SPRAC94D September 2018 – March 2022 AFE030 , AFE031 , TMS320F28075 , TMS320F28075-Q1 , TMS320F28076 , TMS320F28374D , TMS320F28374S , TMS320F28375D , TMS320F28375S , TMS320F28375S-Q1 , TMS320F28376D , TMS320F28376S , TMS320F28377D , TMS320F28377D-EP , TMS320F28377D-Q1 , TMS320F28377S , TMS320F28377S-Q1 , TMS320F28379D , TMS320F28379D-Q1 , TMS320F28379S
- Trademarks
- 1 FSK Overview
- 2 Hardware Overview
- 3 Interfacing With the AFE03x
- 4 Transmit Path
- 5 Receive Path
- 6 Interfacing With a Power Line
- 7 Summary
- 8 References
- 9 Schematics
- 10Revision History
2.1 Block Diagram
Figure 2-3 shows a block diagram of the system. In this example, not all of the connections have been utilized, but all are present on the BoosterPack for future development.
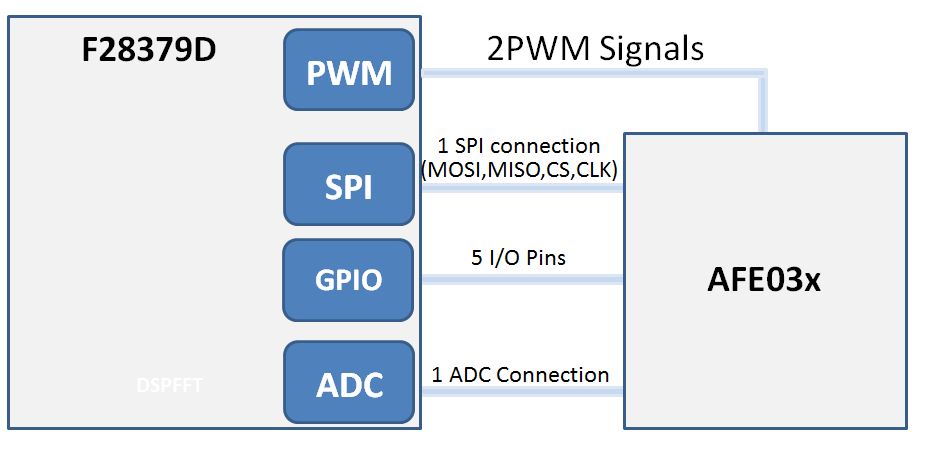 Figure 2-3 C2000 and AFE031 Block Diagram
Figure 2-3 C2000 and AFE031 Block DiagramThe AFE has multiple internal registers that allow configuration of the internal components of the AFE chip, including filter selection, gain selection, and mode selections. These registers can be accessed using the SPI peripheral.
The AFE also has various GPIOs that allow the MCU to set the AFE into certain modes, as well as receive interrupts for critical events on the AFE. The ADC connection allows the MCU to receive or sample an input signal. The PWM signals provide a way to create an output for the AFE. Currently the AFE031 supports two modes of data transmission, PWM mode and DAC mode. An explanation and implementation of both of these modes can be found in Section 3.