SNVSCG7 November 2024 LM5190
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
-
6 Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3
Feature Description
- 6.3.1 Input Voltage Range (VIN)
- 6.3.2 High-Voltage Bias Supply Regulator (VCC, BIAS)
- 6.3.3 Precision Enable (EN)
- 6.3.4 Power-Good Monitor (PGOOD)
- 6.3.5 Switching Frequency (RT)
- 6.3.6 Low Dropout Mode
- 6.3.7 Dual Random Spread Spectrum (DRSS)
- 6.3.8 Soft Start
- 6.3.9 Output Voltage Setpoint (FB)
- 6.3.10 Minimum Controllable On Time
- 6.3.11 Inductor Current Sense (ISNS+, VOUT)
- 6.3.12 Voltage Loop Error Amplifier
- 6.3.13 Current Monitor, Programmable Current Limit, and Current Loop Error Amplifier (IMON/ILIM, ISET)
- 6.3.14 Dual Loop Architecture
- 6.3.15 PWM Comparator
- 6.3.16 Slope Compensation
- 6.3.17 Hiccup Mode Current Limiting
- 6.3.18 High-Side and Low-Side Gate Drivers (HO, LO)
- 6.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6.3.11 Inductor Current Sense (ISNS+, VOUT)
Shunt Current Sensing Implementation illustrates inductor current sensing using a shunt resistor. This configuration continuously monitors the inductor current to provide accurate overcurrent protection across the operating temperature range. For the best current sense accuracy and overcurrent protection, use a low inductance ±1% tolerance shunt resistor between the inductor and the output, with a Kelvin connection to the LM5190 current sense amplifier.
If the peak voltage signal sensed from ISNS+ to VOUT exceeds the current limit threshold of 60mV, the current limit comparator immediately terminates the HO output for cycle-by-cycle peak current limiting. Calculate the shunt resistance using Equation 8.
where
- VCS-TH is current sense threshold of 60mV.
- IOUT(CL) is the overcurrent setpoint that is set higher than the maximum load current to avoid tripping the overcurrent comparator during load transients.
- ΔIL is the peak-to-peak inductor ripple current.
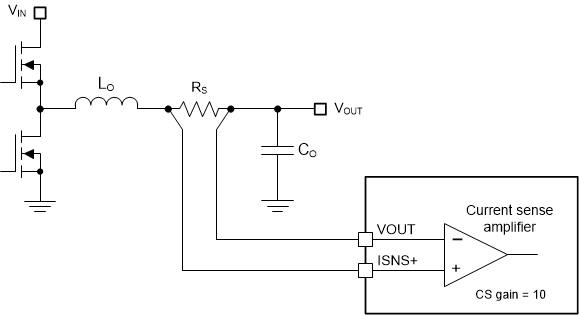 Figure 6-3 Shunt Current Sensing
Implementation
Figure 6-3 Shunt Current Sensing
ImplementationThe soft-start voltage is clamped 60mV above FB if the regulator is in an overcurrent condition or if the output is in UV (undervoltage) condition in CC mode operation. Eight overcurrent events must occur before the SS clamp is enabled. This requirement makes sure that SS can be pulled low during brief overcurrent events, preventing output voltage overshoot during recovery.