SNVSBK9G November 2019 – November 2024 LM63635-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.4.2.1 Sync/FPWM Operation
The forced PWM mode (FPWM) can be used to turn off AUTO mode and force the device to switch at the frequency programmed by the RT pin, even for small loads. This has the disadvantage of lower efficiency at light loads.
When a valid clock signal is present on the SYNC/MODE input, the switching frequency is locked to the external clock. The device mode is also FPWM. The mode can be changed dynamically by the system. See Figure 7-10 for typical examples of SYNC/MODE function changes.
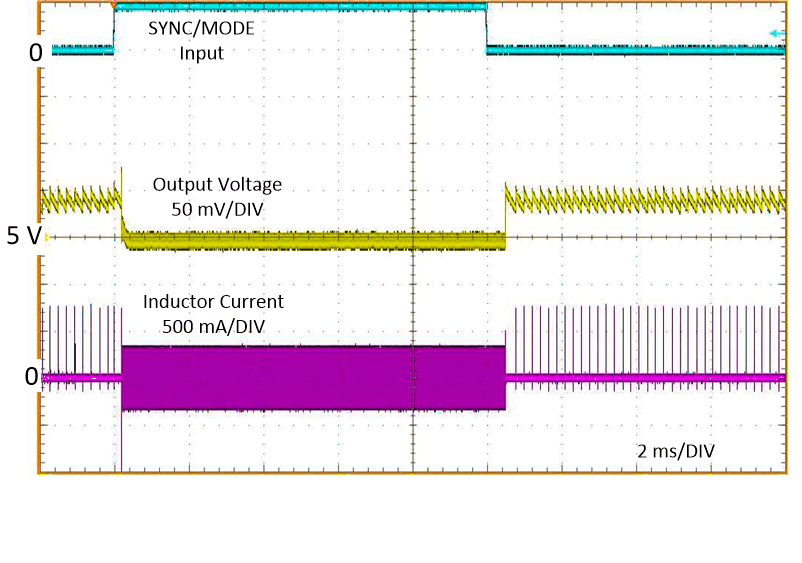 Figure 7-10 Typical
Transition from FPWM to AUTO Mode VIN = 12 V, VOUT = 5 V,
IOUT = 1 mA
Figure 7-10 Typical
Transition from FPWM to AUTO Mode VIN = 12 V, VOUT = 5 V,
IOUT = 1 mA