-
LMR23610-Q1 SIMPLE SWITCHER® 36 V, 1 A Synchronous Step-Down Converter
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Fixed Frequency Peak Current Mode Control
- 7.3.2 Adjustable Output Voltage
- 7.3.3 Enable/Sync
- 7.3.4 VCC, UVLO
- 7.3.5 Minimum ON-time, Minimum OFF-time and Frequency Foldback at Drop-out Conditions
- 7.3.6 Internal Compensation and CFF
- 7.3.7 Bootstrap Voltage (BOOT)
- 7.3.8 Over Current and Short Circuit Protection
- 7.3.9 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 8.2.2.2 Output Voltage Set-Point
- 8.2.2.3 Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.4 Inductor Selection
- 8.2.2.5 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.6 Feed-Forward Capacitor
- 8.2.2.7 Input Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.8 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.9 VCC Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.10 Under Voltage Lockout Set-Point
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
- IMPORTANT NOTICE
LMR23610-Q1 SIMPLE SWITCHER® 36 V, 1 A Synchronous Step-Down Converter
1 Features
- Qualified for Automotive Applications
- AEC-Q100 Qualified With the Following Results:
- Device Temperature Grade 1: -40 °C to 125 °C Ambient Operating Temperature Range
- Device HBM ESD Classification Level H1C
- Device CDM ESD Classification Level C4A - 4 V to 36 V Input Range
- 1 A Continuous Output Current
- Integrated Synchronous Rectification
- Current Mode Control
- Minimum Switch-On Time: 60 ns
- Internal Compensation for Ease of Use
- 400 kHz Switching Frequency With PFM Mode
- Frequency Synchronization to External Clock
- 75 µA Quiescent Current at No Load
- Soft-Start into a Pre-Biased Load
- High Duty Cycle Operation Supported
- Output Short-Circuit Protection with Hiccup Mode
- 8-Pin HSOIC with PowerPAD™ Package Options
- Create a Custom Design Using the LMR23610-Q1 With the WEBENCH® Power Designer
2 Applications
- Automotive Battery Regulation
- Industrial Power Supplies
- Telecom and Datacom Systems
- General Purpose Wide Vin Regulation
space
3 Description
The LMR23610-Q1 SIMPLE SWITCHER® is an easy to use 36 V, 1 A synchronous step down regulator. With a wide input range from 4 V to 36 V, it is suitable for various applications from industrial to automotive for power conditioning from unregulated sources. Peak current mode control is employed to achieve simple control loop compensation and cycle-by-cycle current limiting. A quiescent current of 75 µA makes it suitable for battery powered systems. Internal loop compensation means that the user is free from the tedious task of loop compensation design. This also minimizes the external components. An extended family is available in 1.5 A (LMR23615-Q1), 2.5 A (LMR23625-Q1) and 3 A (LMR23630-Q1) load current options in pin-to-pin compatible packages which allows simple, optimum PCB layout. A precision enable input allows simplification of regulator control and system power sequencing. Protection features include cycle-by-cycle current limit, hiccup mode short circuit protection and thermal shutdown due to excessive power dissipation.
Device Information(1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE (NOM) |
|---|---|---|
| LMR23610AQDDARQ1 | HSOIC (8) | 4.9 mm x 3.9 mm |
- For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at the end of the data sheet.
Simplified Schematic
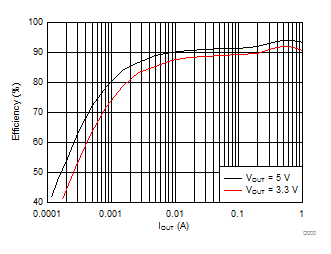
Efficiency vs Load, VIN = 12 V
4 Revision History
NOTE: Page numbers for previous revisions may differ from page numbers in the current version.
Changes from * Revision (December 2016) to A Revision
- Changed the value for HBM from ±2500 to ±2000Go
5 Pin Configuration and Functions

Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O (1) | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| SW | 1 | P | Switching output of the regulator. Internally connected to both power MOSFETs. Connect to power inductor. |
| BOOT | 2 | P | Boot-strap capacitor connection for high-side driver. Connect a high quality 100 nF capacitor from BOOT to SW. |
| VCC | 3 | P | Internal bias supply output for bypassing. Connect a 2.2 μF/ 16 V or higher capacitance bypass capacitor from this pin to AGND. Do not connect external loading to this pin. Never short this pin to ground during operation. |
| FB | 4 | A | Feedback input to regulator, connect the feedback resistor divider tap to this pin. |
| EN/SYNC | 5 | A | Enable input to regulator. High = On, Low = Off. Can be connected to VIN. Do not float. Adjust the input under voltage lockout with two resistors. The internal oscillator can be synchronized to an external clock by coupling a positive pulse into this pin through a small coupling capacitor. See Enable/Sync for detail. |
| AGND | 6 | G | Analog ground pin. Ground reference for internal references and logic. Connect to system ground. |
| VIN | 7 | P | Input supply voltage. |
| PGND | 8 | G | Power ground pin, connected internally to the low side power FET. Connect to system ground, PAD, AGND, ground pins of CIN and COUT. Path to CIN must be as short as possible. |
| PAD | 9 | G | Low impedance connection to AGND. Connect to PGND on PCB. Major heat dissipation path of the die. Must be used for heat sinking to ground plane on PCB. |
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
Over the recommended operating junction temperature range of -40 °C to 125 °C (unless otherwise noted) (1)| PARAMETER | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input Voltages | VIN to PGND | -0.3 | 42 | V |
| EN/SYNC to AGND | -5.5 | VIN + 0.3 | ||
| FB to AGND | -0.3 | 4.5 | ||
| AGND to PGND | -0.3 | 0.3 | ||
| Output Voltages | SW to PGND | -1 | VIN + 0.3 | V |
| SW to PGND less than 10 ns transients | -5 | 42 | ||
| BOOT to SW | -0.3 | 5.5 | ||
| VCC to AGND | -0.3 | 4.5 (2) | ||
| TJ | Junction temperature | -40 | 150 | °C |
| Tstg | Storage temperature | -65 | 150 | °C |
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM) (1) | ±2000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM) | ±1000 | |||
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
Over the recommended operating junction temperature range of -40 °C to 125 °C (unless otherwise noted) (1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input Voltage | VIN | 4 | 36 | V |
| EN/SYNC | -5 | 36 | ||
| FB | -0.3 | 1.2 | ||
| Output Voltage | VOUT | 1 | 28 | V |
| Output Current | IOUT | 0 | 1 | A |
| Temperature | Operating junction temperature, TJ | -40 | 125 | °C |
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC (1) (2) | DDA (8 PINS) | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 42.0 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 5.9 | |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 23.4 | |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 45.8 | |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | 3.6 | |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 23.4 | |
6.5 Electrical Characteristics
Limits apply over the recommended operating junction temperature (TJ) range of -40 °C to +125 °C, unless otherwise stated. Minimum and Maximum limits are specified through test, design or statistical correlation. Typical values represent the most likely parametric norm at TJ = 25 °C, and are provided for reference purposes only.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| POWER SUPPLY (VIN PIN) | ||||||
| VIN | Operation input voltage | 4 | 36 | V | ||
| VIN_UVLO | Under voltage lockout thresholds | Rising threshold | 3.3 | 3.7 | 3.9 | V |
| Falling threshold | 2.9 | 3.3 | 3.5 | |||
| ISHDN | Shutdown supply current | VEN = 0 V, VIN = 12 V, TJ = -40 °C to 125 °C | 2.0 | 4.0 | μA | |
| IQ | Operating quiescent current (non- switching) | VIN =12 V, VFB = 1.1 V, TJ = -40 °C to 125 °C, PFM mode | 75 | μA | ||
| ENABLE (EN PIN) | ||||||
| VEN_H | Enable rising threshold Voltage | 1.4 | 1.55 | 1.7 | V | |
| VEN_HYS | Enable hysteresis voltage | 0.4 | V | |||
| VWAKE | Wake-up threshold | 0.4 | V | |||
| IEN | Input leakage current at EN pin | VIN = 4 V to 36 V, VEN= 2 V | 10 | 100 | nA | |
| VIN = 4 V to 36 V, VEN= 36 V | 1 | μA | ||||
| VOLTAGE REFERENCE (FB PIN) | ||||||
| VREF | Reference voltage | VIN = 4 V to 36 V, TJ = 25 °C | 0.985 | 1.0 | 1.015 | V |
| VIN = 4 V to 36 V, TJ = -40 °C to 125 °C | 0.980 | 1.0 | 1.020 | |||
| ILKG_FB | Input leakage current at FB pin | VFB= 1 V | 10 | nA | ||
| INTERNAL LDO (VCC PIN) | ||||||
| VCC | Internal LDO output voltage | 4.1 | V | |||
| VCC_UVLO | VCC under voltage lockout thresholds | Rising threshold | 2.8 | 3.2 | 3.6 | V |
| Falling threshold | 2.4 | 2.8 | 3.2 | |||
| CURRENT LIMIT | ||||||
| IHS_LIMIT | Peak inductor current limit | 1.4 | 2.0 | 2.6 | A | |
| ILS_LIMIT | Valley inductor current limit | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.1 | A | |
| IL_ZC | Zero cross current limit | -0.04 | A | |||
| INTEGRATED MOSFETS | ||||||
| RDS_ON_HS | High-side MOSFET ON-resistance | VIN = 12 V, IOUT = 1 A | 185 | mΩ | ||
| RDS_ON_LS | Low-side MOSFET ON-resistance | VIN = 12 V, IOUT = 1 A | 105 | mΩ | ||
| THERMAL SHUTDOWN | ||||||
| TSHDN | Thermal shutdown threshold | 162 | 170 | 178 | °C | |
| THYS | Hysteresis | 15 | °C | |||
6.6 Timing Characteristics
Over the recommended operating junction temperature range of -40 °C to 125 °C (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HICCUP MODE | ||||||
| NOC(1) | Number of cycles that LS current limit is tripped to enter Hiccup mode | 64 | Cycles | |||
| TOC | Hiccup retry delay time | 5 | ms | |||
| SOFT START | ||||||
| TSS | Internal soft-start time | The time of internal reference to increase from 0 V to 1.0 V | 1 | 2 | 3 | ms |
6.7 Switching Characteristics
Over the recommended operating junction temperature range of -40 °C to 125 °C (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SW (SW PIN) | ||||||
| fSW | Default switching frequency | 340 | 400 | 460 | kHz | |
| TON_MIN | Minimum turn-on time | 60 | 90 | ns | ||
| TOFF_MIN(1) | Minimum turn-off time | 100 | ns | |||
| SYNC (EN/SYNC PIN) | ||||||
| fSYNC | SYNC frequency range | 200 | 2200 | kHz | ||
| VSYNC | Amplitude of SYNC clock AC signal (measured at SYNC pin) | 2.8 | 5.5 | V | ||
| TSYNC_MIN | Minimum sync clock ON and OFF time | 100 | ns | |||
6.8 Typical Characteristics
Unless otherwise specified the following conditions apply: VIN = 12 V, fSW = 400 kHz, L = 22 µH, COUT = 47 µF × 2, TA = 25°C.
| fSW = 400 kHz | VOUT = 5 V |

| fSW = 1000 kHz (Sync) | VOUT = 5 V |

| VOUT = 5 V |

| VOUT = 5 V |

| VIN = 12 V | VFB = 1.1 V |


| fSW = 400 kHz | VOUT = 3.3 V |

| fSW = 1000 kHz (Sync) | VOUT = 3.3 V |

| VOUT = 5 V |

| VOUT = 3.3 V |


| VIN = 12 V |
7 Detailed Description
7.1 Overview
The LMR23610-Q1 SIMPLE SWITCHER® regulator is an easy to use synchronous step-down DC-DC converter operating from 4 V to 36 V supply voltage. It is capable of delivering up to 1 A DC load current with good thermal performance in a small solution size. An extended family is available in multiple current options from 1 A to 3 A in pin-to-pin compatible packages.
The LMR23610-Q1 employs fixed frequency peak current mode control. The device enters PFM mode at light load to achieve high efficiency. The device is internally compensated, which reduces design time, and requires few external components. The LMR23610-Q1 is capable of synchronization to an external clock within the range of 200 kHz to 2.2 MHz.
Additional features such as precision enable and internal soft-start provide a flexible and easy to use solution for a wide range of applications. Protection features include thermal shutdown, VIN and VCC under-voltage lockout, cycle-by-cycle current limit, and hiccup mode short-circuit protection.
The family requires very few external components and has a pin-out designed for simple, optimum PCB layout.
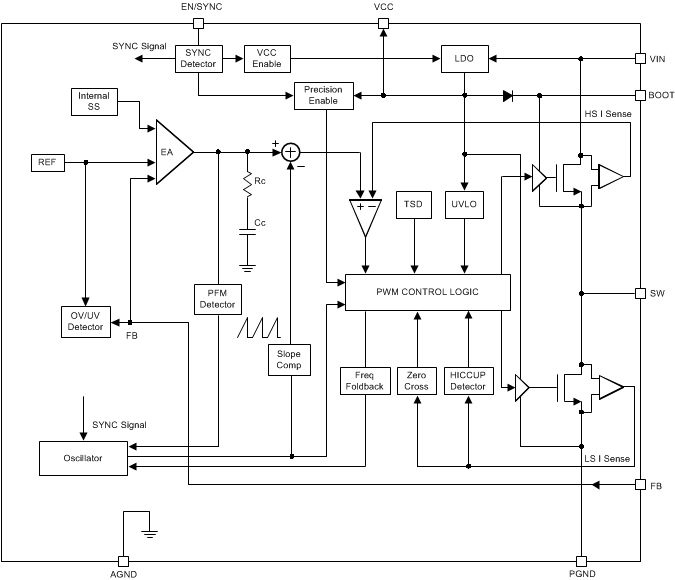
7.2 Functional Block Diagram
7.3 Feature Description
7.3.1 Fixed Frequency Peak Current Mode Control
The following operating description of the LMR23610-Q1 will refer to the Functional Block Diagram and to the waveforms in Figure 13. LMR23610-Q1 is a step-down synchronous buck regulator with integrated high-side (HS) and low-side (LS) switches (synchronous rectifier). The LMR23610-Q1 supplies a regulated output voltage by turning on the HS and LS NMOS switches with controlled duty cycle. During high-side switch ON time, the SW pin voltage swings up to approximately VIN, and the inductor current iL increase with linear slope (VIN – VOUT) / L. When the HS switch is turned off by the control logic, the LS switch is turned on after an anti-shoot-through dead time. Inductor current discharges through the LS switch with a slope of –VOUT / L. The control parameter of a buck converter is defined as Duty Cycle D = tON / TSW, where tON is the high-side switch ON time and TSW is the switching period. The regulator control loop maintains a constant output voltage by adjusting the duty cycle D. In an ideal buck converter, where losses are ignored, D is proportional to the output voltage and inversely proportional to the input voltage: D = VOUT / VIN.
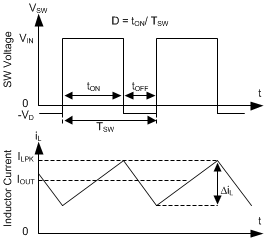 Figure 13. SW Node and Inductor Current Waveforms in
Figure 13. SW Node and Inductor Current Waveforms in Continuous Conduction Mode (CCM)
The LMR23610-Q1 employs fixed frequency peak current mode control. A voltage feedback loop is used to get accurate DC voltage regulation by adjusting the peak current command based on voltage offset. The peak inductor current is sensed from the high-side switch and compared to the peak current threshold to control the ON time of the high-side switch. The voltage feedback loop is internally compensated, which allows for fewer external components, makes it easy to design, and provides stable operation with almost any combination of output capacitors. The regulator operates with fixed switching frequency at normal load condition. At light load condition, the LMR23610-Q1 will operate in PFM mode to maintain high efficiency.
7.3.2 Adjustable Output Voltage
A precision 1.0 V reference voltage is used to maintain a tightly regulated output voltage over the entire operating temperature range. The output voltage is set by a resistor divider from output voltage to the FB pin. It is recommended to use 1% tolerance resistors with a low temperature coefficient for the FB divider. Select the low-side resistor RFBB for the desired divider current and use Equation 1 to calculate high-side RFBT. RFBT in the range from 10 kΩ to 100 kΩ is recommended for most applications. A lower RFBT value can be used if static loading is desired to reduce VOUT offset in PFM operation. Lower RFBT will reduce efficiency at very light load. Less static current goes through a larger RFBT and might be more desirable when light load efficiency is critical. But RFBT larger than 1 MΩ is not recommended because it makes the feedback path more susceptible to noise. Larger RFBT value requires more carefully designed feedback path on the PCB. The tolerance and temperature variation of the resistor dividers affect the output voltage regulation.
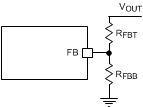 Figure 14. Output Voltage Setting
Figure 14. Output Voltage Setting
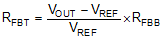
7.3.3 Enable/Sync
The voltage on the EN pin controls the ON or OFF operation of LMR23610-Q1. A voltage less than 1 V (typ) will shut-down the device while a voltage higher than 1.6 V (typ) is required to start the regulator. The EN pin is an input and can not be left open or floating. The simplest way to enable the operation of the LMR23610-Q1 is to connect the EN to VIN. This allows self-start-up of the LMR23610-Q1 when VIN is within the operation range.
Many applications will benefit from the employment of an enable divider RENT and RENB (Figure 15) to establish a precision system UVLO level for the converter. System UVLO can be used for supplies operating from utility power as well as battery power. It can be used for sequencing, ensuring reliable operation, or supply protection, such as a battery discharge level. An external logic signal can also be used to drive EN input for system sequencing and protection.
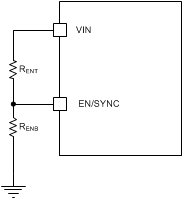 Figure 15. System UVLO by Enable Divider
Figure 15. System UVLO by Enable Divider
The EN pin also can be used to synchronize the internal oscillator to an external clock. The internal oscillator can be synchronized by AC coupling a positive edge into the EN pin. The AC coupled peak-to-peak voltage at the EN pin must exceed the SYNC amplitude threshold of 2.8 V (typ) to trip the internal synchronization pulse detector, and the minimum SYNC clock ON and OFF time must be longer than 100ns (typ). A 3.3 V or a higher amplitude pulse signal coupled through a 1 nF capacitor CSYNC is a good starting point. Keeping RENT // RENB (RENT parallel with RENB) in the 100 kΩ range is a good choice. RENT is required for this synchronization circuit, but RENB can be left unmounted if system UVLO is not needed. LMR23610-Q1 switching action can be synchronized to an external clock from 200 kHz to 2.2 MHz. Figure 17 and Figure 18 show the device synchronized to an external system clock.
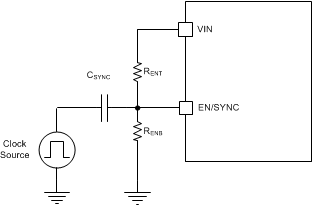 Figure 16. Synchronize to external clock
Figure 16. Synchronize to external clock
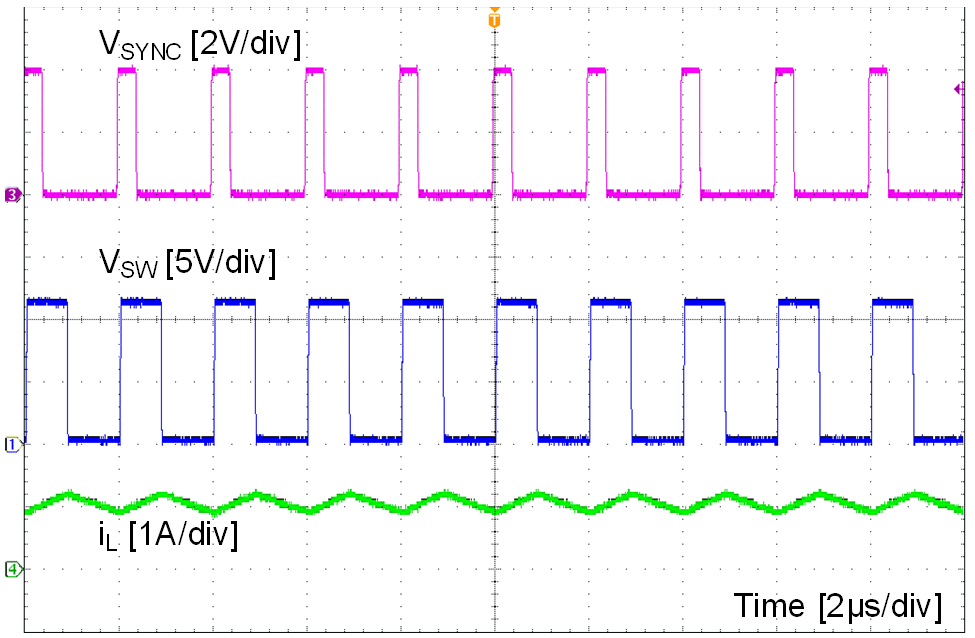 Figure 17. Synchronizing in PWM Mode
Figure 17. Synchronizing in PWM Mode
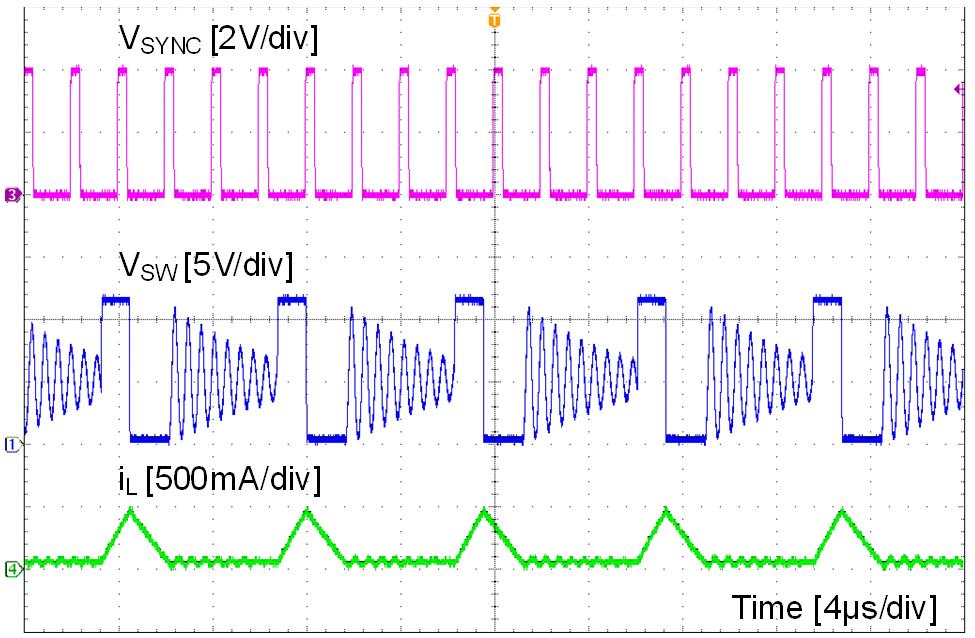 Figure 18. Synchronizing in PFM Mode
Figure 18. Synchronizing in PFM Mode
7.3.4 VCC, UVLO
The LMR23610-Q1 integrates an internal LDO to generate VCC for control circuitry and MOSFET drivers. The nominal voltage for VCC is 4.1 V. The VCC pin is the output of an LDO and must be properly bypassed. A high quality ceramic capacitor with a value of 2.2 µF to 10 µF, 16 V or higher rated voltage should be placed as close as possible to VCC and grounded to the exposed PAD and ground pins. The VCC output pin should not be loaded, or shorted to ground during operation. Shorting VCC to ground during operation may cause damage to the LMR23610-Q1.
VCC under voltage lockout (UVLO) prevents the LMR23610-Q1 from operating until the VCC voltage exceeds 3.2 V (typ). The VCC UVLO threshold has 400 mV (typ) of hysteresis to prevent undesired shutdown due to temporary VIN drops.
7.3.5 Minimum ON-time, Minimum OFF-time and Frequency Foldback at Drop-out Conditions
Minimum ON-time, TON_MIN, is the smallest duration of time that the HS switch can be on. TON_MIN is typically 60 ns in the LMR23610-Q1. Minimum OFF-time, TOFF_MIN, is the smallest duration that the HS switch can be off. TOFF_MIN is typically 100 ns in the LMR23610-Q1. In CCM operation, TON_MIN and TOFF_MIN limit the voltage conversion range given a selected switching frequency.
The minimum duty cycle allowed is:
And the maximum duty cycle allowed is:
Given fixed TON_MIN and TOFF_MIN, the higher the switching frequency the narrower the range of the allowed duty cycle. In the LMR23610-Q1, a frequency foldback scheme is employed to extend the maximum duty cycle when TOFF_MIN is reached. The switching frequency will decrease once longer duty cycle is needed under low VIN conditions. Wide range of frequency foldback allows the LMR23610-Q1 output voltage stay in regulation with a much lower supply voltage VIN. This leads to a lower effective drop-out voltage.
Given an output voltage, the choice of the switching frequency affects the allowed input voltage range, solution size and efficiency. The maximum operation supply voltage can be found by:
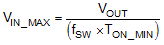
At lower supply voltage, the switching frequency will decrease once TOFF_MIN is tripped. The minimum VIN without frequency foldback can be approximated by:
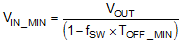
Taking considerations of power losses in the system with heavy load operation, VIN_MAX is higher than the result calculated in Equation 4. With frequency foldback, VIN_MIN is lowered by decreased fSW.
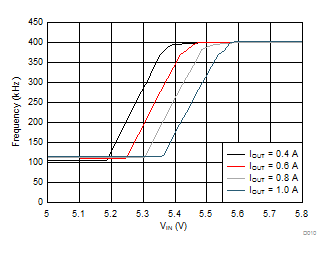 Figure 19. Frequency Foldback at Dropout (VOUT = 5 V, fSW = 400 kHz)
Figure 19. Frequency Foldback at Dropout (VOUT = 5 V, fSW = 400 kHz)
7.3.6 Internal Compensation and CFF
The LMR23610-Q1 is internally compensated as shown in Functional Block Diagram. The internal compensation is designed such that the loop response is stable over the entire operating frequency and output voltage range. Depending on the output voltage, the compensation loop phase margin can be low with all ceramic capacitors. An external feed-forward capacitor CFF is recommended to be placed in parallel with the top resistor divider RFBT for optimum transient performance.
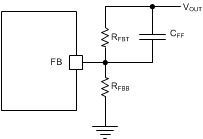 Figure 20. Feedforward Capacitor for Loop Compensation
Figure 20. Feedforward Capacitor for Loop Compensation
The feed-forward capacitor CFF in parallel with RFBT places an additional zero before the cross over frequency of the control loop to boost phase margin. The zero frequency can be found by
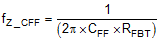
An additional pole is also introduced with CFF at the frequency of
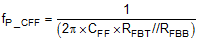
The zero fZ_CFF adds phase boost at the crossover frequency and improves transient response. The pole fP-CFF helps maintaining proper gain margin at frequency beyond the crossover. Table 1 lists the combination of COUT, CFF and RFBT for typical applications, designs with similar COUT but RFBT other than recommended value, please adjust CFF such that (CFF × RFBT) is unchanged and adjust RFBB such that (RFBT / RFBB) is unchanged.
Designs with different combinations of output capacitors need different CFF. Different types of capacitors have different Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR). Ceramic capacitors have the smallest ESR and need the most CFF. Electrolytic capacitors have much larger ESR and the ESR zero frequency
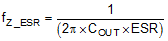
would be low enough to boost the phase up around the crossover frequency. Designs using mostly electrolytic capacitors at the output may not need any CFF.
The CFF creates a time constant with RFBT that couples in the attenuate output voltage ripple to the FB node. If the CFF value is too large, it can couple too much ripple to the FB and affect VOUT regulation. Therefore, CFF should be calculated based on output capacitors used in the system. At cold temperatures, the value of CFF might change based on the tolerance of the chosen component. This may reduce its impedance and ease noise coupling on the FB node. To avoid this, more capacitance can be added to the output or the value of CFF can be reduced.
7.3.7 Bootstrap Voltage (BOOT)
The LMR23610-Q1 provides an integrated bootstrap voltage regulator. A small capacitor between the BOOT and SW pins provides the gate drive voltage for the high-side MOSFET. The BOOT capacitor is refreshed when the high-side MOSFET is off and the low-side switch conducts. The recommended value of the BOOT capacitor is 0.1 μF. A ceramic capacitor with an X7R or X5R grade dielectric with a voltage rating of 16V or higher is recommended for stable performance over temperature and voltage.
7.3.8 Over Current and Short Circuit Protection
The LMR23610-Q1 is protected from over-current conditions by cycle-by-cycle current limit on both the peak and valley of the inductor current. Hiccup mode will be activated if a fault condition persists to prevent over-heating.
High-side MOSFET over-current protection is implemented by the nature of the Peak Current Mode control. The HS switch current is sensed when the HS is turned on after a set blanking time. The HS switch current is compared to the output of the Error Amplifier (EA) minus slope compensation every switching cycle. Please refer to Functional Block Diagram for more details. The peak current of HS switch is limited by a clamped maximum peak current threshold IHS_LIMIT which is constant. So the peak current limit of the high-side switch is not affected by the slope compensation and remains constant over the full duty cycle range.
The current going through LS MOSFET is also sensed and monitored. When the LS switch turns on, the inductor current begins to ramp down. The LS switch will not be turned OFF at the end of a switching cycle if its current is above the LS current limit ILS_LIMIT. The LS switch will be kept ON so that inductor current keeps ramping down, until the inductor current ramps below the LS current limit ILS_LIMIT. Then the LS switch will be turned OFF and the HS switch will be turned on after a dead time. This is somewhat different than the more typical peak current limit, and results in Equation 9 for the maximum load current.
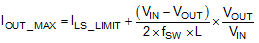
If the current of the LS switch is higher than the LS current limit for 64 consecutive cycles, hiccup current protection mode will be activated. In hiccup mode, the regulator will be shut down and kept off for 5 ms typically before the LMR23610-Q1 tries to start again. If over-current or short-circuit fault condition still exist, hiccup will repeat until the fault condition is removed. Hiccup mode reduces power dissipation under severe over-current conditions, prevents over-heating and potential damage to the device.
7.3.9 Thermal Shutdown
The LMR23610-Q1 provides an internal thermal shutdown to protect the device when the junction temperature exceeds 170 °C (typ). The device is turned off when thermal shutdown activates. Once the die temperature falls below 155 °C (typ), the device reinitiates the power up sequence controlled by the internal soft-start circuitry.
7.4 Device Functional Modes
7.4.1 Shutdown Mode
The EN pin provides electrical ON and OFF control for the LMR23610-Q1. When VEN is below 1 V (typ), the device is in shutdown mode. The LMR23610-Q1 also employs VIN and VCC under voltage lock out protection. If VIN or VCC voltage is below their respective UVLO level, the regulator will be turned off.
7.4.2 Active Mode
The LMR23610-Q1 is in Active Mode when VEN is above the precision enable threshold, VIN and VCC are above their respective UVLO level. The simplest way to enable the LMR23610-Q1 is to connect the EN pin to VIN pin. This allows self startup when the input voltage is in the operating range: 4 V to 36 V. Please refer to VCC, UVLO and Enable/Sync for details on setting these operating levels.
In Active Mode, depending on the load current, the LMR23610-Q1 will be in one of three modes:
- Continuous conduction mode (CCM) with fixed switching frequency when load current is above half of the peak-to-peak inductor current ripple.
- Discontinuous conduction mode (DCM) with fixed switching frequency when load current is lower than half of the peak-to-peak inductor current ripple in CCM operation.
- Pulse frequency modulation mode (PFM) when switching frequency is decreased at very light load.
7.4.3 CCM Mode
CCM operation is employed in the LMR23610-Q1 when the load current is higher than half of the peak-to-peak inductor current. In CCM operation, the frequency of operation is fixed, output voltage ripple will be at a minimum in this mode and the maximum output current of 1 A can be supplied by the LMR23610-Q1.
7.4.4 Light Load Operation
When the load current is lower than half of the peak-to-peak inductor current in CCM, the LMR23610-Q1 will operate in Discontinuous Conduction Mode (DCM), also known as Diode Emulation Mode (DEM). In DCM, the LS switch is turned off when the inductor current drops to IL_ZC (-40 mA typ). Both switching losses and conduction losses are reduced in DCM, compared to forced PWM operation at light load.
At even lighter current loads, Pulse Frequency Modulation (PFM) is activated to maintain high efficiency operation. When either the minimum HS switch ON time (tON_MIN ) or the minimum peak inductor current IPEAK_MIN (300 mA typ) is reached, the switching frequency will decrease to maintain regulation. In PFM, switching frequency is decreased by the control loop when load current reduces to maintain output voltage regulation. Switching loss is further reduced in PFM operation due to less frequent switching actions. The external clock synchronizing will not be valid when LMR23610-Q1 enters into PFM mode.
8 Application and Implementation
NOTE
Information in the following applications sections is not part of the TI component specification, and TI does not warrant its accuracy or completeness. TI’s customers are responsible for determining suitability of components for their purposes. Customers should validate and test their design implementation to confirm system functionality.
8.1 Application Information
The LMR23610-Q1 is a step down DC-to-DC regulator. It is typically used to convert a higher DC voltage to a lower DC voltage with a maximum output current of 1 A. The following design procedure can be used to select components for the LMR23610-Q1. Alternately, the WEBENCH® software may be used to generate complete designs. When generating a design, the WEBENCH® software utilizes iterative design procedure and accesses comprehensive databases of components. Please go to ti.com for more details.
8.2 Typical Applications
The LMR23610-Q1 only requires a few external components to convert from a wide voltage range supply to a fixed output voltage. Figure 21 shows a basic schematic.
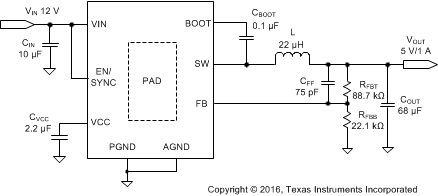 Figure 21. Application Circuit
Figure 21. Application Circuit
The external components have to fulfill the needs of the application, but also the stability criteria of the device's control loop. Table 1 can be used to simplify the output filter component selection.
Table 1. L, COUT and CFF Typical Values
| fSW (kHz) | VOUT (V) | L (µH) | COUT (µF) | CFF (pF) | RFBT (kΩ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 400 | 3.3 | 15 | 82 | 100 | 51 |
| 400 | 5 | 22 | 68 | 75 | 88.7 |
| 400 | 12 | 47 | 33 | See note (5) | 243 |
| 400 | 24 | 47 | 22 | See note (5) | 510 |
- Inductance value is calculated based on VIN = 36 V.
- All the COUT values are after derating. Add more when using ceramic capacitors.
- RFBT = 0 Ω for VOUT = 1 V. RFBB = 22.1 kΩ for all other VOUT setting.
- For designs with RFBT other than recommended value, please adjust CFF such that (CFF × RFBT) is unchanged and adjust RFBB such that (RFBT / RFBB) is unchanged.
- High ESR COUT will give enough phase boost and CFF not needed.
8.2.1 Design Requirements
Detailed design procedure is described based on a design example. For this design example, use the parameters listed in Table 2 as the input parameters.
Table 2. Design Example Parameters
| Input Voltage, VIN | 12 V typical, range from 8 V to 28 V |
| Output Voltage, VOUT | 5 V |
| Maximum Output Current IO_MAX | 1 A |
| Transient Response 0.1 A to 1 A | 5% |
| Output Voltage Ripple | 50 mV |
| Input Voltage Ripple | 400 mV |
| Switching Frequency fSW | 400 kHz |
8.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
8.2.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
Click here to create a custom design using the LMR23610-Q1 device with the WEBENCH® Power Designer.
- Start by entering the input voltage (VIN), output voltage (VOUT), and output current (IOUT) requirements.
- Optimize the design for key parameters such as efficiency, footprint, and cost using the optimizer dial.
- Compare the generated design with other possible solutions from Texas Instruments.
The WEBENCH Power Designer provides a customized schematic along with a list of materials with real-time pricing and component availability.
In most cases, these actions are available:
- Run electrical simulations to see important waveforms and circuit performance
- Run thermal simulations to understand board thermal performance
- Export customized schematic and layout into popular CAD formats
- Print PDF reports for the design, and share the design with colleagues
Get more information about WEBENCH tools at www.ti.com/WEBENCH.
8.2.2.2 Output Voltage Set-Point
The output voltage of LMR23610-Q1 is externally adjustable using a resistor divider network. The divider network is comprised of top feedback resistor RFBT and bottom feedback resistor RFBB. Equation 10 is used to determine the output voltage:
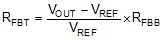
Choose the value of RFBB to be 22.1 kΩ. With the desired output voltage set to 5 V and the VREF = 1.0 V, the RFBB value can then be calculated using Equation 10. The formula yields to a value 88.7 kΩ.
8.2.2.3 Switching Frequency
The default switching frequency of the LMR23610-Q1 is 400 kHz. For other switching frequency, the device must be synchronized to an external clock, please refer to Enable/Sync for more details.
8.2.2.4 Inductor Selection
The most critical parameters for the inductor are the inductance, saturation current and the rated current. The inductance is based on the desired peak-to-peak ripple current ΔiL. Since the ripple current increases with the input voltage, the maximum input voltage is always used to calculate the minimum inductance LMIN. Use Equation 12 to calculate the minimum value of the output inductor. KIND is a coefficient that represents the amount of inductor ripple current relative to the maximum output current of the device. A reasonable value of KIND should be 30% to 50%. During an instantaneous short or over current operation event, the RMS and peak inductor current can be high. The inductor current rating should be higher than the current limit of the device.
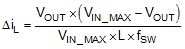
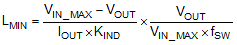
In general, it is preferable to choose lower inductance in switching power supplies, because it usually corresponds to faster transient response, smaller DCR, and reduced size for more compact designs. But too low of an inductance can generate too large of an inductor current ripple such that over current protection at the full load could be falsely triggered. It also generates more conduction loss and inductor core loss. Larger inductor current ripple also implies larger output voltage ripple with same output capacitors. With peak current mode control, it is not recommended to have too small of an inductor current ripple. A larger peak current ripple improves the comparator signal to noise ratio.
For this design example, choose KIND = 0.5, the minimum inductor value is calculated to be 20.5 µH. Choose the nearest standard 22 μH ferrite inductor with a capability of 2 A RMS current and 2.5 A saturation current.
8.2.2.5 Output Capacitor Selection
The output capacitor(s), COUT, should be chosen with care since it directly affects the steady state output voltage ripple, loop stability and the voltage over/undershoot during load current transients.
The output ripple is essentially composed of two parts. One is caused by the inductor current ripple going through the Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) of the output capacitors:

The other is caused by the inductor current ripple charging and discharging the output capacitors:
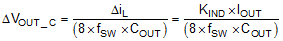
The two components in the voltage ripple are not in phase, so the actual peak-to-peak ripple is smaller than the sum of two peaks.
Output capacitance is usually limited by transient performance specifications if the system requires tight voltage regulation with presence of large current steps and fast slew rate. When a fast large load increase happens, output capacitors provide the required charge before the inductor current can slew up to the appropriate level. The regulator’s control loop usually needs six or more clock cycles to respond to the output voltage droop. The output capacitance must be large enough to supply the current difference for six clock cycles to maintain the output voltage within the specified range. Equation 15 shows the minimum output capacitance needed for specified output undershoot. When a sudden large load decrease happens, the output capacitors absorb energy stored in the inductor. which results in an output voltage overshoot. Equation 16 calculates the minimum capacitance required to keep the voltage overshoot within a specified range.
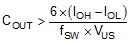
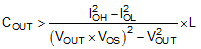
where
- KIND = Ripple ratio of the inductor ripple current (ΔiL / IOUT)
- IOL = Low level output current during load transient
- IOH = High level output current during load transient
- VUS = Target output voltage undershoot
- VOS = Target output voltage overshoot
For this design example, the target output ripple is 50 mV. Presuppose ΔVOUT_ESR = ΔVOUT_C = 50 mV, and chose KIND = 0.5. Equation 13 yields ESR no larger than 100 mΩ and Equation 14 yields COUT no smaller than 3.1 μF. For the target over/undershoot range of this design, VUS = VOS = 5% × VOUT = 250 mV. The COUT can be calculated to be no smaller than 54 μF and 8.5 μF by Equation 15 and Equation 16 respectively. Consider of derating, one 82 μF, 16 V ceramic capacitor with 5 mΩ ESR is used.
8.2.2.6 Feed-Forward Capacitor
The LMR23610-Q1 is internally compensated. Depending on the VOUT and frequency fSW, if the output capacitor COUT is dominated by low ESR (ceramic types) capacitors, it could result in low phase margin. To improve the phase boost an external feedforward capacitor CFF can be added in parallel with RFBT. CFF is chosen such that phase margin is boosted at the crossover frequency without CFF. A simple estimation for the crossover frequency (fX) without CFF is shown in Equation 17, assuming COUT has very small ESR, and COUT value is after derating.
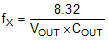
The following equation for CFF was tested:
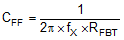
For designs with higher ESR, CFF is not needed when COUT has very high ESR and CFF calculated from Equation 18 should be reduced with medium ESR. Table 1 can be used as a quick starting point.
For the application in this design example, a 75 pF, 50 V, COG capacitor is selected.
8.2.2.7 Input Capacitor Selection
The LMR23610-Q1 device requires high frequency input decoupling capacitor(s) and a bulk input capacitor, depending on the application. The typical recommended value for the high frequency decoupling capacitor is 4.7 μF to 10 μF. A high-quality ceramic capacitor type X5R or X7R with sufficiency voltage rating is recommended. To compensate the derating of ceramic capacitors, a voltage rating of twice the maximum input voltage is recommended. Additionally, some bulk capacitance can be required, especially if the LMR23610-Q1 circuit is not located within approximately 5 cm from the input voltage source. This capacitor is used to provide damping to the voltage spike due to the lead inductance of the cable or the trace. For this design, two 4.7 μF, 50 V, X7R ceramic capacitors are used. A 0.1 μF for high-frequency filtering and place it as close as possible to the device pins.
8.2.2.8 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
Every LMR23610-Q1 design requires a bootstrap capacitor (CBOOT). The recommended capacitor is 0.1 μF and rated 16 V or higher. The bootstrap capacitor is located between the SW pin and the BOOT pin. The bootstrap capacitor must be a high-quality ceramic type with an X7R or X5R grade dielectric for temperature stability.
8.2.2.9 VCC Capacitor Selection
The VCC pin is the output of an internal LDO for LMR23610-Q1. To insure stability of the device, place a minimum of 2.2 μF, 16 V, X7R capacitor from this pin to ground.
8.2.2.10 Under Voltage Lockout Set-Point
The system undervoltage lockout (UVLO) is adjusted using the external voltage divider network of RENT and RENB. The UVLO has two thresholds, one for power up when the input voltage is rising and one for power down or brown outs when the input voltage is falling. The following equation can be used to determine the VIN UVLO level.
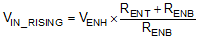
The EN rising threshold (VENH) for LMR23610-Q1 is set to be 1.55 V (typ). Choose the value of RENB to be 287 kΩ to minimize input current from the supply. If the desired VIN UVLO level is at 6.0 V, then the value of RENT can be calculated using the equation below:
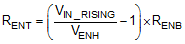
The above equation yields a value of 820 kΩ. The resulting falling UVLO threshold, equals 4.4 V, can be calculated by below equation, where EN hysteresis (VEN_HYS) is 0.4 V (typ).
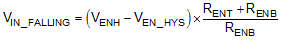
8.2.3 Application Curves
Unless otherwise specified the following conditions apply: VIN = 12 V, fSW = 400 kHz, L = 22 µH, COUT = 47 µF × 2, TA = 25 °C.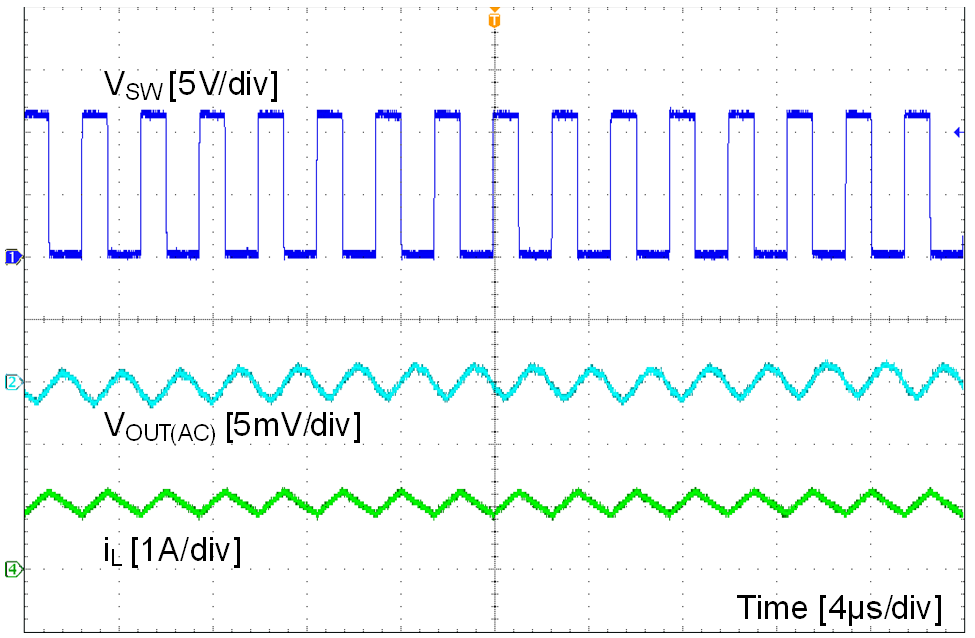
| VOUT = 5 V | IOUT = 1 A | fSW = 400 kHz |
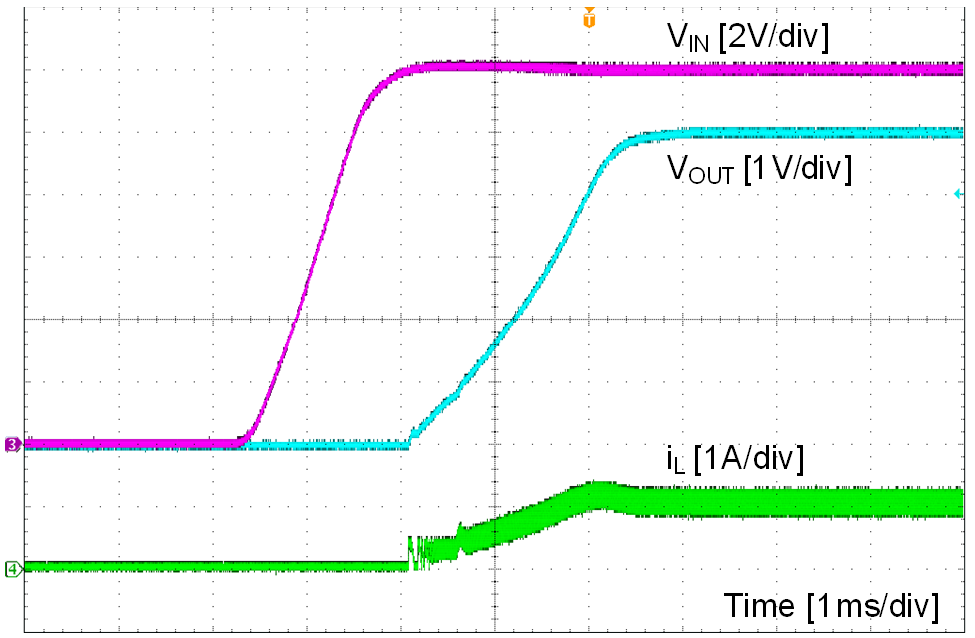
| VIN = 12 V | VOUT = 5 V | IOUT = 1 A |
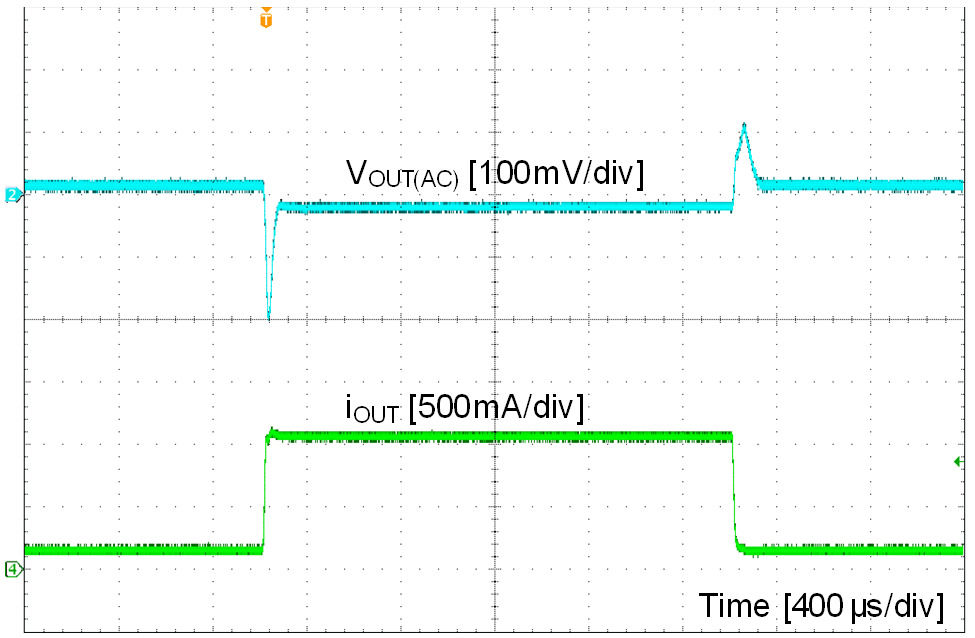
| VIN = 12 V | VOUT = 5 V | IOUT = 0.1 A to 1 A, 100 mA / μs |
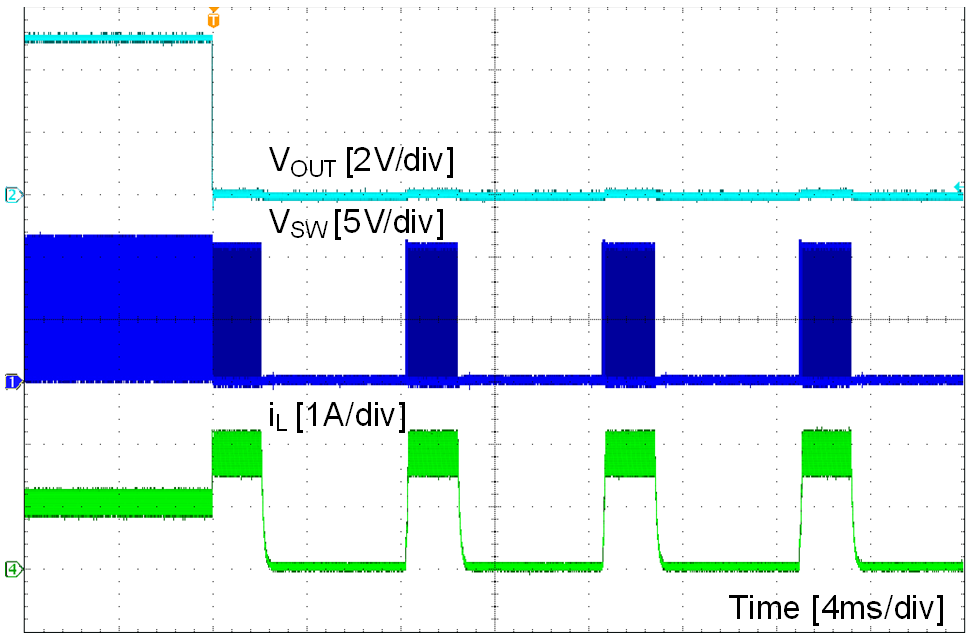
| VOUT = 5 V | IOUT = 1 A to short |
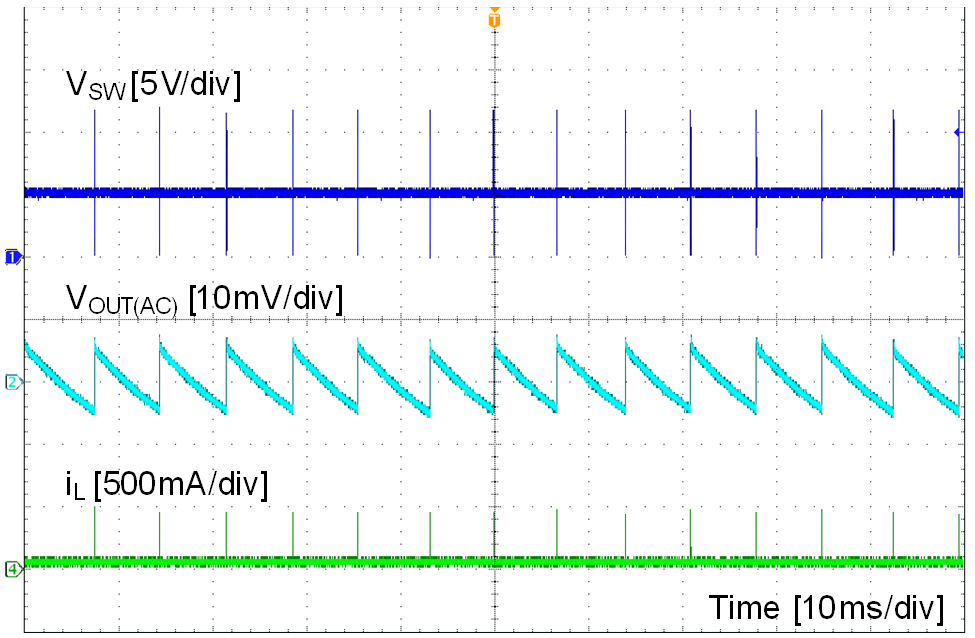
| VOUT = 5 V | IOUT = 0 mA | fSW = 400 kHz |
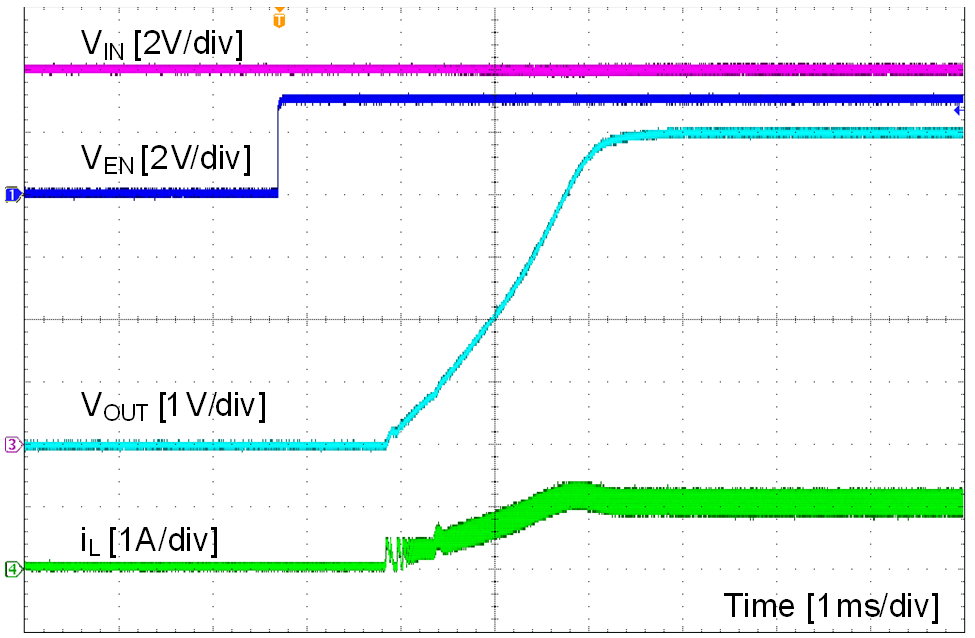
| VIN = 12 V | VOUT = 5 V | IOUT = 1 A |
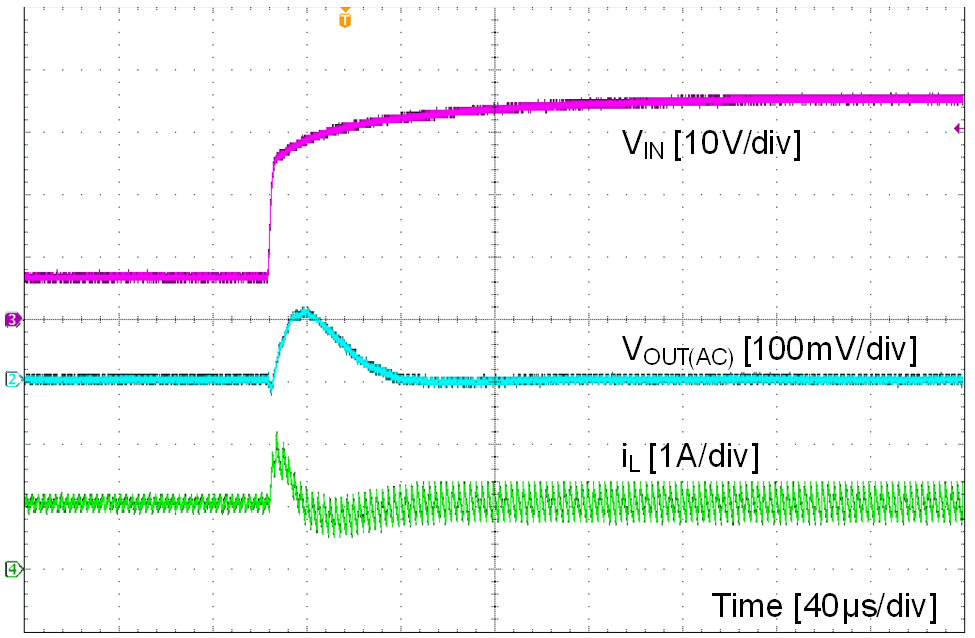
| VOUT = 7 V to 36 V, 2 V / μs | VOUT = 5 V | IOUT = 1 A |
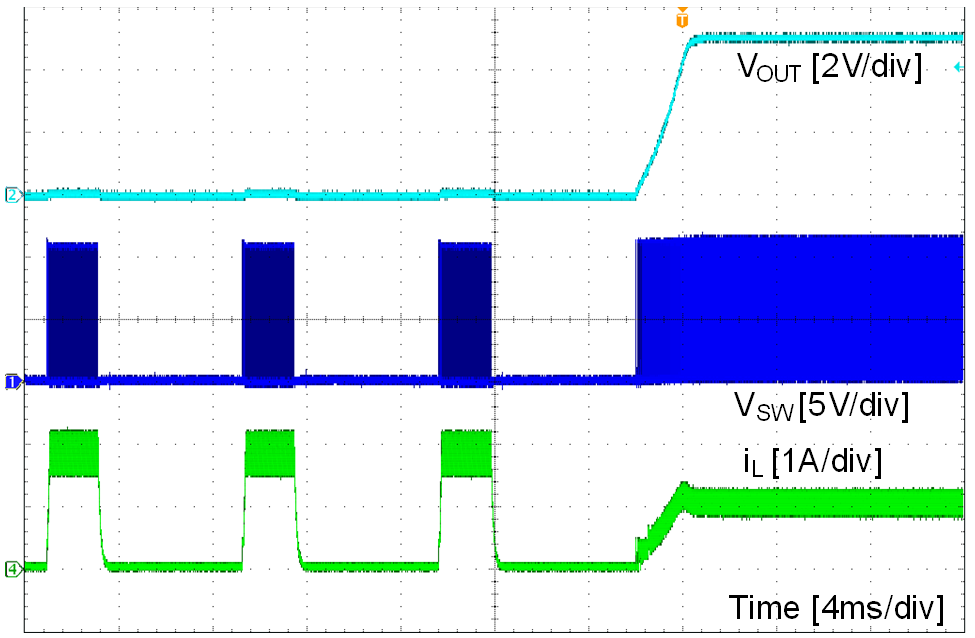
| VOUT = 5 V | IOUT = short to 1 A |
9 Power Supply Recommendations
The LMR23610-Q1 is designed to operate from an input voltage supply range between 4 V and 36 V. This input supply should be able to withstand the maximum input current and maintain a stable voltage. The resistance of the input supply rail should be low enough that an input current transient does not cause a high enough drop at the LMR23610-Q1 supply voltage that can cause a false UVLO fault triggering and system reset. If the input supply is located more than a few inches from the LMR23610-Q1, additional bulk capacitance may be required in addition to the ceramic input capacitors. The amount of bulk capacitance is not critical, but a 47 μF or 100 μF electrolytic capacitor is a typical choice.