SPRACV1B February 2022 – January 2024 AM2434 , AM6411 , AM6412 , AM6421 , AM6441 , AM6442
4.2 Field Oriented Control (FOC) Loop
The MCU+ and Linux SDKs contain a benchmark demo application that includes an example FOC loop implementing the algorithm shown in Figure 4-1 and displaying the performance of the loop. Functions in the include Clark, Park, inverse Park, Sin, Cos, PI controllers and space vector generation.
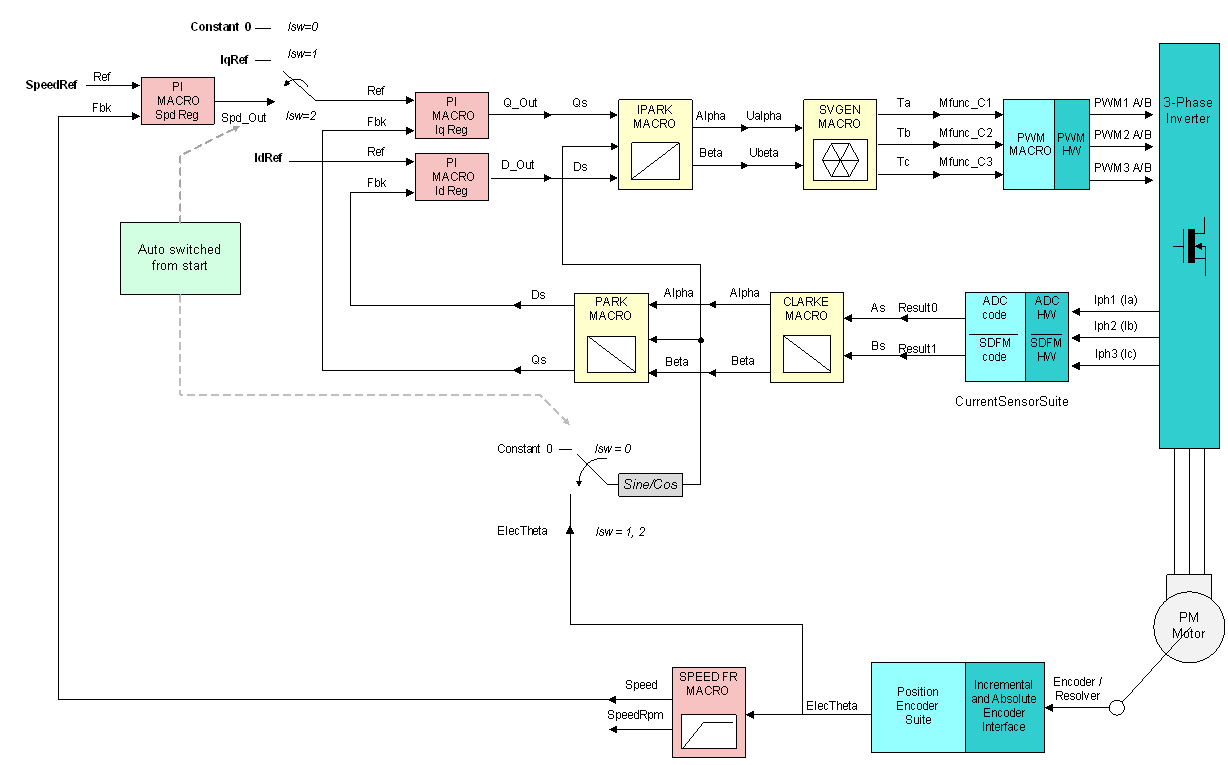 Figure 4-1 Speed Closed Field Oriented Control Loop
Figure 4-1 Speed Closed Field Oriented Control LoopThe performance of the FOC loop on a single Arm Cortex -R5F core of AM64x is shown in the table below. Each of the up to four Arm Cortex-R5F core can independently achieve this performance for the motor it is controlling.
| FOC Loop Execution Time (microseconds) | |
|---|---|
| Average | 0.4 |