SPRAD66B February 2023 – December 2024 AM62A3 , AM62A3-Q1 , AM62A7 , AM62A7-Q1 , AM62D-Q1 , AM62P , AM62P-Q1
- 1
- AM62Ax, AM62Px, AM62Dx LPDDR4 Board Design and Layout Guidelines
- Trademarks
- 1Overview
-
2LPDDR4 Board Design and Layout Guidance
- 2.1 LPDDR4 Introduction
- 2.2 LPDDR4 Device Implementations Supported
- 2.3 LPDDR4 Interface Schematics
- 2.4 Compatible JEDEC LPDDR4 Devices
- 2.5 Placement
- 2.6 LPDDR4 Keepout Region
- 2.7 Net Classes
- 2.8 LPDDR4 Signal Termination
- 2.9 LPDDR4 VREF Routing
- 2.10 LPDDR4 VTT
- 2.11 CK and ADDR_CTRL Topologies
- 2.12 Data Group Topologies
- 2.13 CK0 and ADDR_CTRL Routing Specification
- 2.14 Data Group Routing Specification
- 2.15 Channel, Byte, and Bit Swapping
- 2.16 Data Bus Inversion
- 3LPDDR4 Board Design Simulations
- 4Additional Information: SOC Package Delays
- 5Summary
- 6References
- 7Revision History
3.6.3 Model Verification
Before simulating, TI recommends to verify the models. One verification method described is the impedance plot (or impedance scan). The impedance scans for a 10 layer design are provided.
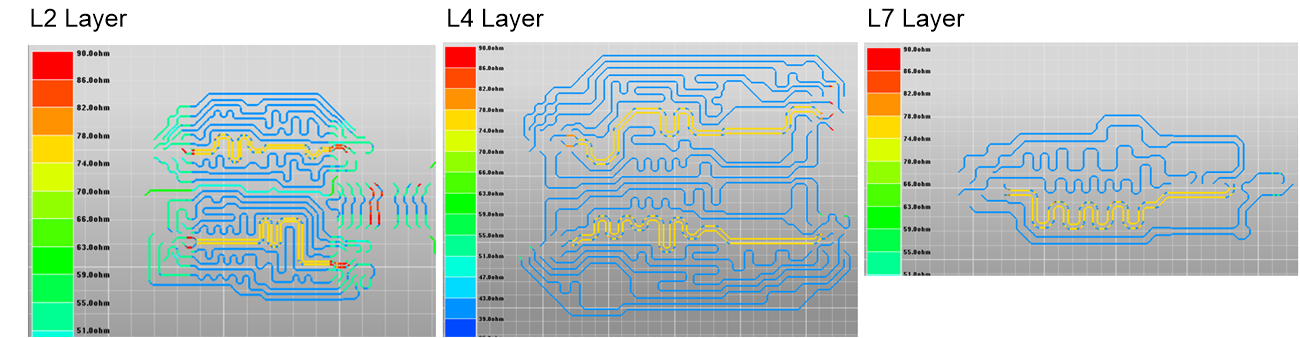 Figure 3-9 Example LPDDR4 Trace Impedance
Scan
Figure 3-9 Example LPDDR4 Trace Impedance
Scan| Layer | DDR Bus | DQ SE Impedance (Ω) | DQS/CLK Difference Impedance (Ω) |
|---|---|---|---|
| L2 | B1 and B3 | 40.9 | 77.7 |
| L2 | CA | 51.7 | 101.4 |
| L4 | B0 and B2 | 41.1 | 77.7 |
| L7 | CA | 41.1 | 77.7 |
For CK and CA signals, the goal is to have the branch segment equal to two times the impedance of the feed trace. Note, this is common for the PCB to limit the achievable impedances. Simulations show users if the compromises are acceptable.
| Board | CA Feed Impedance (Ω) | CA Branch Impedance (Ω) | CA Branch Target (Ω) | Impedance Mismatch (Ω) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Design | 49.1 | 59.6 | 98 (49x2) | 19.3 |
| Final Design | 41.1 | 51.7 | 82 (41x2) | 15.3 |
The simulation results show the improvement made by closer matching the impedances to the targets.
| Board | Total Eye Width Margin (ps) | Total Eye Height Margin (ps) |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Design | 58.00 | 14.00 |
| Final Design | 124.68 | 48.08 |