RSW is the sum of the ON resistance of the internal MOSFET switches shown in Figure 19.
High-capacitance, low-ESR ceramic capacitors reduce the output resistance.