SNVSB35C May 2018 – November 2024 LM26420-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Detailed Description
-
7 Application and Implementation
- 7.1 Application Information
- 7.2 Typical Applications
- 7.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 7.4 Layout
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
4 Pin Configuration and Functions
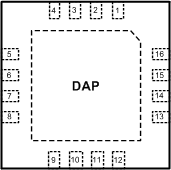 Figure 4-1 RUM Package16-Pin WQFNTop View
Figure 4-1 RUM Package16-Pin WQFNTop View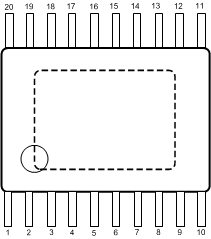 Figure 4-2 PWP Package20-Pin HTSSOPTop View
Figure 4-2 PWP Package20-Pin HTSSOPTop ViewTable 4-1 Pin Functions: 16-Pin WQFN
| PIN | TYPE(1) | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NUMBER | NAME | ||
| 1,2 | VIND1 | P | Power input supply for Buck 1 |
| 3 | SW1 | P | Output switch for Buck 1. Connect to the inductor. |
| 4 | PGND1 | G | Power ground pin for Buck 1 |
| 5 | FB1 | A | Feedback pin for Buck 1. Connect to external resistor divider to set output voltage. |
| 6 | PG1 | G | Power-Good Indicator for Buck 1. Pin is connected through a resistor to an external supply (open-drain output). |
| 7 | PG2 | G | Power-Good Indicator for Buck 2. Pin is connected through a resistor to an external supply (open-drain output). |
| 8 | FB2 | A | Feedback pin for Buck 2. Connect to external resistor divider to set output voltage. |
| 9 | PGND2 | G | Power ground pin for Buck 2 |
| 10 | SW2 | P | Output switch for Buck 2. Connect to the inductor. |
| 11, 12 | VIND2 | A | Power Input supply for Buck 2 |
| 13 | EN2 | A | Enable control input. Logic high enable operation for Buck 2. Do not allow this pin to float or be greater than VIN + 0.3 V. |
| 14 | AGND | G | Signal ground pin. Place the bottom resistor of the feedback network as close as possible to pin. |
| 15 | VINC | A | Input supply for control circuitry |
| 16 | EN1 | A | Enable control input. Logic high enable operation for Buck 1. Do not allow this pin to float or be greater than VIN + 0.3 V. |
| DAP | Die Attach Pad | — | Connect to system ground for low thermal impedance and as a primary electrical GND connection. |
(1) A = analog, P = power, G = ground
Table 4-2 Pin Functions: 20-Pin HTSSOP
| PIN | TYPE(1) | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NUMBER | NAME | ||
| 1 | VINC | A | Input supply for control circuitry |
| 2 | EN1 | A | Enable control input. Logic high enable operation for Buck 1. Do not allow this pin to float or be greater than VIN + 0.3 V. |
| 3, 4 | VIND1 | A | Power Input supply for Buck 1 |
| 5 | SW1 | P | Output switch for Buck 1. Connect to the inductor. |
| 6,7 | PGND1 | G | Power ground pin for Buck 1 |
| 8 | FB1 | A | Feedback pin for Buck 1. Connect to external resistor divider to set output voltage. |
| 9 | PG1 | G | Power Good Indicator for Buck 1. Pin is connected through a resistor to an external supply (open-drain output). |
| 10, 11, DAP | Die Attach Pad | — | Connect to system ground for low thermal impedance, but this pin cannot be used as a primary GND connection. |
| 12 | PG2 | G | Power Good Indicator for Buck 2. Pin is connected through a resistor to an external supply (open-drain output). |
| 13 | FB2 | A | Feedback pin for Buck 2. Connect to external resistor divider to set output voltage. |
| 14, 15 | PGND2 | G | Power ground pin for Buck 2 |
| 16 | SW2 | P | Output switch for Buck 2. Connect to the inductor. |
| 17, 18 | VIND2 | A | Power Input supply for Buck 2 |
| 19 | EN2 | A | Enable control input. Logic high enable operation for Buck 2. Do not allow this pin to float or be greater than VIN + 0.3 V. |
| 20 | AGND | G | Signal ground pin. Place the bottom resistor of the feedback network as close as possible to pin. |
(1) A = analog, P = power, G = ground