SPRUI30H November 2015 – May 2024 DRA745 , DRA746 , DRA750 , DRA756
- 1
- Read This First
-
1 Introduction
- 1.1 DRA75x, DRA74x Overview
- 1.2 DRA75x, DRA74x Environment
- 1.3
DRA75x, DRA74x Description
- 1.3.1 MPU Subsystem
- 1.3.2 DSP Subsystems
- 1.3.3 EVE Subsystems
- 1.3.4 IPU Subsystems
- 1.3.5 IVA-HD Subsystem
- 1.3.6 Display Subsystem
- 1.3.7 Video Processing Subsystem
- 1.3.8 Video Capture
- 1.3.9 3D GPU Subsystem
- 1.3.10 BB2D Subsystem
- 1.3.11 On-Chip Debug Support
- 1.3.12 Power, Reset, and Clock Management
- 1.3.13 On-Chip Memory
- 1.3.14 Memory Management
- 1.3.15 External Memory Interfaces
- 1.3.16 System and Connectivity Peripherals
- 1.4 DRA75x, DRA74x Family
- 1.5 DRA75x, DRA74x Device Identification
- 1.6 DRA75x, DRA74x Package Characteristics Overview
- 2 Memory Mapping
-
3 Power, Reset, and Clock Management
- 3.1
Device Power Management Introduction
- 3.1.1
Device Power-Management Architecture Building Blocks
- 3.1.1.1 Clock Management
- 3.1.1.2 Power Management
- 3.1.1.3 Voltage Management
- 3.1.2 Power-Management Techniques
- 3.1.1
Device Power-Management Architecture Building Blocks
- 3.2 PRCM Subsystem Overview
- 3.3 PRCM Subsystem Environment
- 3.4 PRCM Subsystem Integration
- 3.5
Reset Management Functional Description
- 3.5.1 Overview
- 3.5.2 General Characteristics of Reset Signals
- 3.5.3 Reset Sources
- 3.5.4 Reset Logging
- 3.5.5 Reset Domains
- 3.5.6
Reset Sequences
- 3.5.6.1 MPU Subsystem Power-On Reset Sequence
- 3.5.6.2 MPU Subsystem Warm Reset Sequence
- 3.5.6.3 MPU Subsystem Reset Sequence on Sleep and Wake-Up Transitions From RETENTION State
- 3.5.6.4 IVA Subsystem Power-On Reset Sequence
- 3.5.6.5 IVA Subsystem Software Warm Reset Sequence
- 3.5.6.6 DSP1 Subsystem Power-On Reset Sequence
- 3.5.6.7 DSP1 Subsystem Software Warm Reset Sequence
- 3.5.6.8 DSP2 Subsystem Power-On Reset Sequence
- 3.5.6.9 DSP2 Subsystem Software Warm Reset Sequence
- 3.5.6.10 IPU1 Subsystem Power-On Reset Sequence
- 3.5.6.11 IPU1 Subsystem Software Warm Reset Sequence
- 3.5.6.12 IPU2 Subsystem Power-On Reset Sequence
- 3.5.6.13 IPU2 Subsystem Software Warm Reset Sequence
- 3.5.6.14 EVE1 Subsystem Power-On Reset Sequence
- 3.5.6.15 EVE1 Subsystem Software Warm Reset Sequence
- 3.5.6.16 EVE2 Subsystem Power-On Reset Sequence
- 3.5.6.17 EVE2 Subsystem Software Warm Reset Sequence
- 3.5.6.18 Global Warm Reset Sequence
- 3.6
Clock Management Functional Description
- 3.6.1 Overview
- 3.6.2 External Clock Inputs
- 3.6.3
Internal Clock Sources and Generators
- 3.6.3.1 PRM Clock Source
- 3.6.3.2 CM Clock Source
- 3.6.3.3 Generic DPLL Overview
- 3.6.3.4 DPLL_PER Description
- 3.6.3.5 DPLL_CORE Description
- 3.6.3.6 DPLL_ABE Description
- 3.6.3.7 DPLL_MPU Description
- 3.6.3.8 DPLL_IVA Description
- 3.6.3.9 DPLL_USB Description
- 3.6.3.10 DPLL_EVE Description
- 3.6.3.11 DPLL_DSP Description
- 3.6.3.12 DPLL_GMAC Description
- 3.6.3.13 DPLL_GPU Description
- 3.6.3.14 DPLL_DDR Description
- 3.6.3.15 DPLL_PCIE_REF Description
- 3.6.3.16 APLL_PCIE Description
- 3.6.4
Clock Domains
- 3.6.4.1 CD_WKUPAON Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.2 CD_DSP1 Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.3 CD_DSP2 Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.4 CD_CUSTEFUSE Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.5 CD_MPU Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.6 CD_L4PER1 Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.7 CD_L4PER2 Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.8 CD_L4PER3 Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.9 CD_L4SEC Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.10 CD_L3INIT Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.11 CD_IVA Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.12 CD_GPU Description
- 3.6.4.13 CD_EMU Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.14 CD_DSS Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.15 CD_L4_CFG Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.16 CD_L3_INSTR Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.17 CD_L3_MAIN1 Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.18 CD_EMIF Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.19 CD_IPU Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.20 CD_IPU1 Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.21 CD_IPU2 Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.22 CD_DMA Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.23 CD_ATL Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.24 CD_CAM Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.25 CD_GMAC Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.26 CD_VPE Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.27 CD_EVE1 Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.28 CD_EVE2 Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.29 CD_RTC Clock Domain
- 3.6.4.30 CD_PCIE Clock Domain
- 3.7
Power Management Functional Description
- 3.7.1 PD_WKUPAON Description
- 3.7.2 PD_DSP1 Description
- 3.7.3 PD_DSP2 Description
- 3.7.4 PD_CUSTEFUSE Description
- 3.7.5 PD_MPU Description
- 3.7.6 PD_IPU Description
- 3.7.7 PD_L3INIT Description
- 3.7.8 PD_L4PER Description
- 3.7.9 PD_IVA Description
- 3.7.10 PD_GPU Description
- 3.7.11 PD_EMU Description
- 3.7.12 PD_DSS Description
- 3.7.13 PD_CORE Description
- 3.7.14 PD_CAM Description
- 3.7.15 PD_MPUAON Description
- 3.7.16 PD_MMAON Description
- 3.7.17 PD_COREAON Description
- 3.7.18 PD_VPE Description
- 3.7.19 PD_EVE1 Description
- 3.7.20 PD_EVE2 Description
- 3.7.21 PD_RTC Description
- 3.8 Voltage-Management Functional Description
- 3.9 Device Low-Power States
- 3.10
PRCM Module Programming Guide
- 3.10.1 DPLLs Low-Level Programming Models
- 3.10.2 Clock Management Low-Level Programming Models
- 3.10.3 Power Management Low-Level Programming Models
- 3.11 546
- 3.12 PRCM Software Configuration for OPP_PLUS
- 3.13
PRCM Register Manual
- 3.13.1 PRCM Instance Summary
- 3.13.2 CM_CORE_AON__CKGEN Registers
- 3.13.3 CM_CORE_AON__DSP1 Registers
- 3.13.4 CM_CORE_AON__DSP2 Registers
- 3.13.5 CM_CORE_AON__EVE1 Registers
- 3.13.6 CM_CORE_AON__EVE2 Registers
- 3.13.7 CM_CORE_AON__INSTR Registers
- 3.13.8 CM_CORE_AON__IPU Registers
- 3.13.9 CM_CORE_AON__MPU Registers
- 3.13.10 CM_CORE_AON__OCP_SOCKET Registers
- 3.13.11 CM_CORE_AON__RESTORE Registers
- 3.13.12 CM_CORE_AON__RTC Registers
- 3.13.13 CM_CORE_AON__VPE Registers
- 3.13.14 CM_CORE__CAM Registers
- 3.13.15 CM_CORE__CKGEN Registers
- 3.13.16 CM_CORE__COREAON Registers
- 3.13.17 CM_CORE__CORE Registers
- 3.13.18 CM_CORE__CUSTEFUSE Registers
- 3.13.19 CM_CORE__DSS Registers
- 3.13.20 CM_CORE__GPU Registers
- 3.13.21 CM_CORE__IVA Registers
- 3.13.22 CM_CORE__L3INIT Registers
- 3.13.23 CM_CORE__L4PER Registers
- 3.13.24 CM_CORE__OCP_SOCKET Registers
- 3.13.25 CM_CORE__RESTORE Registers
- 3.13.26 CAM_PRM Registers
- 3.13.27 CKGEN_PRM Registers
- 3.13.28 CORE_PRM Registers
- 3.13.29 CUSTEFUSE_PRM Registers
- 3.13.30 DEVICE_PRM Registers
- 3.13.31 DSP1_PRM Registers
- 3.13.32 DSP2_PRM Registers
- 3.13.33 DSS_PRM Registers
- 3.13.34 EMU_CM Registers
- 3.13.35 EMU_PRM Registers
- 3.13.36 EVE1_PRM Registers
- 3.13.37 EVE2_PRM Registers
- 3.13.38 GPU_PRM Registers
- 3.13.39 INSTR_PRM Registers
- 3.13.40 IPU_PRM Registers
- 3.13.41 IVA_PRM Registers
- 3.13.42 L3INIT_PRM Registers
- 3.13.43 L4PER_PRM Registers
- 3.13.44 MPU_PRM Registers
- 3.13.45 OCP_SOCKET_PRM Registers
- 3.13.46 RTC_PRM Registers
- 3.13.47 VPE_PRM Registers
- 3.13.48 WKUPAON_CM Registers
- 3.13.49 WKUPAON_PRM Registers
- 3.1
Device Power Management Introduction
-
4 Dual Cortex-A15 MPU Subsystem
- 4.1 Dual Cortex-A15 MPU Subsystem Overview
- 4.2 Dual Cortex-A15 MPU Subsystem Integration
- 4.3
Dual Cortex-A15 MPU Subsystem Functional Description
- 4.3.1 MPU Subsystem Block Diagram
- 4.3.2 Cortex-A15 MPCore (MPU_CLUSTER)
- 4.3.3 MPU_AXI2OCP
- 4.3.4 Memory Adapter
- 4.3.5 Realtime Counter (Master Counter)
- 4.3.6 MPU Watchdog Timer
- 4.3.7 MPU Subsystem Power Management
- 4.3.8 MPU Subsystem AMBA Interface Configuration
- 4.4
Dual Cortex-A15 MPU Subsystem Register Manual
- 4.4.1 Dual Cortex-A15 MPU Subsystem Instance Summary
- 4.4.2 MPU_CS_STM Registers
- 4.4.3 MPU_INTC Registers
- 4.4.4 MPU_PRCM_OCP_SOCKET Registers
- 4.4.5 MPU_PRCM_DEVICE Registers
- 4.4.6 MPU_PRCM_PRM_C0 Registers
- 4.4.7 MPU_PRCM_CM_C0 Registers
- 4.4.8 MPU_PRCM_PRM_C1 Registers
- 4.4.9 MPU_PRCM_CM_C1 Registers
- 4.4.10 MPU_WUGEN Registers
- 4.4.11 MPU_WD_TIMER Registers
- 4.4.12 MPU_AXI2OCP_MISC Registers
- 4.4.13 MPU_MA_LSM Registers
- 4.4.14 MPU_MA_WP Registers
-
5 DSP Subsystems
- 5.1 DSP Subsystems Overview
- 5.2 DSP Subsystem Integration
- 5.3
DSP Subsystems Functional Description
- 5.3.1 DSP Subsystems Block Diagram
- 5.3.2
DSP Subsystem Components
- 5.3.2.1 C66x DSP Subsystem Introduction
- 5.3.2.2
DSP TMS320C66x CorePac
- 5.3.2.2.1 DSP TMS320C66x CorePac CPU
- 5.3.2.2.2 DSP TMS320C66x CorePac Internal Memory Controllers and Memories
- 5.3.2.2.3
DSP C66x CorePac Internal Peripherals
- 5.3.2.2.3.1 DSP C66x CorePac Interrupt Controller (DSP INTC)
- 5.3.2.2.3.2 DSP C66x CorePac Power-Down Controller (DSP PDC)
- 5.3.2.2.3.3 DSP C66x CorePac Bandwidth Manager (BWM)
- 5.3.2.2.3.4 DSP C66x CorePac Memory Protection Hardware
- 5.3.2.2.3.5 DSP C66x CorePac Internal DMA (IDMA) Controller
- 5.3.2.2.3.6 DSP C66x CorePac External Memory Controller
- 5.3.2.2.3.7 DSP C66x CorePac Extended Memory Controller
- 5.3.2.2.3.8 L1P Memory Error Detection Logic
- 5.3.2.2.3.9 L2 Memory Error Detection and Correction Logic
- 5.3.2.3 DSP Debug and Trace Support
- 5.3.3 DSP System Control Logic
- 5.3.4 DSP Interrupt Requests
- 5.3.5 DSP DMA Requests
- 5.3.6 DSP Intergated Memory Management Units
- 5.3.7 DSP Integrated EDMA Subsystem
- 5.3.8 DSP L2 interconnect Network
- 5.3.9 DSP Boot Configuration
- 5.3.10 DSP Internal and External Memory Views
- 5.4 DSP Subsystem Register Manual
- 6 IVA Subsystem
-
7 Dual Cortex-M4 IPU Subsystem
- 7.1 Dual Cortex-M4 IPU Subsystem Overview
- 7.2 Dual Cortex-M4 IPU Subsystem Integration
- 7.3 Dual Cortex-M4 IPU Subsystem Functional Description
- 7.4 Dual Cortex-M4 IPU Subsystem Register Manual
-
8 Embedded Vision Engine
- 8.1
Embedded Vision Engine (EVE) Subsystem
- 8.1.1 EVE Overview
- 8.1.2 EVE Integration
- 8.1.3
EVE Functional Description
- 8.1.3.1 EVE Connection ID (ConnID) Mapping
- 8.1.3.2 EVE Processors Overview
- 8.1.3.3 Internal Memory Overview
- 8.1.3.4 Program Cache Architecture
- 8.1.3.5 EDMA
- 8.1.3.6 General-Purpose Inputs/Outputs
- 8.1.3.7 CME Signaling
- 8.1.3.8 Multi-EVE and VIP Usage Models
- 8.1.3.9 Memory Management Unit
- 8.1.3.10 Interrupt Control
- 8.1.3.11 Interprocessor Communication
- 8.1.3.12 Powerdown
- 8.1.3.13 Hardware-Assisted Software Self-Test – MISRs
- 8.1.3.14 Error Recovery – ARP32 and OCP Disconnect
- 8.1.3.15 Lock and Unlock Feature
- 8.1.3.16 EVE Memory Map
- 8.1.3.17 Debug Support
- 8.1.3.18 EVE L2_FNOC Interconnect
- 8.1.4 EVE Programming Model
- 8.1.5 EVE Subsystem Register Manual
- 8.1.6
Subsystem Counter Timer Module
- 8.1.6.1 Introduction
- 8.1.6.2 Functional Description
- 8.1.6.3 Use Case Examples
- 8.1.6.4 SCTM Register Manual
- 8.1.7 Software Message and System Event Trace
- 8.2
ARP32 CPU and Instruction Set
- 8.2.1 Overview
- 8.2.2 Features
- 8.2.3 Block Diagram
- 8.2.4
Architecture
- 8.2.4.1 Interface Description
- 8.2.4.2 Pipeline
- 8.2.4.3 Data Format
- 8.2.4.4 Endian Support
- 8.2.4.5 Architectural Register File
- 8.2.4.6
CPU Control Registers
- 8.2.4.6.1 Control Status Register (CSR)
- 8.2.4.6.2 Interrupt Enable Register (IER)
- 8.2.4.6.3 Interrupt Flag Register (IFR)
- 8.2.4.6.4 Interrupt Set Register (ISR)
- 8.2.4.6.5 Interrupt Clear Register (ICR)
- 8.2.4.6.6 Nonmaskable Interrupt (NMI) Return Pointer Register (NRP)
- 8.2.4.6.7 Interrupt Return Pointer Register (IRP)
- 8.2.4.6.8 Stack Pointer Register (SP)
- 8.2.4.6.9 Global Data Pointer Register (GDP)
- 8.2.4.6.10 Link Register (LR)
- 8.2.4.6.11 Loop 0 Start Address Register (LSA0)
- 8.2.4.6.12 Loop 0 End Address Register (LEA0)
- 8.2.4.6.13 Loop 0 Iteration Count Register (LCNT0)
- 8.2.4.6.14 Loop 1 Start Address Register (LSA1)
- 8.2.4.6.15 Loop 1 End Address Register (LEA1)
- 8.2.4.6.16 Loop 1 Iteration Count Register (LCNT1)
- 8.2.4.6.17 Loop 0 Iteration Count Reload Value Register (LCNT0RLD)
- 8.2.4.6.18 Shadow Control Status Register (SCSR)
- 8.2.4.6.19 NMI Shadow Control Status Register (NMISCSR)
- 8.2.4.6.20 CPU Identification Register (CPUID)
- 8.2.4.6.21 Decode Program Counter Register (DPC)
- 8.2.4.6.22 Time Stamp Counter Registers (TSCL and TSCH)
- 8.2.4.7 CPU Shadow Registers
- 8.2.4.8 Functional Units
- 8.2.4.9 Instruction Fetch
- 8.2.4.10 Alignment of 32-bit Instructions
- 8.2.4.11 Instruction Execution in Branch Delay Slot
- 8.2.4.12 Address Space
- 8.2.4.13 Program Counter Convention
- 8.2.4.14 Stack Pointer Convention
- 8.2.4.15 Global Data Pointer Convention
- 8.2.4.16 Conditional Execution
- 8.2.4.17
Hardware Loop Acceleration
- 8.2.4.17.1 Overview
- 8.2.4.17.2 Loop Registers
- 8.2.4.17.3 Loop Setup Instructions
- 8.2.4.17.4 Loop Operation
- 8.2.4.17.5 Call and Branch within Loop Context
- 8.2.4.17.6 Dynamic Changes to Loop Iteration Count
- 8.2.4.17.7 Interrupt Processing During HLA
- 8.2.4.17.8 HLA Usage in Interrupt Context
- 8.2.4.17.9 HLA Usage Restrictions
- 8.2.4.17.10 HLA Mapping Examples
- 8.2.4.18
Interrupts
- 8.2.4.18.1 Overview
- 8.2.4.18.2 Interrupt Processing
- 8.2.4.18.3 Interrupt Acknowledgment
- 8.2.4.18.4 Interrupt Priorities
- 8.2.4.18.5 Interrupt Service Table (IST)
- 8.2.4.18.6 Interrupt Flags
- 8.2.4.18.7 Interrupt Behavior
- 8.2.4.18.8 Interrupt Context Save and Restore
- 8.2.4.18.9 Nested Interrupts
- 8.2.4.18.10 Non-nested Interrupt Latency
-
8.2.A Instruction Set
- 8.2.A.1 Instruction Operation and Execution Notations
- 8.2.A.2 Instruction Syntax and Opcode Notations
-
8.2.A.3 Instruction Scheduling Restrictions
- 8.2.A.3.1 Restrictions Applicable to a Branch Delay Slot
- 8.2.A.3.2 Restrictions on Loops Using Hardware Loop Assist (HLA)
- 8.2.A.3.3 Restrictions on Other Types of Control Flow Instructions
- 8.2.A.3.4 Restrictions for Write Data Bypass to Control Register Reads
- 8.2.A.3.5 Restrictions for Write Data Bypass to Shadow Register Reads
- 8.2.A.3.6 Restrictions for Link Register Update
- 8.2.A.4 Instruction Set Encoding
-
8.2.A.5 Instruction Descriptions
- ABS
- ADD
- ADD
- ADD
- ADD
- ADD
- AND
- AND
- B(cc)
- B(cc)
- B(cc)
- BIRP
- BKPT
- BNRP
- CALL
- CALL
- CLR
- CLR
- CMP
- CMP
- CMP
- CMPU
- CMPU
- CMPU
- DIV
- DIVU
- EXT
- EXT
- EXTU
- EXTU
- IDLE
- LDB(U)
- LDB(U)
- LDB(U)
- LDB(U)
- LDB(U)
- LDB(U)
- LDB(U)
- LDB(U)
- LDH(U)
- LDH(U)
- LDH(U)
- LDH(U)
- LDH(U)
- LDH(U)
- LDH(U)
- LDH(U)
- LDW
- LDW
- LDW
- LDW
- LDW
- LDW
- LDW
- LDW
- LDRF
- LMBD
- MAX
- MAXU
- MIN
- MINU
- MOD
- MODU
- MPY
- MPYU
- MV
- MVC
- MVC
- MVC
- MVCH
- MVK
- MVKH
- MVKLS
- MVKS
- MVS
- MVS
- NEG
- NOP
- NOT
- OR
- OR
- RET
- REV
- ROT
- ROTC
- SADD
- SATN
- SET
- SET
- SHL
- SHL
- SHRA
- SHRA
- SHRU
- SHRU
- SLA
- SSUB
- STB
- STB
- STB
- STB
- STB
- STB
- STB
- STB
- STH
- STH
- STH
- STH
- STH
- STH
- STH
- STH
- STW
- STW
- STW
- STW
- STW
- STW
- STW
- STW
- STHI
- STRF
- SUB
- SUB
- SUB
- SUB
- SUB
- SWI
- XOR
- XOR
- 8.2.B Clock, Reset, and Dynamic Power Management
- 8.2.C Notes on Programming Model
- 8.3
VCOP CPU and Instruction Set
- 8.3.1 Module Overview
- 8.3.2 Features
- 8.3.3 Block Diagram
- 8.3.4 System Interfaces
- 8.3.5
Functional Description
- 8.3.5.1 Scalar-Vector Architecture
- 8.3.5.2 Vector Core Overview
- 8.3.5.3 Vector Control
- 8.3.5.4 Vector-Scalar Synchronization
- 8.3.5.5
Vector Computation
- 8.3.5.5.1 Vector Loop
- 8.3.5.5.2 Vector Register Initialization
- 8.3.5.5.3 Address Generator (agen)
- 8.3.5.5.4 Vector Load
- 8.3.5.5.5 Vector Arithmetic/Logic Operations
- 8.3.5.5.6 Vector Store
- 8.3.5.5.7 Table Lookup Operation
- 8.3.5.5.8 Histogram Operation
- 8.3.5.5.9 Circular Buffer Addressing Support
- 8.3.5.5.10 Load/Store Address Alignment Constraints
- 8.3.5.6 Load/Store Buffer and Scheduling
- 8.3.5.7 VCOP Per-Loop Overhead
- 8.3.5.8 VCOP Error Handling
- 8.3.5.9
Vector Operation Details
- 8.3.5.9.1 VABS
- 8.3.5.9.2 VABSDIF
- 8.3.5.9.3 VADD
- 8.3.5.9.4 VADDH
- 8.3.5.9.5 VADDSUB
- 8.3.5.9.6 VADD3
- 8.3.5.9.7 VADIF3
- 8.3.5.9.8 VAND
- 8.3.5.9.9 VANDN
- 8.3.5.9.10 VAND3
- 8.3.5.9.11 VBINLOG
- 8.3.5.9.12 VBITC
- 8.3.5.9.13 VBITDI
- 8.3.5.9.14 VBITI
- 8.3.5.9.15 VBITPK
- 8.3.5.9.16 VBITR
- 8.3.5.9.17 VBITTR
- 8.3.5.9.18 VBITUNPK
- 8.3.5.9.19 VCMOV
- 8.3.5.9.20 VCMPEQ
- 8.3.5.9.21 VCMPGE
- 8.3.5.9.22 VCMPGT
- 8.3.5.9.23 VDINTRLV
- 8.3.5.9.24 VDINTRLV2
- 8.3.5.9.25 VEXITNZ
- 8.3.5.9.26 VINTRLV
- 8.3.5.9.27 VINTRLV2
- 8.3.5.9.28 VINTRLV4
- 8.3.5.9.29 VLMBD
- 8.3.5.9.30 VMADD
- 8.3.5.9.31 VMAX
- 8.3.5.9.32 VMAXSETF
- 8.3.5.9.33 VMIN
- 8.3.5.9.34 VMINSETF
- 8.3.5.9.35 VMPY
- 8.3.5.9.36 VMSUB
- 8.3.5.9.37 VNOP
- 8.3.5.9.38 VNOT
- 8.3.5.9.39 VOR
- 8.3.5.9.40 VOR3
- 8.3.5.9.41 VRND
- 8.3.5.9.42 VSAD
- 8.3.5.9.43 VSEL
- 8.3.5.9.44 VSHF
- 8.3.5.9.45 VSHFOR
- 8.3.5.9.46 VSHF16
- 8.3.5.9.47 VSIGN
- 8.3.5.9.48 VSORT2
- 8.3.5.9.49 VSUB
- 8.3.5.9.50 VSWAP
- 8.3.5.9.51 VXOR
- 8.3.6 Debug Support
- 8.3.7 VCOP Register Manual
- 8.1
Embedded Vision Engine (EVE) Subsystem
-
9 Video Input Port
- 9.1 VIP Overview
- 9.2 VIP Environment
- 9.3 VIP Integration
- 9.4
VIP Functional Description
- 9.4.1 VIP Block Diagram
- 9.4.2 VIP Software Reset
- 9.4.3 VIP Power and Clocks Management
- 9.4.4
VIP Slice
- 9.4.4.1 VIP Slice Processing Path Overview
- 9.4.4.2 VIP Slice Processing Path Multiplexers
- 9.4.4.3
VIP Slice Processing Path Examples
- 9.4.4.3.1 Input: A=RGB, B=YUV422; Output: A=RGB, B=RGB
- 9.4.4.3.2 Input: A=YUV422 8/16, B=YUV422; Output: A=Scaled YUV420, B=RGB
- 9.4.4.3.3 Input: A=RGB, B=YUV422; Output: A=RGB, B=Scaled YUV420
- 9.4.4.3.4 Input: A=YUV444, B=YUV422; Output: A=YUV422, A=Scaled YUV422, B=YUV422
- 9.4.4.3.5 Input: A=YUV444; Output: A=Scaled YUV420, A=YUV420
- 9.4.4.3.6 Input: A=YUV444; Output: A=Scaled YUV420, A=YUV444
- 9.4.4.3.7 Input: A=YUV422 8/16; Output: A=Scaled YUV420, A=YUV444
- 9.4.4.3.8 Input: A=YUV422 8/16, B=YUV422; Output: A=Scaled YUV420, B=YUV420
- 9.4.4.3.9 Input: A=YUV422 8/16, B=YUV422; Output: A=YUV420, B=YUV420
- 9.4.5
VIP Parser
- 9.4.5.1 Features
- 9.4.5.2 Repacker
- 9.4.5.3 Analog Video
- 9.4.5.4 Digitized Video
- 9.4.5.5 Frame Buffers
- 9.4.5.6
Input Data Interface
- 9.4.5.6.1 8b Interface Mode
- 9.4.5.6.2 16b Interface Mode
- 9.4.5.6.3 24b Interface Mode
- 9.4.5.6.4 Signal Relationships
- 9.4.5.6.5 General 5 Pin Interfaces
- 9.4.5.6.6 Signal Subsets—4 Pin VSYNC, ACTVID, and FID
- 9.4.5.6.7 Signal Subsets—4 Pin VSYNC, HSYNC, and FID
- 9.4.5.6.8 Vertical Sync
- 9.4.5.6.9 Field ID Determination Using Dedicated Signal
- 9.4.5.6.10 Field ID Determination Using VSYNC Skew
- 9.4.5.6.11 Rationale for FID Determination By VSYNC Skew
- 9.4.5.6.12 ACTVID Framing
- 9.4.5.6.13 Ancillary Data Storage in Descrete Sync Mode
- 9.4.5.7 BT.656 Style Embedded Sync
- 9.4.5.8
Source Multiplexing
- 9.4.5.8.1 Multiplexing Scenarios
- 9.4.5.8.2 2-Way Multiplexing
- 9.4.5.8.3 4-Way Multiplexing
- 9.4.5.8.4 Line Multiplexing
- 9.4.5.8.5 Super Frame Concept in Line Multiplexing
- 9.4.5.8.6 8-bit Data Interface in Line Multiplexing
- 9.4.5.8.7 16-bit Data Interface in Line Multiplexing
- 9.4.5.8.8 Split Lines in Line Multiplex Mode
- 9.4.5.8.9 Meta Data
- 9.4.5.8.10 TI Line Mux Mode, Split Lines, and Channel ID Remapping
- 9.4.5.9 Channel ID Extraction for 2x/4x Multiplexed Source
- 9.4.5.10 Embedded Sync Mux Modes and Data Bus Widths
- 9.4.5.11 Ancillary and Active Video Cropping
- 9.4.5.12 Interrupts
- 9.4.5.13 VDET Interrupt
- 9.4.5.14 Source Video Size
- 9.4.5.15 Clipping
- 9.4.5.16 Current and Last FID Value
- 9.4.5.17 Disable Handling
- 9.4.5.18 Picture Size Interrupt
- 9.4.5.19 Discrete Sync Signals
- 9.4.5.20 VIP Overflow Detection and Recovery
- 9.4.6 VIP Color Space Converter (CSC)
- 9.4.7
VIP Scaler (SC)
- 9.4.7.1 SC Features
- 9.4.7.2 SC Functional Description
- 9.4.7.3 SC Code
- 9.4.7.4
SC Coefficient Data Files
- 9.4.7.4.1
HS Polyphase Filter Coefficients
- 9.4.7.4.1.1 ppfcoef_scale_eq_1_32_phases_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.1.2 ppfcoef_scale_eq_8div16_32_phases_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.1.3 ppfcoef_scale_eq_9div16_32_phases_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.1.4 ppfcoef_scale_eq_10div16_32_phases_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.1.5 ppfcoef_scale_eq_11div16_32_phases_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.1.6 ppfcoef_scale_eq_12div16_32_phases_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.1.7 ppfcoef_scale_eq_13div16_32_phases_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.1.8 ppfcoef_scale_eq_14div16_32_phases_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.1.9 ppfcoef_scale_eq_15div16_32_phases_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.2
VS Polyphase Filter Coefficients
- 9.4.7.4.2.1 ppfcoef_scale_eq_1_32_phases_ver_5tap_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.2.2 ppfcoef_scale_eq_3_32_phases_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.2.3 ppfcoef_scale_eq_4_32_phases_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.2.4 ppfcoef_scale_eq_5_32_phases_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.2.5 ppfcoef_scale_eq_6_32_phases_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.2.6
ppfcoef_scale_eq_7_32_phases_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.2.6.1 ppfcoef_scale_eq_8div16_32_phases_ver_5tap_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.2.6.2 ppfcoef_scale_eq_9div16_32_phases_ver_5tap_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.2.6.3 ppfcoef_scale_eq_10div16_32_phases_ver_5tap_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.2.6.4 ppfcoef_scale_eq_11div16_32_phases_ver_5tap_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.2.6.5 ppfcoef_scale_eq_12div16_32_phases_ver_5tap_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.2.6.6 ppfcoef_scale_eq_13div16_32_phases_ver_5tap_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.2.6.7 ppfcoef_scale_eq_14div16_32_phases_ver_5tap_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.2.6.8 ppfcoef_scale_eq_15div16_32_phases_ver_5tap_flip.dat
- 9.4.7.4.3 VS (Bilinear Filter Coefficients)
- 9.4.7.4.1
HS Polyphase Filter Coefficients
- 9.4.8
VIP Video Port Direct Memory Access (VPDMA)
- 9.4.8.1 VPDMA Introduction
- 9.4.8.2 VPDMA Basic Definitions
- 9.4.8.3 1612
- 9.4.8.4 VPDMA Client Buffering and Functionality
- 9.4.8.5 VPDMA Channels Assignment
- 9.4.8.6 VPDMA MFLAG Mechanism
- 9.4.8.7 VPDMA Interrupts
- 9.4.8.8
VPDMA Descriptors
- 9.4.8.8.1 Data Transfer Descriptors
- 9.4.8.8.2 Configuration Descriptor
- 9.4.8.8.3 Control Descriptor
- 9.4.8.9 VPDMA Configuration
- 9.4.8.10
VPDMA Data Formats
- 9.4.8.10.1
YUV Data Formats
- 9.4.8.10.1.1 Y 4:4:4 (Data Type 0)
- 9.4.8.10.1.2 Y 4:2:2 (Data Type 1)
- 9.4.8.10.1.3 Y 4:2:0 (Data Type 2)
- 9.4.8.10.1.4 C 4:4:4 (Data Type 4)
- 9.4.8.10.1.5 C 4:2:2 (Data Type 5)
- 9.4.8.10.1.6 C 4:2:0 (Data Type 6)
- 9.4.8.10.1.7 YC 4:2:2 (Data Type 7)
- 9.4.8.10.1.8 YC 4:4:4 (Data Type 8)
- 9.4.8.10.1.9 CY 4:2:2 (Data Type 23)
- 9.4.8.10.2
RGB Data Formats
- 9.4.8.10.2.1 RGB16-565 (Data Type 0)
- 9.4.8.10.2.2 ARGB-1555 (Data Type 1)
- 9.4.8.10.2.3 ARGB-4444 (Data Type 2)
- 9.4.8.10.2.4 RGBA-5551 (Data Type 3)
- 9.4.8.10.2.5 RGBA-4444 (Data Type 4)
- 9.4.8.10.2.6 ARGB24-6666 (Data Type 5)
- 9.4.8.10.2.7 RGB24-888 (Data Type 6)
- 9.4.8.10.2.8 ARGB32-8888 (Data Type 7)
- 9.4.8.10.2.9 RGBA24-6666 (Data Type 8)
- 9.4.8.10.2.10 RGBA32-8888 (Data Type 9)
- 9.4.8.10.3 Miscellaneous Data Type
- 9.4.8.10.1
YUV Data Formats
- 9.5 VIP Register Manual
-
10Video Processing Engine
- 10.1 VPE Overview
- 10.2 VPE Integration
- 10.3
VPE Functional Description
- 10.3.1 VPE Block Diagram
- 10.3.2 VPE VC1 Range Mapping/Range Reduction
- 10.3.3 VPE Deinterlacer (DEI)
- 10.3.4
VPE Scaler (SC)
- 10.3.4.1 SC Features
- 10.3.4.2 SC Functional Description
- 10.3.4.3 SC Code
- 10.3.4.4
SC Coefficient Data Files
- 10.3.4.4.1
HS Polyphase Filter Coefficients
- 10.3.4.4.1.1 ppfcoef_scale_eq_1_32_phases_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.1.2 ppfcoef_scale_eq_8div16_32_phases_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.1.3 ppfcoef_scale_eq_9div16_32_phases_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.1.4 ppfcoef_scale_eq_10div16_32_phases_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.1.5 ppfcoef_scale_eq_11div16_32_phases_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.1.6 ppfcoef_scale_eq_12div16_32_phases_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.1.7 ppfcoef_scale_eq_13div16_32_phases_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.1.8 ppfcoef_scale_eq_14div16_32_phases_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.1.9 ppfcoef_scale_eq_15div16_32_phases_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.2
VS Polyphase Filter Coefficients
- 10.3.4.4.2.1 ppfcoef_scale_eq_1_32_phases_ver_5tap_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.2.2 ppfcoef_scale_eq_3_32_phases_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.2.3 ppfcoef_scale_eq_4_32_phases_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.2.4 ppfcoef_scale_eq_5_32_phases_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.2.5 ppfcoef_scale_eq_6_32_phases_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.2.6
ppfcoef_scale_eq_7_32_phases_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.2.6.1 ppfcoef_scale_eq_8div16_32_phases_ver_5tap_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.2.6.2 ppfcoef_scale_eq_9div16_32_phases_ver_5tap_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.2.6.3 ppfcoef_scale_eq_10div16_32_phases_ver_5tap_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.2.6.4 ppfcoef_scale_eq_11div16_32_phases_ver_5tap_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.2.6.5 ppfcoef_scale_eq_12div16_32_phases_ver_5tap_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.2.6.6 ppfcoef_scale_eq_13div16_32_phases_ver_5tap_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.2.6.7 ppfcoef_scale_eq_14div16_32_phases_ver_5tap_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.2.6.8 ppfcoef_scale_eq_15div16_32_phases_ver_5tap_flip.dat
- 10.3.4.4.2.6.9 ppcoef_scale_1x_ver_5tap.dat
- 10.3.4.4.3 VS (Bilinear Filter Coefficients)
- 10.3.4.4.1
HS Polyphase Filter Coefficients
- 10.3.5 VPE Color Space Converter (CSC)
- 10.3.6 VPE Chroma Up-Sampler (CHR_US)
- 10.3.7 VPE Chroma Down-Sampler (CHR_DS)
- 10.3.8 VPE YUV422 to YUV444 Conversion
- 10.3.9
VPE Video Port Direct Memory Access (VPDMA)
- 10.3.9.1 VPDMA Introduction
- 10.3.9.2 VPDMA Basic Definitions
- 10.3.9.3 VPDMA Client Buffering and Functionality
- 10.3.9.4 VPDMA Channels Assignment
- 10.3.9.5 VPDMA Interrupts
- 10.3.9.6
VPDMA Descriptors
- 10.3.9.6.1
Data Transfer Descriptors
- 10.3.9.6.1.1 Data Packet Descriptor Word 0 (Data)
- 10.3.9.6.1.2 Data Packet Descriptor Word 1
- 10.3.9.6.1.3 Data Packet Descriptor Word 2
- 10.3.9.6.1.4 Data Packet Descriptor Word 3
- 10.3.9.6.1.5 Data Packet Descriptor Word 4
- 10.3.9.6.1.6 Data Packet Descriptor Word 5
- 10.3.9.6.1.7 Data Packet Descriptor Word 6/7 (Data)
- 10.3.9.6.2 Configuration Descriptor
- 10.3.9.6.3 Control Descriptor
- 10.3.9.6.1
Data Transfer Descriptors
- 10.3.9.7 VPDMA Configuration
- 10.3.9.8
VPDMA Data Formats
- 10.3.9.8.1
YUV Data Formats
- 10.3.9.8.1.1 Y 4:4:4 (Data Type 0)
- 10.3.9.8.1.2 Y 4:2:2 (Data Type 1)
- 10.3.9.8.1.3 Y 4:2:0 (Data Type 2)
- 10.3.9.8.1.4 C 4:4:4 (Data Type 4)
- 10.3.9.8.1.5 C 4:2:2 (Data Type 5)
- 10.3.9.8.1.6 C 4:2:0 (Data Type 6)
- 10.3.9.8.1.7 YC 4:2:2 (Data Type 7)
- 10.3.9.8.1.8 YC 4:4:4 (Data Type 8)
- 10.3.9.8.1.9 CY 4:2:2 (Data Type 23)
- 10.3.9.8.2
RGB Data Formats
- 10.3.9.8.2.1
Input Data Formats
- 10.3.9.8.2.1.1 RGB16-565 (Data Type 0)
- 10.3.9.8.2.1.2 ARGB-1555 (Data Type 1)
- 10.3.9.8.2.1.3 ARGB-4444 (Data Type 2)
- 10.3.9.8.2.1.4 RGBA-5551 (Data Type 3)
- 10.3.9.8.2.1.5 RGBA-4444 (Data Type 4)
- 10.3.9.8.2.1.6 ARGB24-6666 (Data Type 5)
- 10.3.9.8.2.1.7 RGB24-888 (Data Type 6)
- 10.3.9.8.2.1.8 ARGB32-8888 (Data Type 7)
- 10.3.9.8.2.1.9 RGBA24-6666 (Data Type 8)
- 10.3.9.8.2.1.10 RGBA32-8888 (Data Type 9)
- 10.3.9.8.2.2
Output Data Formats
- 10.3.9.8.2.2.1 RGB16-565 (Data Type 0)
- 10.3.9.8.2.2.2 ARGB-1555 (Data Type 1)
- 10.3.9.8.2.2.3 ARGB-4444 (Data Type 2)
- 10.3.9.8.2.2.4 RGBA-5551 (Data Type 3)
- 10.3.9.8.2.2.5 RGBA-4444 (Data Type 4)
- 10.3.9.8.2.2.6 ARGB24-6666 (Data Type 5)
- 10.3.9.8.2.2.7 RGB24-888 (Data Type 6)
- 10.3.9.8.2.2.8 ARGB32-8888 (Data Type 7)
- 10.3.9.8.2.2.9 RGBA24-6666 (Data Type 8)
- 10.3.9.8.2.2.10 RGBA32-8888 (Data Type 9)
- 10.3.9.8.2.1
Input Data Formats
- 10.3.9.8.3 Miscellaneous Data Type
- 10.3.9.8.1
YUV Data Formats
- 10.3.10 VPE Software Reset
- 10.3.11 VPE Power and Clocks Management
- 10.4 VPE Register Manual
-
11Display Subsystem
- 11.1
Display Subsystem Overview
- 11.1.1 Display Subsystem Environment
- 11.1.2 Display Subsystem Integration
- 11.1.3
Display Subsystem DPLL Controllers Functional Description
- 11.1.3.1 DPLL Controllers Overview
- 11.1.3.2 OCP2SCP2 Functional Description
- 11.1.3.3
DPLL_VIDEO Functional Description
- 11.1.3.3.1 DPLL_VIDEO Controller Architecture
- 11.1.3.3.2 DPLL_VIDEO Operations
- 11.1.3.3.3 DPLL_VIDEO Error Handling
- 11.1.3.3.4 DPLL_VIDEO Software Reset
- 11.1.3.3.5 DPLL_VIDEO Power Management
- 11.1.3.3.6 DPLL_VIDEO HSDIVIDER Loading Operation
- 11.1.3.3.7 DPLL_VIDEO Clock Sequence
- 11.1.3.3.8 DPLL_VIDEO Go Sequence
- 11.1.3.3.9 DPLL_VIDEO Recommended Values
- 11.1.3.4
DPLL_HDMI Functional Description
- 11.1.3.4.1 DPLL_HDMI and PLLCTRL_HDMI Overview
- 11.1.3.4.2 DPLL_HDMI and PLLCTRL_HDMI Architecture
- 11.1.3.4.3 DPLL_HDMI Operations
- 11.1.3.4.4 DPLL_HDMI Register Access
- 11.1.3.4.5 DPLL_HDMI Error Handling
- 11.1.3.4.6 DPLL_HDMI Software Reset
- 11.1.3.4.7 DPLL_HDMI Power Management
- 11.1.3.4.8 DPLL_HDMI Lock Sequence
- 11.1.3.4.9 DPLL_HDMI Go Sequence
- 11.1.3.4.10 DPLL_HDMI Recommended Values
- 11.1.4 Display Subsystem Programming Guide
- 11.1.5 Display Subsystem Register Manual
- 11.2
Display Controller
- 11.2.1 DISPC Overview
- 11.2.2 DISPC Environment
- 11.2.3 DISPC Integration
- 11.2.4
DISPC Functional Description
- 11.2.4.1 DISPC Clock Configuration
- 11.2.4.2 DISPC Software Reset
- 11.2.4.3 DISPC Power Management
- 11.2.4.4 DISPC Interrupt Requests
- 11.2.4.5 DISPC DMA Requests
- 11.2.4.6
DISPC DMA Engine
- 11.2.4.6.1 DISPC Addressing and Bursts
- 11.2.4.6.2 DISPC Immediate Base Address Flip Mechanism
- 11.2.4.6.3 DISPC DMA Buffers
- 11.2.4.6.4 DISPC MFLAG Mechanism and Arbitration
- 11.2.4.6.5 DISPC Predecimation
- 11.2.4.6.6 DISPC Progressive-to-Interlaced Format Conversion
- 11.2.4.6.7 DISPC Arbitration
- 11.2.4.6.8 DISPC DMA Power Modes
- 11.2.4.7 DISPC Rotation and Mirroring
- 11.2.4.8 DISPC Memory Format
- 11.2.4.9 DISPC Graphics Pipeline
- 11.2.4.10 DISPC Video Pipelines
- 11.2.4.11 DISPC Write-Back Pipeline
- 11.2.4.12 DISPC Hardware Cursor
- 11.2.4.13
DISPC LCD Outputs
- 11.2.4.13.1 DISPC Overlay Manager
- 11.2.4.13.2 DISPC Gamma Correction Unit
- 11.2.4.13.3 DISPC Color Phase Rotation Unit
- 11.2.4.13.4 DISPC Color Space Conversion
- 11.2.4.13.5 DISPC BT.656 and BT.1120 Modes
- 11.2.4.13.6 DISPC Active Matrix
- 11.2.4.13.7 DISPC Synchronized Buffer Update
- 11.2.4.13.8 DISPC Timing Generator and Panel Settings
- 11.2.4.14 DISPC TV Output
- 11.2.4.15 DISPC Frame Width Considerations
- 11.2.4.16 DISPC Extended 3D Support
- 11.2.4.17 DISPC Shadow Registers
- 11.2.5
DISPC Programming Guide
- 11.2.5.1
DISPC Low-Level Programming Models
- 11.2.5.1.1 DISPC Global Initialization
- 11.2.5.1.2
DISPC Operational Modes Configuration
- 11.2.5.1.2.1 DISPC DMA Configuration
- 11.2.5.1.2.2 DISPC GFX Pipeline Configuration
- 11.2.5.1.2.3
DISPC Video Pipeline Configuration
- 11.2.5.1.2.3.1 DISPC Main Sequence – Configure the Video Pipeline
- 11.2.5.1.2.3.2 DISPC Subsequence – Configure the Video Window
- 11.2.5.1.2.3.3 DISPC Subsequence – Configure the Video Pipeline Processing
- 11.2.5.1.2.3.4 DISPC Subsequence – Configure the VC-1 Range Mapping
- 11.2.5.1.2.3.5 DISPC Subsequence – Configure the Video Color Space Conversion
- 11.2.5.1.2.3.6 DISPC Subsequence – Configure the Video Scaler Unit
- 11.2.5.1.2.3.7 DISPC Subsequence – Configure the Video Pipeline Layer Output
- 11.2.5.1.2.4 DISPC WB Pipeline Configuration
- 11.2.5.1.2.5
DISPC LCD Output Configuration
- 11.2.5.1.2.5.1 DISPC Main Sequence – Configure the LCD Output
- 11.2.5.1.2.5.2 DISPC Subsequence – Configure the Overlay Manager
- 11.2.5.1.2.5.3 DISPC Subsequence – Configure the Gamma Table for Gamma Correction
- 11.2.5.1.2.5.4 DISPC Subsequence – Configure the Color Phase Rotation
- 11.2.5.1.2.5.5 DISPC Subsequence – Configure the LCD Panel Timings and Parameters
- 11.2.5.1.2.5.6 DISPC Subsequence – Configure BT.656 or BT.1120 Mode
- 11.2.5.1.2.6 DISPC TV Output Configuration
- 11.2.5.1
DISPC Low-Level Programming Models
- 11.2.6 DISPC Register Manual
- 11.3 High-Definition Multimedia Interface
- 11.1
Display Subsystem Overview
- 123D Graphics Accelerator
- 132D Graphics Accelerator
-
14Interconnect
- 14.1 Interconnect Overview
- 14.2
L3_MAIN Interconnect
- 14.2.1 L3_MAIN Interconnect Overview
- 14.2.2 L3_MAIN Interconnect Integration
- 14.2.3
L3_MAIN Interconnect Functional Description
- 14.2.3.1 Module Use in L3_MAIN Interconnect
- 14.2.3.2 Module Distribution
- 14.2.3.3 Bandwidth Regulators
- 14.2.3.4 Bandwidth Limiters
- 14.2.3.5 Flag Muxing
- 14.2.3.6 Statistic Collectors Group
- 14.2.3.7 L3_MAIN Protection and Firewalls
- 14.2.3.8 L3_MAIN Interconnect Error Handling
- 14.2.4
L3_MAIN Interconnect Programming Guide
- 14.2.4.1 L3 _MAIN Interconnect Low-Level Programming Models
- 14.2.4.2
Operational Modes Configuration
- 14.2.4.2.1
L3_MAIN Interconnect Error Analysis Mode
- 14.2.4.2.1.1
Main Sequence: L3_MAIN Interconnect Error Analysis Mode
- 14.2.4.2.1.1.1 Subsequence: L3_MAIN Custom Error Identification
- 14.2.4.2.1.1.2 Subsequence: L3_MAIN Interconnect Protection Violation Error Identification
- 14.2.4.2.1.1.3 Subsequence: L3_MAIN Interconnect Standard Error Identification
- 14.2.4.2.1.1.4 Subsequence: L3_MAIN Interconnect FLAGMUX Configuration
- 14.2.4.2.1.1
Main Sequence: L3_MAIN Interconnect Error Analysis Mode
- 14.2.4.2.1
L3_MAIN Interconnect Error Analysis Mode
- 14.2.5
L3_MAIN Interconnect Register Manual
- 14.2.5.1
L3_MAIN Register Group Summary
- 14.2.5.1.1 L3_MAIN Firewall Registers Summary and Description
- 14.2.5.1.2 L3_MAIN Host Register Summary and Description
- 14.2.5.1.3 L3_MAIN TARG Register Summary and Description
- 14.2.5.1.4 L3_MAIN FLAGMUX Registers Summary and Description
- 14.2.5.1.5 L3_MAIN FLAGMUX CLK1MERGE Registers Summary and Description
- 14.2.5.1.6 L3_MAIN FLAGMUX TIMEOUT Registers Summary and Description
- 14.2.5.1.7 L3_MAIN BW Regulator Register Summary and Description
- 14.2.5.1.8 L3_MAIN Bandwidth Limiter Register Summary and Description
- 14.2.5.1.9 L3_MAIN STATCOLL Register Summary and Description
- 14.2.5.1
L3_MAIN Register Group Summary
- 14.3
L4 Interconnects
- 14.3.1 L4 Interconnect Overview
- 14.3.2 L4 Interconnect Integration
- 14.3.3 L4 Interconnect Functional Description
- 14.3.4
L4 Interconnect Programming Guide
- 14.3.4.1
L4 Interconnect Low-level Programming Models
- 14.3.4.1.1 Global Initialization
- 14.3.4.1.2
Operational Modes Configuration
- 14.3.4.1.2.1
L4 Interconnect Error Analysis Mode
- 14.3.4.1.2.1.1 Main Sequence: L4 Interconnect Error Analysis Mode
- 14.3.4.1.2.1.2 Subsequence: L4 Interconnect Protection Violation Error Identification
- 14.3.4.1.2.1.3 Subsequence: L4 Interconnect Unsupported Command/Address Hole Error Identification
- 14.3.4.1.2.1.4 Subsequence: L4 Interconnect Reset TA and Module
- 14.3.4.1.2.2 L4 Interconnect Time-Out Configuration Mode
- 14.3.4.1.2.3 L4 Interconnect Firewall Configuration Mode
- 14.3.4.1.2.1
L4 Interconnect Error Analysis Mode
- 14.3.4.1
L4 Interconnect Low-level Programming Models
- 14.3.5 L4 Interconnects Register Manual
-
15Memory Subsystem
- 15.1 Memory Subsystem Overview
- 15.2
Dynamic Memory Manager
- 15.2.1 DMM Overview
- 15.2.2 DMM Integration
- 15.2.3
DMM Functional Description
- 15.2.3.1 DMM Block Diagram
- 15.2.3.2 DMM Clock Configuration
- 15.2.3.3 DMM Power Management
- 15.2.3.4 DMM Interrupt Requests
- 15.2.3.5 DMM
- 15.2.3.6
TILER
- 15.2.3.6.1
TILER Concepts
- 15.2.3.6.1.1
TILER Rationale
- 15.2.3.6.1.1.1 The TILER is a 4-GiB Virtual Address Space Composed of Eight Views
- 15.2.3.6.1.1.2 A View is a 512-MiB Virtual Address Space Composed of Four Containers
- 15.2.3.6.1.1.3 A Container is a 128-MiB Virtual Address Space
- 15.2.3.6.1.1.4 A Page is a 4-kiB Virtual Address Space
- 15.2.3.6.1.1.5 A Tile is a 1-kiB Address Space
- 15.2.3.6.1.1.6 2356
- 15.2.3.6.1.1.7 A Subtile is a 128-Bit Address Space
- 15.2.3.6.1.2 TILER Modes
- 15.2.3.6.1.3 Object Container Definition
- 15.2.3.6.1.4 Page Definition
- 15.2.3.6.1.5 Orientation
- 15.2.3.6.1.6 Tile Definition
- 15.2.3.6.1.7 Subtiles
- 15.2.3.6.1.8
TILER Virtual Addressing
- 15.2.3.6.1.8.1 Page Mode Virtual Addressing and Characteristics
- 15.2.3.6.1.8.2 Tiled Mode Virtual Addressing and Characteristics
- 15.2.3.6.1.8.3
Element Ordering in the TILER Container
- 15.2.3.6.1.8.3.1 Natural View or 0-Degree View (Orientation 0)
- 15.2.3.6.1.8.3.2 0-Degree View With Vertical Mirror or 180-Degree View With Horizontal Mirror (Orientation 1)
- 15.2.3.6.1.8.3.3 0-Degree View With Horizontal Mirror or 180-Degree View With Vertical Mirror (Orientation 2)
- 15.2.3.6.1.8.3.4 180-Degree View (Orientation 3)
- 15.2.3.6.1.8.3.5 90-Degree View With Vertical Mirror or 270-Degree View With Horizontal Mirror (Orientation 4)
- 15.2.3.6.1.8.3.6 270-Degree View (Orientation 5)
- 15.2.3.6.1.8.3.7 90-Degree View (Orientation 6)
- 15.2.3.6.1.8.3.8 90-Degree View With Horizontal Mirror or 270-Degree View With Vertical Mirror (Orientation 7)
- 15.2.3.6.1.1
TILER Rationale
- 15.2.3.6.2 TILER Macro-Architecture
- 15.2.3.6.3 TILER Guidelines for Initiators
- 15.2.3.6.1
TILER Concepts
- 15.2.4 DMM Use Cases and Tips
- 15.2.5
DMM Basic Programming Model
- 15.2.5.1 Global Initialization
- 15.2.5.2 DMM Module Global Initialization
- 15.2.5.3 DMM Operational Modes Configuration
- 15.2.5.4 Addressing an Object in Tiled Mode
- 15.2.5.5 Addressing an Object in Page Mode
- 15.2.5.6 Sharing Containers Between Different Modes
- 15.2.6 DMM Register Manual
- 15.3
EMIF Controller
- 15.3.1 EMIF Controller Overview
- 15.3.2 EMIF Module Environment
- 15.3.3 EMIF Module Integration
- 15.3.4
EMIF Functional Description
- 15.3.4.1 Block Diagram
- 15.3.4.2 Clock Management
- 15.3.4.3 Reset
- 15.3.4.4 System Power Management
- 15.3.4.5 Interrupt Requests
- 15.3.4.6 SDRAM Refresh Scheduling
- 15.3.4.7 SDRAM Initialization
- 15.3.4.8 DDR3 Read-Write Leveling
- 15.3.4.9 EMIF Access Cycles
- 15.3.4.10 Turnaround Time
- 15.3.4.11 PHY DLL Calibration
- 15.3.4.12
SDRAM Address Mapping
- 15.3.4.12.1 Address Mapping for IBANK_POS = 0 and EBANK_POS = 0
- 15.3.4.12.2 Address Mapping for IBANK_POS = 1 and EBANK_POS = 0
- 15.3.4.12.3 Address Mapping for IBANK_POS = 2 and EBANK_POS = 0
- 15.3.4.12.4 Address Mapping for IBANK_POS = 3 and EBANK_POS = 0
- 15.3.4.12.5 Address Mapping for IBANK_POS = 0 and EBANK_POS = 1
- 15.3.4.12.6 Address Mapping for IBANK_POS = 1 and EBANK_POS = 1
- 15.3.4.12.7 Address Mapping for IBANK_POS = 2 and EBANK_POS = 1
- 15.3.4.12.8 2457
- 15.3.4.12.9 Address Mapping for IBANK_POS = 3 and EBANK_POS = 1
- 15.3.4.13 DDR3 Output Impedance Calibration
- 15.3.4.14 Error Correction And Detection Feature
- 15.3.4.15 Class of Service
- 15.3.4.16 Performance Counters
- 15.3.4.17 Forcing CKE to tri-state
- 15.3.5 EMIF Programming Guide
- 15.3.6 EMIF Register Manual
- 15.4
General-Purpose Memory Controller
- 15.4.1 GPMC Overview
- 15.4.2 GPMC Environment
- 15.4.3 GPMC Integration
- 15.4.4
GPMC Functional Description
- 15.4.4.1 GPMC Block Diagram
- 15.4.4.2 GPMC Clock Configuration
- 15.4.4.3 GPMC Software Reset
- 15.4.4.4 GPMC Power Management
- 15.4.4.5 GPMC Interrupt Requests
- 15.4.4.6 L3 Interconnect Interface
- 15.4.4.7 GPMC Address and Data Bus
- 15.4.4.8
Address Decoder and Chip-Select Configuration
- 15.4.4.8.1 Chip-Select Base Address and Region Size
- 15.4.4.8.2 Access Protocol
- 15.4.4.8.3
External Signals
- 15.4.4.8.3.1
Wait Pin Monitoring Control
- 15.4.4.8.3.1.1 Wait Monitoring During Asynchronous Read Access
- 15.4.4.8.3.1.2 Wait Monitoring During Asynchronous Write Access
- 15.4.4.8.3.1.3 Wait Monitoring During Synchronous Read Access
- 15.4.4.8.3.1.4 Wait Monitoring During Synchronous Write Access
- 15.4.4.8.3.1.5 Wait With NAND Device
- 15.4.4.8.3.1.6 Idle Cycle Control Between Successive Accesses
- 15.4.4.8.3.1.7 Slow Device Support (TIMEPARAGRANULARITY Parameter)
- 15.4.4.8.3.2 Reset
- 15.4.4.8.3.3 Byte Enable (nBE1/nBE0)
- 15.4.4.8.3.1
Wait Pin Monitoring Control
- 15.4.4.8.4 Error Handling
- 15.4.4.9
Timing Setting
- 15.4.4.9.1 Read Cycle Time and Write Cycle Time (RDCYCLETIME / WRCYCLETIME)
- 15.4.4.9.2 nCS: Chip-Select Signal Control Assertion/Deassertion Time (CSONTIME / CSRDOFFTIME / CSWROFFTIME / CSEXTRADELAY)
- 15.4.4.9.3 nADV/ALE: Address Valid/Address Latch Enable Signal Control Assertion/Deassertion Time (ADVONTIME / ADVRDOFFTIME / ADVWROFFTIME / ADVEXTRADELAY/ADVAADMUXONTIME/ADVAADMUXRDOFFTIME/ADVAADMUXWROFFTIME)
- 15.4.4.9.4 nOE/nRE: Output Enable/Read Enable Signal Control Assertion/Deassertion Time (OEONTIME / OEOFFTIME / OEEXTRADELAY / OEAADMUXONTIME / OEAADMUXOFFTIME)
- 15.4.4.9.5 nWE: Write Enable Signal Control Assertion/Deassertion Time (WEONTIME / WEOFFTIME / WEEXTRADELAY)
- 15.4.4.9.6 GPMC_CLK
- 15.4.4.9.7 GPMC_CLK and Control Signals Setup and Hold
- 15.4.4.9.8 Access Time (RDACCESSTIME / WRACCESSTIME)
- 15.4.4.9.9 Page Burst Access Time (PAGEBURSTACCESSTIME)
- 15.4.4.9.10 Bus Keeping Support
- 15.4.4.10
NOR Access Description
- 15.4.4.10.1 Asynchronous Access Description
- 15.4.4.10.2 Synchronous Access Description
- 15.4.4.10.3
Asynchronous and Synchronous Accesses in Nonmultiplexed Mode
- 15.4.4.10.3.1 Asynchronous Single-Read Operation on Nonmultiplexed Device
- 15.4.4.10.3.2 Asynchronous Single-Write Operation on Nonmultiplexed Device
- 15.4.4.10.3.3 Asynchronous Multiple (Page Mode) Read Operation on Nonmultiplexed Device
- 15.4.4.10.3.4 Synchronous Operations on a Nonmultiplexed Device
- 15.4.4.10.4 Page and Burst Support
- 15.4.4.10.5 System Burst vs External Device Burst Support
- 15.4.4.11 pSRAM Access Specificities
- 15.4.4.12
NAND Access Description
- 15.4.4.12.1
NAND Memory Device in Byte or 16-bit Word Stream Mode
- 15.4.4.12.1.1 Chip-Select Configuration for NAND Interfacing in Byte or Word Stream Mode
- 15.4.4.12.1.2 NAND Device Command and Address Phase Control
- 15.4.4.12.1.3 Command Latch Cycle
- 15.4.4.12.1.4 Address Latch Cycle
- 15.4.4.12.1.5 NAND Device Data Read and Write Phase Control in Stream Mode
- 15.4.4.12.1.6 NAND Device General Chip-Select Timing Control Requirement
- 15.4.4.12.1.7 Read and Write Access Size Adaptation
- 15.4.4.12.2 NAND Device-Ready Pin
- 15.4.4.12.3
ECC Calculator
- 15.4.4.12.3.1 Hamming Code
- 15.4.4.12.3.2
BCH Code
- 15.4.4.12.3.2.1 Requirements
- 15.4.4.12.3.2.2
Memory Mapping of BCH Codeword
- 15.4.4.12.3.2.2.1 Memory Mapping of Data Message
- 15.4.4.12.3.2.2.2 Memory-Mapping of the ECC
- 15.4.4.12.3.2.2.3
Wrapping Modes
- 4.4.12.3.2.2.3.1 Manual Mode (0x0)
- 4.4.12.3.2.2.3.2 Mode 0x1
- 4.4.12.3.2.2.3.3 Mode 0xA (10)
- 4.4.12.3.2.2.3.4 Mode 0x2
- 4.4.12.3.2.2.3.5 Mode 0x3
- 4.4.12.3.2.2.3.6 Mode 0x7
- 4.4.12.3.2.2.3.7 Mode 0x8
- 4.4.12.3.2.2.3.8 Mode 0x4
- 4.4.12.3.2.2.3.9 Mode 0x9
- 4.4.12.3.2.2.3.10 Mode 0x5
- 4.4.12.3.2.2.3.11 Mode 0xB (11)
- 4.4.12.3.2.2.3.12 Mode 0x6
- 15.4.4.12.3.2.3 Supported NAND Page Mappings and ECC Schemes
- 15.4.4.12.4
Prefetch and Write-Posting Engine
- 15.4.4.12.4.1 General Facts About the Engine Configuration
- 15.4.4.12.4.2 Prefetch Mode
- 15.4.4.12.4.3 FIFO Control in Prefetch Mode
- 15.4.4.12.4.4 Write-Posting Mode
- 15.4.4.12.4.5 FIFO Control in Write-Posting Mode
- 15.4.4.12.4.6 Optimizing NAND Access Using the Prefetch and Write-Posting Engine
- 15.4.4.12.4.7 Interleaved Accesses Between Prefetch and Write-Posting Engine and Other Chip-Selects
- 15.4.4.12.1
NAND Memory Device in Byte or 16-bit Word Stream Mode
- 15.4.5 GPMC Basic Programming Model
- 15.4.6 GPMC Use Cases and Tips
- 15.4.7 GPMC Register Manual
- 15.5 Error Location Module
- 15.6
On-Chip Memory (OCM) Subsystem
- 15.6.1 OCM Subsystem Overview
- 15.6.2 OCM Subsystem Integration
- 15.6.3
OCM Subsystem Functional Desctiption
- 15.6.3.1 Block Diagram
- 15.6.3.2 Resets
- 15.6.3.3 Clock Management
- 15.6.3.4 Interrupt Requests
- 15.6.3.5 OCM Subsystem Memory Regions
- 15.6.3.6 OCM Controller Modes Of Operation
- 15.6.3.7 ECC Associated FIFOs
- 15.6.3.8 ECC Counters And Corrected Bit Distribution Register
- 15.6.3.9 ECC Support
- 15.6.3.10 Circular Buffer (CBUF) Support
- 15.6.3.11 CBUF Mode Error Handling
- 15.6.3.12 Status Reporting
- 15.6.4 OCM Subsystem Register Manual
-
16DMA Controllers
- 16.1
System DMA
- 16.1.1 DMA_SYSTEM Module Overview
- 16.1.2 DMA_SYSTEM Controller Environment
- 16.1.3 DMA_SYSTEM Module Integration
- 16.1.4
DMA_SYSTEM Functional Description
- 16.1.4.1 DMA_SYSTEM Controller Power Management
- 16.1.4.2 DMA_SYSTEM Controller Interrupt Requests
- 16.1.4.3 Logical Channel Transfer Overview
- 16.1.4.4 FIFO Queue Memory Pool
- 16.1.4.5 Addressing Modes
- 16.1.4.6 Packed Accesses
- 16.1.4.7 Burst Transactions
- 16.1.4.8 Endianism Conversion
- 16.1.4.9 Transfer Synchronization
- 16.1.4.10 Thread Budget Allocation
- 16.1.4.11 FIFO Budget Allocation
- 16.1.4.12 Chained Logical Channel Transfers
- 16.1.4.13 Reprogramming an Active Channel
- 16.1.4.14 Packet Synchronization
- 16.1.4.15 Graphics Acceleration Support
- 16.1.4.16 Supervisor Modes
- 16.1.4.17 Posted and Nonposted Writes
- 16.1.4.18 Disabling a Channel During Transfer
- 16.1.4.19 FIFO Draining Mechanism
- 16.1.4.20
Linked List
- 16.1.4.20.1 Overview
- 16.1.4.20.2 Link-List Transfer Profile
- 16.1.4.20.3 Descriptors
- 16.1.4.20.4
Linked-List Control and Monitoring
- 16.1.4.20.4.1 Transfer Mode Setting
- 16.1.4.20.4.2 Starting a Linked List
- 16.1.4.20.4.3 Monitoring a Linked-List Progression
- 16.1.4.20.4.4 Interrupt During Linked-List Execution
- 16.1.4.20.4.5 Pause a Linked List
- 16.1.4.20.4.6 Stop a Linked List (Abort or Drain)
- 16.1.4.20.4.7 Status Bit Behavior
- 16.1.4.20.4.8 Linked-List Channel Linking
- 16.1.5
DMA_SYSTEM Basic Programming Model
- 16.1.5.1 Setup Configuration
- 16.1.5.2 Software-Triggered (Nonsynchronized) Transfer
- 16.1.5.3 Hardware-Synchronized Transfer
- 16.1.5.4 Synchronized Transfer Monitoring Using CDAC
- 16.1.5.5 Concurrent Software and Hardware Synchronization
- 16.1.5.6 Chained Transfer
- 16.1.5.7 90-Degree Clockwise Image Rotation
- 16.1.5.8 Graphic Operations
- 16.1.5.9 Linked-List Programming Guidelines
- 16.1.6 DMA_SYSTEM Register Manual
- 16.2
Enhanced DMA
- 16.2.1 EDMA Module Overview
- 16.2.2 EDMA Controller Environment
- 16.2.3 EDMA Controller Integration
- 16.2.4
EDMA Controller Functional Description
- 16.2.4.1 Block Diagram
- 16.2.4.2 Types of EDMA controller Transfers
- 16.2.4.3
Parameter RAM (PaRAM)
- 16.2.4.3.1 PaRAM
- 16.2.4.3.2
EDMA Channel PaRAM Set Entry Fields
- 16.2.4.3.2.1 Channel Options Parameter (OPT)
- 16.2.4.3.2.2 Channel Source Address (SRC)
- 16.2.4.3.2.3 Channel Destination Address (DST)
- 16.2.4.3.2.4 Count for 1st Dimension (ACNT)
- 16.2.4.3.2.5 Count for 2nd Dimension (BCNT)
- 16.2.4.3.2.6 Count for 3rd Dimension (CCNT)
- 16.2.4.3.2.7 BCNT Reload (BCNTRLD)
- 16.2.4.3.2.8 Source B Index (SBIDX)
- 16.2.4.3.2.9 Destination B Index (DBIDX)
- 16.2.4.3.2.10 Source C Index (SCIDX)
- 16.2.4.3.2.11 Destination C Index (DCIDX)
- 16.2.4.3.2.12 Link Address (LINK)
- 16.2.4.3.3 Null PaRAM Set
- 16.2.4.3.4 Dummy PaRAM Set
- 16.2.4.3.5 Dummy Versus Null Transfer Comparison
- 16.2.4.3.6 Parameter Set Updates
- 16.2.4.3.7 Linking Transfers
- 16.2.4.3.8 Constant Addressing Mode Transfers/Alignment Issues
- 16.2.4.3.9 Element Size
- 16.2.4.4 Initiating a DMA Transfer
- 16.2.4.5 Completion of a DMA Transfer
- 16.2.4.6 Event, Channel, and PaRAM Mapping
- 16.2.4.7 EDMA Channel Controller Regions
- 16.2.4.8 Chaining EDMA Channels
- 16.2.4.9 EDMA Interrupts
- 16.2.4.10 Memory Protection
- 16.2.4.11 Event Queue(s)
- 16.2.4.12 EDMA Transfer Controller (EDMA_TPTC)
- 16.2.4.13 Event Dataflow
- 16.2.4.14 EDMA controller Prioritization
- 16.2.4.15 EDMA Power, Reset and Clock Management
- 16.2.4.16 Emulation Considerations
- 16.2.5
EDMA Transfer Examples
- 16.2.5.1 Block Move Example
- 16.2.5.2 Subframe Extraction Example
- 16.2.5.3 Data Sorting Example
- 16.2.5.4 Peripheral Servicing Example
- 16.2.5.5 Setting Up an EDMA Transfer
- 16.2.6 EDMA Debug Checklist and Programming Tips
- 16.2.7 EDMA Register Manual
- 16.1
System DMA
-
17Interrupt Controllers
- 17.1 Interrupt Controllers Overview
- 17.2 Interrupt Controllers Environment
- 17.3
Interrupt Controllers Integration
- 17.3.1 Interrupt Requests to MPU_INTC
- 17.3.2 Interrupt Requests to DSP1_INTC
- 17.3.3 Interrupt Requests to DSP2_INTC
- 17.3.4 Interrupt Requests to IPU1_Cx_INTC
- 17.3.5 Interrupt Requests to IPU2_Cx_INTC
- 17.3.6 Interrupt Requests to EVE1_INTC1
- 17.3.7 Interrupt Requests to EVE2_INTC1
- 17.3.8 Mapping of Device Interrupts to IRQ_CROSSBAR Inputs
- 17.4 Interrupt Controllers Functional Description
-
18Control Module
- 18.1 Control Module Overview
- 18.2 Control Module Environment
- 18.3 Control Module Integration
- 18.4
Control Module Functional Description
- 18.4.1 Control Module Clock Configuration
- 18.4.2 Control Module Resets
- 18.4.3 Control Module Power Management
- 18.4.4 Hardware Requests
- 18.4.5 Control Module Initialization
- 18.4.6
Functional Description Of The Various Register Types In CTRL_MODULE_CORE Submodule
- 18.4.6.1 Pad Configuration
- 18.4.6.2
Thermal Management Related Registers
- 18.4.6.2.1 Temperature Sensors Control Registers
- 18.4.6.2.2 Registers For The Thermal Alert Comparators
- 18.4.6.2.3 Thermal Shutdown Comparators
- 18.4.6.2.4 Temperature Timestamp Registers
- 18.4.6.2.5 Other Thermal Management Related Registers
- 18.4.6.2.6 Summary of the Thermal Management Related Registers
- 18.4.6.2.7 ADC Values Versus Temperature
- 18.4.6.3 PBIAS Cell And MMC1 I/O Cells Control Registers
- 18.4.6.4 IRQ_CROSSBAR Module Functional Description
- 18.4.6.5 DMA_CROSSBAR Module Functional Description
- 18.4.6.6 SDRAM Initiator Priority Registers
- 18.4.6.7 L3_MAIN Initiator Priority Registers
- 18.4.6.8 Memory Region Lock Registers
- 18.4.6.9 NMI Mapping To Respective Cores
- 18.4.6.10 Software Controls for the DDR2/DDR3 I/O Cells
- 18.4.6.11 Reference Voltage for the Device DDR2/DDR3 Receivers
- 18.4.6.12 AVS Class 0 Associated Registers
- 18.4.6.13 ABB Associated Registers
- 18.4.6.14 Registers For Other Miscellaneous Functions
- 18.4.7 Functional Description Of The Various Register Types In CTRL_MODULE_WKUP Submodule
- 18.5 Control Module Register Manual
- 18.6 IODELAYCONFIG Module Integration
- 18.7 IODELAYCONFIG Module Register Manual
-
19Mailbox
- 19.1 Mailbox Overview
- 19.2 Mailbox Integration
- 19.3 Mailbox Functional Description
- 19.4 Mailbox Programming Guide
- 19.5 Mailbox Register Manual
-
20Memory Management Units
- 20.1 MMU Overview
- 20.2 MMU Integration
- 20.3
MMU Functional Description
- 20.3.1 MMU Block Diagram
- 20.3.2 MMU Software Reset
- 20.3.3 MMU Power Management
- 20.3.4 MMU Interrupt Requests
- 20.3.5 MMU Error Handling
- 20.4 MMU Low-level Programming Models
- 20.5 MMU Register Manual
- 21Spinlock
-
22Timers
- 22.1 Timers Overview
- 22.2
General-Purpose Timers
- 22.2.1 General-Purpose Timers Overview
- 22.2.2 GP Timer Environment
- 22.2.3 GP Timer Integration
- 22.2.4
GP Timer Functional Description
- 22.2.4.1 GP Timer Block Diagram
- 22.2.4.2 TIMER1, TIMER2 and TIMER10 Power Management
- 22.2.4.3 Power Management of Other GP Timers
- 22.2.4.4 Software Reset
- 22.2.4.5 GP Timer Interrupts
- 22.2.4.6 Timer Mode Functionality
- 22.2.4.7 Capture Mode Functionality
- 22.2.4.8 Compare Mode Functionality
- 22.2.4.9 Prescaler Functionality
- 22.2.4.10 Pulse-Width Modulation
- 22.2.4.11 Timer Counting Rate
- 22.2.4.12 Timer Under Emulation
- 22.2.4.13 Accessing GP Timer Registers
- 22.2.4.14 Posted Mode Selection
- 22.2.5 GP Timer Low-Level Programming Models
- 22.2.6 GP Timer Register Manual
- 22.3 32-kHz Synchronized Timer (COUNTER_32K)
- 22.4
Watchdog Timer
- 22.4.1 Watchdog Timer Overview
- 22.4.2 Watchdog Timer Integration
- 22.4.3
Watchdog Timer Functional Description
- 22.4.3.1 Power Management
- 22.4.3.2 Interrupts
- 22.4.3.3 General Watchdog Timer Operation
- 22.4.3.4 Reset Context
- 22.4.3.5 Overflow/Reset Generation
- 22.4.3.6 Prescaler Value/Timer Reset Frequency
- 22.4.3.7 Triggering a Timer Reload
- 22.4.3.8 Start/Stop Sequence for Watchdog Timer (Using the WSPR Register)
- 22.4.3.9 Modifying Timer Count/Load Values and Prescaler Setting
- 22.4.3.10 Watchdog Counter Register Access Restriction (WCRR)
- 22.4.3.11 Watchdog Timer Interrupt Generation
- 22.4.3.12 Watchdog Timer Under Emulation
- 22.4.3.13 Accessing Watchdog Timer Registers
- 22.4.4 Watchdog Timer Low-Level Programming Model
- 22.4.5 Watchdog Timer Register Manual
-
23Real-Time Clock (RTC)
- 23.1 RTC Overview
- 23.2 RTC Environment
- 23.3 RTC Integration
- 23.4 RTC Functional Description
- 23.5 RTC Low-Level Programming Guide
- 23.6 RTC Register Manual
-
24Serial Communication Interfaces
- 24.1
Multimaster High-Speed I2C Controller
- 24.1.1 HS I2C Overview
- 24.1.2
HS I2C Environment
- 24.1.2.1 HS I2C Typical Application
- 24.1.2.2
HS I2C Typical Connection Protocol and Data Format
- 24.1.2.2.1 HS I2C Serial Data Format
- 24.1.2.2.2 HS I2C Data Validity
- 24.1.2.2.3 HS I2C Start and Stop Conditions
- 24.1.2.2.4 HS I2C Addressing
- 24.1.2.2.5 HS I2C Master Transmitter
- 24.1.2.2.6 HS I2C Master Receiver
- 24.1.2.2.7 HS I2C Slave Transmitter
- 24.1.2.2.8 HS I2C Slave Receiver
- 24.1.2.2.9 HS I2C Bus Arbitration
- 24.1.2.2.10 HS I2C Clock Generation and Synchronization
- 24.1.3 HS I2C Integration
- 24.1.4
HS I2C Functional Description
- 24.1.4.1 HS I2C Block Diagram
- 24.1.4.2 HS I2C Clocks
- 24.1.4.3 HS I2C Software Reset
- 24.1.4.4 HS I2C Power Management
- 24.1.4.5 HS I2C Interrupt Requests
- 24.1.4.6 HS I2C DMA Requests
- 24.1.4.7 HS I2C Programmable Multislave Channel Feature
- 24.1.4.8 HS I2C FIFO Management
- 24.1.4.9 HS I2C Noise Filter
- 24.1.4.10 HS I2C System Test Mode
- 24.1.5 HS I2C Programming Guide
- 24.1.6 HS I2C Register Manual
- 24.2
HDQ/1-Wire
- 24.2.1 HDQ1W Overview
- 24.2.2 HDQ1W Environment
- 24.2.3 HDQ1W Integration
- 24.2.4 HDQ1W Functional Description
- 24.2.5 HDQ1W Low-Level Programming Model
- 24.2.6 HDQ1W Register Manual
- 24.3
UART/IrDA/CIR
- 24.3.1 UART/IrDA/CIR Overview
- 24.3.2
UART/IrDA/CIR Environment
- 24.3.2.1 UART Interface
- 24.3.2.2 IrDA Functional Interfaces
- 24.3.2.3 CIR Functional Interfaces
- 24.3.3 UART/IrDA/CIR Integration
- 24.3.4
UART/IrDA/CIR Functional Description
- 24.3.4.1 Block Diagram
- 24.3.4.2 Clock Configuration
- 24.3.4.3 Software Reset
- 24.3.4.4 Power Management
- 24.3.4.5 Interrupt Requests
- 24.3.4.6 FIFO Management
- 24.3.4.7 Mode Selection
- 24.3.4.8
Protocol Formatting
- 24.3.4.8.1
UART Mode
- 24.3.4.8.1.1 UART Clock Generation: Baud Rate Generation
- 24.3.4.8.1.2 Choosing the Appropriate Divisor Value
- 24.3.4.8.1.3 UART Data Formatting
- 24.3.4.8.2
IrDA Mode (UART3 Only)
- 24.3.4.8.2.1 IrDA Clock Generation: Baud Generator
- 24.3.4.8.2.2 Choosing the Appropriate Divisor Value
- 24.3.4.8.2.3
IrDA Data Formatting
- 24.3.4.8.2.3.1 IR RX Polarity Control
- 24.3.4.8.2.3.2 IrDA Reception Control
- 24.3.4.8.2.3.3 IR Address Checking
- 24.3.4.8.2.3.4 Frame Closing
- 24.3.4.8.2.3.5 Store and Controlled Transmission
- 24.3.4.8.2.3.6 Error Detection
- 24.3.4.8.2.3.7 Underrun During Transmission
- 24.3.4.8.2.3.8 Overrun During Receive
- 24.3.4.8.2.3.9 Status FIFO
- 24.3.4.8.2.4 SIR Mode Data Formatting
- 24.3.4.8.2.5 MIR and FIR Mode Data Formatting
- 24.3.4.8.3 CIR Mode (UART3 Only)
- 24.3.4.8.1
UART Mode
- 24.3.5 UART/IrDA/CIR Basic Programming Model
- 24.3.6 UART/IrDA/CIR Register Manual
- 24.4
Multichannel Serial Peripheral Interface
- 24.4.1 McSPI Overview
- 24.4.2 McSPI Environment
- 24.4.3 McSPI Integration
- 24.4.4
McSPI Functional Description
- 24.4.4.1 McSPI Block Diagram
- 24.4.4.2 Reset
- 24.4.4.3
Master Mode
- 24.4.4.3.1 Master Mode Features
- 24.4.4.3.2 Master Transmit-and-Receive Mode (Full Duplex)
- 24.4.4.3.3 Master Transmit-Only Mode (Half Duplex)
- 24.4.4.3.4 Master Receive-Only Mode (Half Duplex)
- 24.4.4.3.5 Single-Channel Master Mode
- 24.4.4.3.6 Start-Bit Mode
- 24.4.4.3.7 Chip-Select Timing Control
- 24.4.4.3.8 Programmable SPI Clock
- 24.4.4.4 Slave Mode
- 24.4.4.5 3-Pin or 4-Pin Mode
- 24.4.4.6 FIFO Buffer Management
- 24.4.4.7 Interrupts
- 24.4.4.8 DMA Requests
- 24.4.4.9 Power Saving Management
- 24.4.5
McSPI Programming Guide
- 24.4.5.1 Global Initialization
- 24.4.5.2
Operational Mode Configuration
- 24.4.5.2.1
McSPI Operational Modes
- 24.4.5.2.1.1 Common Transfer Sequence
- 24.4.5.2.1.2 End of Transfer Sequences
- 24.4.5.2.1.3 Transmit-and-Receive (Master and Slave)
- 24.4.5.2.1.4 Transmit-Only (Master and Slave)
- 24.4.5.2.1.5 Master Normal Receive-Only
- 24.4.5.2.1.6 Master Turbo Receive-Only
- 24.4.5.2.1.7 Slave Receive-Only
- 24.4.5.2.1.8
Transfer Procedures With FIFO
- 24.4.5.2.1.8.1 Common Transfer Sequence in FIFO Mode
- 24.4.5.2.1.8.2 End of Transfer Sequences in FIFO Mode
- 24.4.5.2.1.8.3 Transmit-and-Receive With Word Count
- 24.4.5.2.1.8.4 Transmit-and-Receive Without Word Count
- 24.4.5.2.1.8.5 Transmit-Only
- 24.4.5.2.1.8.6 Receive-Only With Word Count
- 24.4.5.2.1.8.7 Receive-Only Without Word Count
- 24.4.5.2.1
McSPI Operational Modes
- 24.4.5.3 Common Transfer Procedures Without FIFO – Polling Method
- 24.4.6 McSPI Register Manual
- 24.5 Quad Serial Peripheral Interface
- 24.6
Multichannel Audio Serial Port
- 24.6.1 McASP Overview
- 24.6.2 McASP Environment
- 24.6.3 McASP Integration
- 24.6.4
McASP Functional Description
- 24.6.4.1 McASP Block Diagram
- 24.6.4.2 McASP Clock and Frame-Sync Configurations
- 24.6.4.3 Serializers
- 24.6.4.4 Format Units
- 24.6.4.5 State-Machines
- 24.6.4.6 TDM Sequencers
- 24.6.4.7 McASP Software Reset
- 24.6.4.8 McASP Power Management
- 24.6.4.9 Transfer Modes
- 24.6.4.10 Data Transmission and Reception
- 24.6.4.11 McASP Audio FIFO (AFIFO)
- 24.6.4.12 McASP Events and Interrupt Requests
- 24.6.4.13 DMA Requests
- 24.6.4.14 Loopback Modes
- 24.6.4.15 Error Reporting
- 24.6.5
McASP Low-Level Programming Model
- 24.6.5.1
Global Initialization
- 24.6.5.1.1 Surrounding Modules Global Initialization
- 24.6.5.1.2
McASP Global Initialization
- 24.6.5.1.2.1
Main Sequence – McASP Global Initialization for DIT-Transmission
- 24.6.5.1.2.1.1 Subsequence – Transmit Format Unit Configuration for DIT-Transmission
- 24.6.5.1.2.1.2 Subsequence – Transmit Frame Synchronization Generator Configuration for DIT-Transmission
- 24.6.5.1.2.1.3 Subsequence – Transmit Clock Generator Configuration for DIT-Transmission
- 24.6.5.1.2.1.4 Subsequence - McASP Pins Functional Configuration
- 24.6.5.1.2.1.5 Subsequence – DIT-specific Subframe Fields Configuration
- 24.6.5.1.2.2
Main Sequence – McASP Global Initialization for TDM-Reception
- 24.6.5.1.2.2.1 Subsequence – Receive Format Unit Configuration in TDM Mode
- 24.6.5.1.2.2.2 Subsequence – Receive Frame Synchronization Generator Configuration in TDM Mode
- 24.6.5.1.2.2.3 Subsequence – Receive Clock Generator Configuration
- 24.6.5.1.2.2.4 Subsequence—McASP Receiver Pins Functional Configuration
- 24.6.5.1.2.3
Main Sequence – McASP Global Initialization for TDM -Transmission
- 24.6.5.1.2.3.1 Subsequence – Transmit Format Unit Configuration in TDM Mode
- 24.6.5.1.2.3.2 Subsequence – Transmit Frame Synchronization Generator Configuration in TDM Mode
- 24.6.5.1.2.3.3 Subsequence – Transmit Clock Generator Configuration for TDM Cases
- 24.6.5.1.2.3.4 Subsequence—McASP Transmit Pins Functional Configuration
- 24.6.5.1.2.1
Main Sequence – McASP Global Initialization for DIT-Transmission
- 24.6.5.2 Operational Modes Configuration
- 24.6.5.1
Global Initialization
- 24.6.6 McASP Register Manual
- 24.7 SuperSpeed USB DRD
- 24.8
SATA Controller
- 24.8.1 SATA Controller Overview
- 24.8.2 SATA Controller Environment
- 24.8.3 SATA Controller Integration
- 24.8.4
SATA Controller Functional Description
- 24.8.4.1 SATA Controller Block Diagram
- 24.8.4.2 SATA Controller Link Layer Protocol and Data Format
- 24.8.4.3 Resets
- 24.8.4.4 Power Management
- 24.8.4.5
Interrupt Requests
- 24.8.4.5.1 Interrupt Generation
- 24.8.4.5.2 Levels of Interrupt Control
- 24.8.4.5.3
Interrupt Events Description
- 24.8.4.5.3.1 Task File Error Status
- 24.8.4.5.3.2 Host Bus Fatal Error
- 24.8.4.5.3.3 Interface Fatal Error Status
- 24.8.4.5.3.4 Interface Non-Fatal Error Status
- 24.8.4.5.3.5 Overflow Status
- 24.8.4.5.3.6 Incorrect Port Multiplier Status
- 24.8.4.5.3.7 PHYReady Change Status
- 24.8.4.5.3.8 Port Connect Change Status
- 24.8.4.5.3.9 Descriptor Processed
- 24.8.4.5.3.10 Unknown FIS Interrupt
- 24.8.4.5.3.11 Set Device Bits Interrupt
- 24.8.4.5.3.12 DMA Setup FIS Interrupt
- 24.8.4.5.3.13 PIO Setup FIS Interrupt
- 24.8.4.5.3.14 Device to Host Register FIS Interrupt
- 24.8.4.5.4 Interrupt Condition Control
- 24.8.4.5.5 Command Completion Coalescing Interrupts
- 24.8.4.6 System Memory FIS Descriptors
- 24.8.4.7 Transport Layer FIS-Based Interactions
- 24.8.4.8 DMA Port Configuration
- 24.8.4.9 Port Multiplier Operation
- 24.8.4.10 Activity LED Generation Functionality
- 24.8.4.11 Supported Types of SATA Transfers
- 24.8.4.12 SATA Controller AHCI Hardware Register Interface
- 24.8.5 SATA Controller Low Level Programming Model
- 24.8.6 SATA Controller Register Manual
- 24.9
PCIe Controller
- 24.9.1 PCIe Controller Subsystem Overview
- 24.9.2 PCIe Controller Environment
- 24.9.3 PCIe Controllers Integration
- 24.9.4
PCIe SS Controller Functional Description
- 24.9.4.1 PCIe Controller Functional Block Diagram
- 24.9.4.2 PCIe Traffics
- 24.9.4.3 PCIe Controller Ports on L3_MAIN Interconnect
- 24.9.4.4 PCIe Controller Reset Management
- 24.9.4.5 PCIe Controller Power Management
- 24.9.4.6
PCIe Controller Interrupt Requests
- 24.9.4.6.1 PCIe Controller Main Hardware Management
- 24.9.4.6.2 PCIe Controller Legacy and MSI Virtual Interrupts Management
- 24.9.4.6.3 PCIe Controller MSI Hardware Interrupt Events
- 24.9.4.7 PCIe Controller Address Spaces and Address Translation
- 24.9.4.8 PCIe Traffic Requesting and Responding
- 24.9.4.9 PCIe Programming Register Interface
- 24.9.5 PCIe Controller Low Level Programming Model
- 24.9.6 PCIe Standard Registers vs PCIe Subsystem Hardware Registers Mapping
- 24.9.7
PCIe Controller Register Manual
- 24.9.7.1 PCIe Controller Instance Summary
- 24.9.7.2 PCIe_SS_EP_CFG_PCIe Registers
- 24.9.7.3 PCIe_SS_EP_CFG_DBICS Registers
- 24.9.7.4 PCIe_SS_RC_CFG_DBICS Registers
- 24.9.7.5 PCIe_SS_PL_CONF Registers
- 24.9.7.6 PCIe_SS_EP_CFG_DBICS2 Registers
- 24.9.7.7 PCIe_SS_RC_CFG_DBICS2 Registers
- 24.9.7.8 PCIe_SS_TI_CONF Registers
- 24.10
DCAN
- 24.10.1 DCAN Overview
- 24.10.2 DCAN Environment
- 24.10.3 DCAN Integration
- 24.10.4
DCAN Functional Description
- 24.10.4.1 Module Clocking Requirements
- 24.10.4.2 Interrupt Functionality
- 24.10.4.3 DMA Functionality
- 24.10.4.4 Local Power-Down Mode
- 24.10.4.5 Parity Check Mechanism
- 24.10.4.6 Debug/Suspend Mode
- 24.10.4.7
Configuration of Message Objects Description
- 24.10.4.7.1 Configuration of a Transmit Object for Data Frames
- 24.10.4.7.2 Configuration of a Transmit Object for Remote Frames
- 24.10.4.7.3 Configuration of a Single Receive Object for Data Frames
- 24.10.4.7.4 Configuration of a Single Receive Object for Remote Frames
- 24.10.4.7.5 Configuration of a FIFO Buffer
- 24.10.4.8
Message Handling
- 24.10.4.8.1 Message Handler Overview
- 24.10.4.8.2 Receive/Transmit Priority
- 24.10.4.8.3 Transmission of Messages in Event Driven CAN Communication
- 24.10.4.8.4 Updating a Transmit Object
- 24.10.4.8.5 Changing a Transmit Object
- 24.10.4.8.6 Acceptance Filtering of Received Messages
- 24.10.4.8.7 Reception of Data Frames
- 24.10.4.8.8 Reception of Remote Frames
- 24.10.4.8.9 Reading Received Messages
- 24.10.4.8.10 Requesting New Data for a Receive Object
- 24.10.4.8.11 Storing Received Messages in FIFO Buffers
- 24.10.4.8.12 Reading From a FIFO Buffer
- 24.10.4.9 CAN Bit Timing
- 24.10.4.10 Message Interface Register Sets
- 24.10.4.11 Message RAM
- 24.10.4.12 CAN Operation
- 24.10.4.13 GPIO Support
- 24.10.5 DCAN Register Manual
- 24.11
Gigabit Ethernet Switch (GMAC_SW)
- 24.11.1 GMAC_SW Overview
- 24.11.2 GMAC_SW Environment
- 24.11.3 GMAC_SW Integration
- 24.11.4
GMAC_SW Functional Description
- 24.11.4.1 Functional Block Diagram
- 24.11.4.2 GMAC_SW Ports
- 24.11.4.3 Clocking
- 24.11.4.4 Software IDLE
- 24.11.4.5 Interrupt Functionality
- 24.11.4.6 Reset Isolation
- 24.11.4.7 Software Reset
- 24.11.4.8
CPSW_3G
- 24.11.4.8.1 CPDMA RX and TX Interfaces
- 24.11.4.8.2
Address Lookup Engine (ALE)
- 24.11.4.8.2.1
Address Table Entry
- 24.11.4.8.2.1.1 Free Table Entry
- 24.11.4.8.2.1.2 Multicast Address Table Entry
- 24.11.4.8.2.1.3 VLAN/Multicast Address Table Entry
- 24.11.4.8.2.1.4 Unicast Address Table Entry
- 24.11.4.8.2.1.5 OUI Unicast Address Table Entry
- 24.11.4.8.2.1.6 VLAN/Unicast Address Table Entry
- 24.11.4.8.2.1.7 VLAN Table Entry
- 24.11.4.8.2.2 Packet Forwarding Processes
- 24.11.4.8.2.3 Learning Process
- 24.11.4.8.2.4 VLAN Aware Mode
- 24.11.4.8.2.5 VLAN Unaware Mode
- 24.11.4.8.2.1
Address Table Entry
- 24.11.4.8.3 Packet Priority Handling
- 24.11.4.8.4 FIFO Memory Control
- 24.11.4.8.5 FIFO Transmit Queue Control
- 24.11.4.8.6 Audio Video Bridging
- 24.11.4.8.7
Ethernet MAC Sliver (CPGMAC_SL)
- 24.11.4.8.7.1
G/MII Media Independent Interface
- 24.11.4.8.7.1.1 Data Reception
- 24.11.4.8.7.1.2
Data Transmission
- 24.11.4.8.7.1.2.1 Transmit Control
- 24.11.4.8.7.1.2.2 CRC Insertion
- 24.11.4.8.7.1.2.3 MTXER
- 24.11.4.8.7.1.2.4 Adaptive Performance Optimization (APO)
- 24.11.4.8.7.1.2.5 Inter-Packet-Gap Enforcement
- 24.11.4.8.7.1.2.6 Back Off
- 24.11.4.8.7.1.2.7 Programmable Transmit Inter-Packet Gap
- 24.11.4.8.7.1.2.8 Speed, Duplex and Pause Frame Support Negotiation
- 24.11.4.8.7.2 RMII Interface
- 24.11.4.8.7.3 RGMII Interface
- 24.11.4.8.7.4 Frame Classification
- 24.11.4.8.7.1
G/MII Media Independent Interface
- 24.11.4.8.8 Embedded Memories
- 24.11.4.8.9 Flow Control
- 24.11.4.8.10 Short Gap
- 24.11.4.8.11 Switch Latency
- 24.11.4.8.12 Emulation Control
- 24.11.4.8.13 FIFO Loopback
- 24.11.4.8.14 Device Level Ring (DLR) Support
- 24.11.4.8.15 Energy Efficient Ethernet Support (802.3az)
- 24.11.4.8.16 CPSW_3G Network Statistics
- 24.11.4.9
Static Packet Filter (SPF)
- 24.11.4.9.1 SPF Overview
- 24.11.4.9.2 SPF Functional Description
- 24.11.4.9.3 Programming Guide
- 24.11.4.10 Common Platform Time Sync (CPTS)
- 24.11.4.11 CPPI Buffer Descriptors
- 24.11.4.12 MDIO
- 24.11.5 GMAC_SW Programming Guide
- 24.11.6
GMAC_SW Register Manual
- 24.11.6.1 GMAC_SW Instance Summary
- 24.11.6.2 SS Registers
- 24.11.6.3 PORT Registers
- 24.11.6.4 CPDMA registers
- 24.11.6.5 STATS Registers
- 24.11.6.6 STATERAM Registers
- 24.11.6.7 CPTS registers
- 24.11.6.8 ALE registers
- 24.11.6.9 SL registers
- 24.11.6.10 MDIO registers
- 24.11.6.11 WR registers
- 24.11.6.12 SPF Registers
- 24.12
Media Local Bus (MLB)
- 24.12.1 MLB Overview
- 24.12.2 MLB Environment
- 24.12.3 MLB Integration
- 24.12.4 MLB Functional Description
- 24.12.5 MLB Programming Guide
- 24.12.6 MLB Register Manual
- 24.1
Multimaster High-Speed I2C Controller
-
25eMMC/SD/SDIO
- 25.1 eMMC/SD/SDIO Overview
- 25.2 eMMC/SD/SDIO Environment
- 25.3 eMMC/SD/SDIO Integration
- 25.4
eMMC/SD/SDIO Functional Description
- 25.4.1 Block Diagram
- 25.4.2 Resets
- 25.4.3 Power Management
- 25.4.4 Interrupt Requests
- 25.4.5 DMA Modes
- 25.4.6 Mode Selection
- 25.4.7 Buffer Management
- 25.4.8 Transfer Process
- 25.4.9 Transfer or Command Status and Errors Reporting
- 25.4.10 Auto Command 12 Timings
- 25.4.11 Transfer Stop
- 25.4.12 Output Signals Generation
- 25.4.13 Sampling Clock Tuning
- 25.4.14 Card Boot Mode Management
- 25.4.15 MMC CE-ATA Command Completion Disable Management
- 25.4.16 Test Registers
- 25.4.17 eMMC/SD/SDIO Hardware Status Features
- 25.5
eMMC/SD/SDIO Programming Guide
- 25.5.1
Low-Level Programming Models
- 25.5.1.1 Global Initialization
- 25.5.1.2
Operational Modes Configuration
- 25.5.1.2.1
Basic Operations for eMMC/SD/SDIO Host Controller
- 25.5.1.2.1.1 Card Detection, Identification, and Selection
- 25.5.1.2.1.2 Read/Write Transfer Flow in DMA Mode With Interrupt
- 25.5.1.2.1.3 Read/Write Transfer Flow in DMA Mode With Polling
- 25.5.1.2.1.4 Read/Write Transfer Flow Without DMA With Polling
- 25.5.1.2.1.5 Read/Write Transfer Flow in CE-ATA Mode
- 25.5.1.2.1.6 Suspend-Resume Flow
- 25.5.1.2.1.7 Basic Operations – Steps Detailed
- 25.5.1.2.2 Bus Voltage Selection
- 25.5.1.2.3 Boot Mode Configuration
- 25.5.1.2.4 SDR104/HS200 DLL Tuning Procedure
- 25.5.1.2.1
Basic Operations for eMMC/SD/SDIO Host Controller
- 25.5.1
Low-Level Programming Models
- 25.6 eMMC/SD/SDIO Register Manual
-
26Shared PHY Component Subsystem
- 26.1
SATA PHY Subsystem
- 26.1.1 SATA PHY Subsystem Overview
- 26.1.2 SATA PHY Subsystem Environment
- 26.1.3 SATA PHY Subsystem Integration
- 26.1.4
SATA PHY Subsystem Functional Description
- 26.1.4.1 SATA PLL Controller L4 Interface Adapter Functional Description
- 26.1.4.2 SATA PHY Serializer and Deserializer Functional Descriptions
- 26.1.4.3
SATA Clock Generator Subsystem Functional Description
- 26.1.4.3.1 SATA DPLL Clock Generator Overview
- 26.1.4.3.2 SATA DPLL Clock Generator Reset
- 26.1.4.3.3 SATA DPLL Low-Power Modes
- 26.1.4.3.4 SATA DPLL Clocks Configuration
- 26.1.4.3.5 SATA DPLL Subsystem Architecture
- 26.1.4.3.6 SATA DPLL Clock Generator Modes and State Transitions
- 26.1.4.3.7 SATA PLL Controller Functions
- 26.1.5 SATA PHY Subsystem Low-Level Programming Model
- 26.2
USB3_PHY Subsystem
- 26.2.1 USB3_PHY Subsystem Overview
- 26.2.2 USB3_PHY Subsystem Environment
- 26.2.3 USB3_PHY Subsystem Integration
- 26.2.4
USB3_PHY Subsystem Functional Description
- 26.2.4.1 Super-Speed USB PLL Controller L4 Interface Adapter Functional Description
- 26.2.4.2 USB3_PHY Serializer and Deserializer Functional Descriptions
- 26.2.4.3
USB3_PHY Clock Generator Subsystem Functional Description
- 26.2.4.3.1 USB3_PHY DPLL Clock Generator Overview
- 26.2.4.3.2 USB3_PHY DPLL Clock Generator Reset
- 26.2.4.3.3 USB3_PHY DPLL Low-Power Modes
- 26.2.4.3.4 USB3_PHY DPLL Clocks Configuration
- 26.2.4.3.5 USB3_PHY DPLL Subsystem Architecture
- 26.2.4.3.6 USB3_PHY DPLL Clock Generator Modes and State Transitions
- 26.2.4.3.7 USB3_PHY PLL Controller Functions
- 26.2.5 USB3_PHY Subsystem Low-Level Programming Model
- 26.3 USB3 PHY and SATA PHY Register Manual
- 26.4
PCIe PHY Subsystem
- 26.4.1 PCIe PHY Subsystem Overview
- 26.4.2 PCIe PHY Subsystem Environment
- 26.4.3 PCIe Shared PHY Subsystem Integration
- 26.4.4
PCIe PHY Subsystem Functional Description
- 26.4.4.1 PCIe PHY Subsystem Block Diagram
- 26.4.4.2 OCP2SCP Functional Description
- 26.4.4.3 PCIe PHY Serializer and Deserializer Functional Descriptions
- 26.4.4.4
PCIe PHY Clock Generator Subsystem Functional Description
- 26.4.4.4.1
PCIe PHY DPLL Clock Generator
- 26.4.4.4.1.1 PCIe PHY DPLL Clock Generator Overview
- 26.4.4.4.1.2 PCIe PHY DPLL Clock Generator Reset
- 26.4.4.4.1.3 PCIe PHY DPLL Low-Power Modes
- 26.4.4.4.1.4 PCIe PHY DPLL Clocks Configuration
- 26.4.4.4.1.5 PCIe PHY DPLL Subsystem Architecture
- 26.4.4.4.1.6
PCIe PHY DPLL Clock Generator Modes and State Transitions
- 26.4.4.4.1.6.1 PCIe PHY Clock Generator Power Up
- 26.4.4.4.1.6.2 PCIe PHY DPLL Sequences
- 26.4.4.4.1.6.3 PCIe PHY DPLL Locked Mode
- 26.4.4.4.1.6.4 PCIe PHY DPLL Idle-Bypass Mode
- 26.4.4.4.1.6.5 PCIe PHY DPLL Low Power Stop Mode
- 26.4.4.4.1.6.6 PCIe PHY DPLL Clock Programming Sequence
- 26.4.4.4.1.6.7 PCIe PHY DPLL Recommended Values
- 26.4.4.4.2
PCIe PHY APLL Clock Generator
- 26.4.4.4.2.1 PCIe PHY APLL Clock Generator Overview
- 26.4.4.4.2.2 PCIe PHY APLL Clock Generator Reset
- 26.4.4.4.2.3 PCIe PHY APLL Low-Power Mode
- 26.4.4.4.2.4 PCIe PHY APLL Clocks Configuration
- 26.4.4.4.2.5 PCIe PHY APLL Subsystem Architecture
- 26.4.4.4.2.6 PCIe PHY APLL Clock Generator Modes and State Transitions
- 26.4.4.4.3 ACSPCIE reference clock buffer
- 26.4.4.4.1
PCIe PHY DPLL Clock Generator
- 26.4.5 PCIePHY Subsystem Low-Level Programming Model
- 26.4.6 PCIe PHY Subsystem Register Manual
- 26.1
SATA PHY Subsystem
-
27General-Purpose Interface
- 27.1 General-Purpose Interface Overview
- 27.2 General-Purpose Interface Environment
- 27.3 General-Purpose Interface Integration
- 27.4
General-Purpose Interface Functional Description
- 27.4.1 General-Purpose Interface Block Diagram
- 27.4.2 General-Purpose Interface Interrupt and Wake-Up Features
- 27.4.3 General-Purpose Interface Clock Configuration
- 27.4.4 General-Purpose Interface Hardware and Software Reset
- 27.4.5 General-Purpose Interface Power Management
- 27.4.6 General-Purpose Interface Interrupt and Wake-Up Requests
- 27.4.7 General-Purpose Interface Channels Description
- 27.4.8 General-Purpose Interface Data Input/Output Capabilities
- 27.4.9 General-Purpose Interface Set-and-Clear Protocol
- 27.5 General-Purpose Interface Programming Guide
- 27.6 General-Purpose Interface Register Manual
-
28Keyboard Controller
- 28.1 Keyboard Controller Overview
- 28.2 Keyboard Controller Environment
- 28.3 Keyboard Controller Integration
- 28.4
Keyboard Controller Functional Description
- 28.4.1 Keyboard Controller Block Diagram
- 28.4.2 Keyboard Controller Software Reset
- 28.4.3 Keyboard Controller Power Management
- 28.4.4 Keyboard Controller Interrupt Requests
- 28.4.5 Keyboard Controller Software Mode
- 28.4.6 Keyboard Controller Hardware Decoding Modes
- 28.4.7 Keyboard Controller Key Coding Registers
- 28.4.8 Keyboard Controller Register Access
- 28.5
Keyboard Controller Programming Guide
- 28.5.1
Keyboard Controller Low-Level Programming Models
- 28.5.1.1 Global Initialization
- 28.5.1.2 Operational Modes Configuration
- 28.5.1.3 Keyboard Controller Events Servicing
- 28.5.1
Keyboard Controller Low-Level Programming Models
- 28.6 Keyboard Controller Register Manual
-
29Pulse-Width Modulation Subsystem
- 29.1 PWM Subsystem Resources
- 29.2 Enhanced PWM (ePWM) Module
- 29.3 Enhanced Capture (eCAP) Module
- 29.4 Enhanced Quadrature Encoder Pulse (eQEP) Module
-
30Viterbi-Decoder Coprocessor
- 30.1 VCP Overview
- 30.2 VCP Integration
- 30.3
VCP Functional Description
- 30.3.1 VCP Block Diagram
- 30.3.2 VCP Internal Interfaces
- 30.3.3 Functional Overview
- 30.3.4 VCP Architecture
- 30.3.5 VCP Input Data
- 30.3.6 Soft Input Dynamic Ranges
- 30.3.7 VCP Memory Sleep Mode
- 30.3.8 Decision Data
- 30.3.9 Endianness
- 30.3.10 VCP Output Parameters
- 30.3.11 Event Generation
- 30.3.12 Operational Modes
- 30.3.13 Errors and Status
- 30.4 VCP Modules Programming Guide
- 30.5 VCP Register Manual
- 31Audio Tracking Logic
-
32Initialization
- 32.1 Initialization Overview
- 32.2 Preinitialization
- 32.3
Device Initialization by ROM Code
- 32.3.1 Booting Overview
- 32.3.2 Memory Maps
- 32.3.3 Overall Booting Sequence
- 32.3.4 Startup and Configuration
- 32.3.5 Peripheral Booting
- 32.3.6 Fast External Booting
- 32.3.7
Memory Booting
- 32.3.7.1 Overview
- 32.3.7.2 Non-XIP Memory
- 32.3.7.3 XIP Memory
- 32.3.7.4 NAND
- 32.3.7.5 SPI/QSPI Flash Devices
- 32.3.7.6
eMMC Memories and SD Cards
- 32.3.7.6.1 eMMC Memories
- 32.3.7.6.2 SD Cards
- 32.3.7.6.3 Initialization and Detection
- 32.3.7.6.4 Read Sector Procedure
- 32.3.7.6.5 File System Handling
- 32.3.7.7 SATA Device Boot Operation
- 32.3.8 Image Format
- 32.3.9 Tracing
- 32.4 Services for HLOS Support
-
33On-Chip Debug Support
- 33.1 Introduction
- 33.2 Debug Interfaces
- 33.3 Debugger Connection
- 33.4 Primary Debug Support
- 33.5 Real-Time Debug
- 33.6 Power, Reset, and Clock Management Debug Support
- 33.7 Performance Monitoring
- 33.8 MPU Memory Adaptor (MPU_MA) Watchpoint
- 33.9 Processor Trace
- 33.10
System Instrumentation
- 33.10.1 MIPI STM (CT_STM)
- 33.10.2 System Trace Export
- 33.10.3 Software Instrumentation
- 33.10.4 OCP Watchpoint
- 33.10.5 IVA Pipeline
- 33.10.6 EVE SMSET
- 33.10.7
L3 NOC Statistics Collector
- 33.10.7.1 L3 Target Load Monitoring
- 33.10.7.2
L3 Master Latency Monitoring
- 33.10.7.2.1 SC_LAT0 Configuration
- 33.10.7.2.2 SC_LAT1 Configuration
- 33.10.7.2.3 SC_LAT2 Configuration
- 33.10.7.2.4 SC_LAT3 Configuration
- 33.10.7.2.5 SC_LAT4 Configuration
- 33.10.7.2.6 SC_LAT5 Configuration
- 33.10.7.2.7 SC_LAT6 Configuration
- 33.10.7.2.8 SC_LAT7 Configuration
- 33.10.7.2.9 SC_LAT8 Configuration
- 33.10.7.2.10 Statistics Collector Alarm Mode
- 33.10.7.2.11 Statistics Collector Suspend Mode
- 33.10.8 PM Instrumentation
- 33.10.9 CM Instrumentation
- 33.10.10 Master-ID Encoding
- 33.11 Concurrent Debug Modes
- 33.12 DRM Register Manual
- 34Glossary
- 35Revision History
20.3.1.2.2 First-Level Translation Table
The first-level translation table describes the translation properties for 1-MiB sections. To describe a 4-GiB address range requires 4096 32-bit entries (so-called first-level descriptors).
The first-level translation table start address must be aligned on a multiple of the table size with a 128-byte minimum. Consequently, an alignment of at least 16K bytes is required for a complete 4096-entry table; that is, at least the last fourteen address bits must be zero.
The start address of the first-level translation table is specified by the so-called translation table base. The table is indexed by the upper 12-bits of the virtual address. Figure 20-8 shows this mechanism.
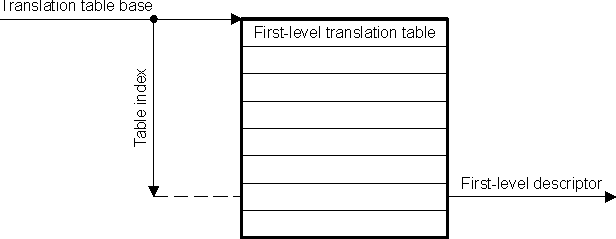 Figure 20-8 First-level Descriptor Address Calculation
Figure 20-8 First-level Descriptor Address CalculationTo summarize, the translation table base and the translation table index together define the first-level descriptor address. Figure 20-9 outlines the precise mechanism used to calculate this address.
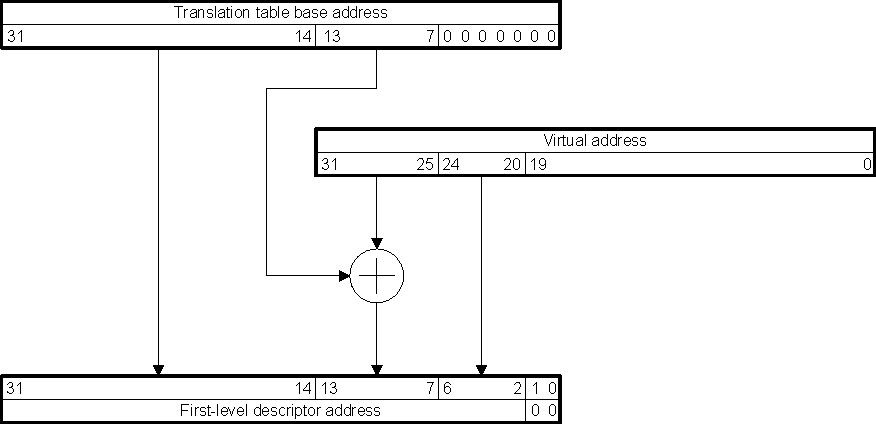 Figure 20-9 Detailed First-Level Descriptor Address Calculation
Figure 20-9 Detailed First-Level Descriptor Address CalculationAs an example of this mechanism, consider a translation table base address of 0x8000:0000 and a virtual address of 0x1234:5678. In this case, the first-level descriptor address is 0x8000:0000 + (0x123 << 2) = 0x8000:048C.