SNVU890 January 2024
2.2.3 Step 3: Measure SW Voltage
To observe the SW node, connect a probe with a small pigtail to the via next to the SW pin, as shown in Figure 3-2. This verifies that the measurement loop is small and, hence, accurately reflects the behavior of the SW node. If a large loop is used, due to the high dv/dt on the SW node and the parasitic impedance (inductance) of the loop, then a large amount of ringing is observed on the SW node measurements. This ringing is not representative of the device performance, but is rather a measurement artifact. The probe connection must be made prior to the board being powered up and one must verify that appropriate safety precautions are taken.
Connect the scope probe to measure the SW node as shown in Figure 3-2. Notice the small pigtail used to minimize the ground loop.
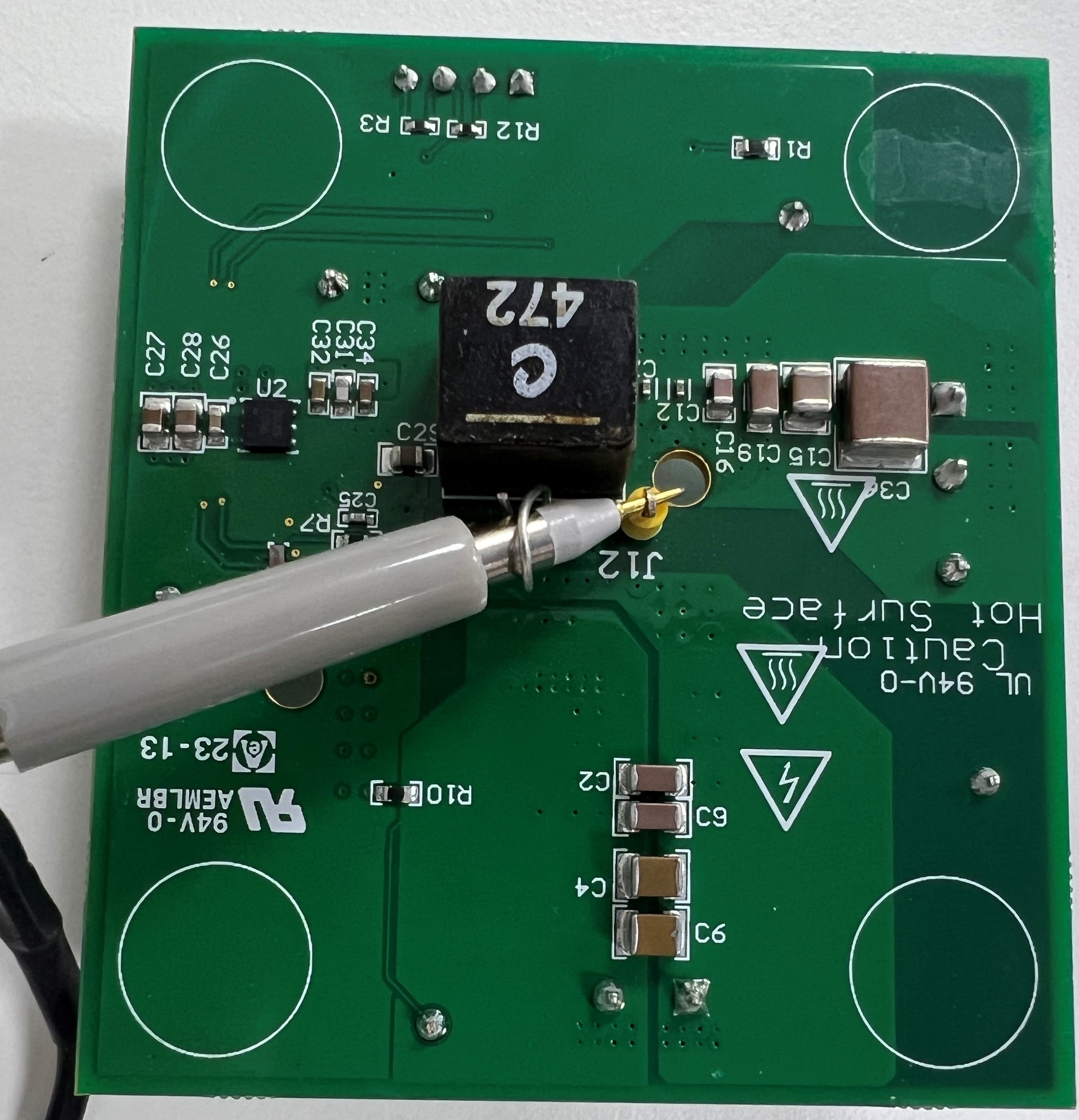 Figure 2-2 Measuring
the SW Node
Figure 2-2 Measuring
the SW Node