SPRUII0F May 2019 – June 2024 TMS320F28384D , TMS320F28384D-Q1 , TMS320F28384S , TMS320F28384S-Q1 , TMS320F28386D , TMS320F28386D-Q1 , TMS320F28386S , TMS320F28386S-Q1 , TMS320F28388D , TMS320F28388S
- 1
- Read This First
- 1 ► C28x SYSTEM RESOURCES
- 2 C2000™ Microcontrollers Software Support
-
3 C28x System Control and Interrupts
- 3.1 C28x System Control Introduction
- 3.2 System Control Functional Description
- 3.3
Resets
- 3.3.1 Reset Sources
- 3.3.2 External Reset (XRSn)
- 3.3.3 Simulate External Reset
- 3.3.4 Power-On Reset (POR)
- 3.3.5 Debugger Reset (SYSRS)
- 3.3.6 Simulate CPU1 Reset
- 3.3.7 Watchdog Reset (WDRS)
- 3.3.8 NMI Watchdog Reset (NMIWDRS)
- 3.3.9 Secure Code Copy Reset (SCCRESET)
- 3.3.10 ESC Reset Output
- 3.3.11 Test Reset (TRST)
- 3.4 Peripheral Interrupts
- 3.5
Exceptions and Non-Maskable
Interrupts
- 3.5.1 Configuring and Using NMIs
- 3.5.2 Emulation Considerations
- 3.5.3
NMI Sources
- 3.5.3.1 Missing Clock Detection
- 3.5.3.2 RAM Uncorrectable Error
- 3.5.3.3 Flash Uncorrectable ECC Error
- 3.5.3.4 ROM Uncorrectable Error
- 3.5.3.5 NMI Vector Fetch Mismatch
- 3.5.3.6 CPU2 Watchdog or NMI Watchdog Reset
- 3.5.3.7 CM NMI Watchdog Reset
- 3.5.3.8 EtherCAT Reset out
- 3.5.3.9 CRC Fail
- 3.5.3.10 ERAD NMI
- 3.5.4 Illegal Instruction Trap (ITRAP)
- 3.6 Safety Features
- 3.7 Clocking
- 3.8 Clock Configuration Semaphore
- 3.9 32-Bit CPU Timers 0/1/2
- 3.10 Watchdog Timers
- 3.11 Low-Power Modes
- 3.12
Memory Controller Module
- 3.12.1
Functional Description
- 3.12.1.1 Dedicated RAM (Dx RAM)
- 3.12.1.2 Local Shared RAM (LSx RAM)
- 3.12.1.3 Global Shared RAM (GSx RAM)
- 3.12.1.4 CPU Message RAM (CPU MSG RAM)
- 3.12.1.5 CLA Message RAM (CLA MSGRAM)
- 3.12.1.6 CLA-DMA MSG RAM
- 3.12.1.7 Access Arbitration
- 3.12.1.8 Access Protection
- 3.12.1.9 Memory Error Detection, Correction and Error Handling
- 3.12.1.10 Application Test Hooks for Error Detection and Correction
- 3.12.1.11 ROM Test
- 3.12.1.12 RAM Initialization
- 3.12.1
Functional Description
- 3.13 JTAG
- 3.14 System Control Register Configuration Restrictions
- 3.15
Software
- 3.15.1 SYSCTL Examples
- 3.15.2
MEMCFG Examples
- 3.15.2.1 Correctable & Uncorrectable Memory Error Handling
- 3.15.2.2 Shared RAM Management (CPU1) - C28X_DUAL
- 3.15.2.3 Shared RAM Management (CPU2) - C28X_DUAL
- 3.15.2.4 Demonstrate memconfig diagnostics and error handling. - CM
- 3.15.2.5 Shared RAM Management (CPU1) - C28X_DUAL
- 3.15.2.6 Shared RAM Management (CPU2) - C28X_DUAL
- 3.15.3 NMI Examples
- 3.15.4 TIMER Examples
- 3.15.5 WATCHDOG Examples
- 3.16
System Control Registers
- 3.16.1 SYSCTRL Base Address Table (C28)
- 3.16.2 ACCESS_PROTECTION_REGS Registers
- 3.16.3 CLK_CFG_REGS Registers
- 3.16.4 CM_CONF_REGS Registers
- 3.16.5 CPU_SYS_REGS Registers
- 3.16.6 CPU_ID_REGS Registers
- 3.16.7 CPU1_PERIPH_AC_REGS Registers
- 3.16.8 CPUTIMER_REGS Registers
- 3.16.9 DEV_CFG_REGS Registers
- 3.16.10 DMA_CLA_SRC_SEL_REGS Registers
- 3.16.11 MEM_CFG_REGS Registers
- 3.16.12 MEMORY_ERROR_REGS Registers
- 3.16.13 NMI_INTRUPT_REGS Registers
- 3.16.14 PIE_CTRL_REGS Registers
- 3.16.15 ROM_PREFETCH_REGS Registers
- 3.16.16 ROM_WAIT_STATE_REGS Registers
- 3.16.17 SYNC_SOC_REGS Registers
- 3.16.18 SYS_STATUS_REGS Registers
- 3.16.19 TEST_ERROR_REGS Registers
- 3.16.20 UID_REGS Registers
- 3.16.21 WD_REGS Registers
- 3.16.22 XINT_REGS Registers
- 3.16.23
Register to Driverlib Function Mapping
- 3.16.23.1 ASYSCTL Registers to Driverlib Functions
- 3.16.23.2 CPUTIMER Registers to Driverlib Functions
- 3.16.23.3 DCSM Registers to Driverlib Functions
- 3.16.23.4 MEMCFG Registers to Driverlib Functions
- 3.16.23.5 NMI Registers to Driverlib Functions
- 3.16.23.6 PIE Registers to Driverlib Functions
- 3.16.23.7 SYSCTL Registers to Driverlib Functions
- 3.16.23.8 WWD Registers to Driverlib Functions
- 3.16.23.9 XINT Registers to Driverlib Functions
- 4 C28x Processor
-
5 ROM Code and Peripheral Booting
- 5.1 Introduction
- 5.2 Device Boot Sequence
- 5.3 Device Boot Modes
- 5.4 Device Boot Configurations
- 5.5 Device Boot Flow Diagrams
- 5.6 Device Reset and Exception Handling
- 5.7
Boot ROM Description
- 5.7.1 CPU1 Boot ROM Configuration Registers
- 5.7.2 Booting CPU2 and CM
- 5.7.3 Entry Points
- 5.7.4 Wait Points
- 5.7.5 Memory Maps
- 5.7.6 ROM Tables
- 5.7.7 Boot Modes and Loaders
- 5.7.8 GPIO Assignments for CPU1
- 5.7.9 Secure ROM Function APIs
- 5.7.10 Clock Initializations
- 5.7.11 Boot Status information
- 5.7.12 ROM Version
- 5.8 Application Notes for Using the Bootloaders
- 5.9 Software
-
6 Dual Code Security Module (DCSM)
- 6.1 Introduction
- 6.2 Functional Description
- 6.3 Flash and OTP Erase/Program
- 6.4 Secure Copy Code
- 6.5 SecureCRC
- 6.6 CSM Impact on Other On-Chip Resources
- 6.7
Incorporating Code Security in User Applications
- 6.7.1 Environments That Require Security Unlocking
- 6.7.2 CSM Password Match Flow
- 6.7.3 C Code Example to Unsecure C28x Zone1
- 6.7.4 C Code Example to Resecure C28x Zone1
- 6.7.5 Environments That Require ECSL Unlocking
- 6.7.6 ECSL Password Match Flow
- 6.7.7 ECSL Disable Considerations for any Zone
- 6.7.8 Device Unique ID
- 6.8 Software
- 6.9 DCSM Registers
- 7 Background CRC-32 (BGCRC)
-
8 Control Law Accelerator (CLA)
- 8.1 Introduction
- 8.2 CLA Interface
- 8.3 CLA, DMA, and CPU Arbitration
- 8.4 CLA Configuration and Debug
- 8.5 Pipeline
- 8.6
Software
- 8.6.1
CLA Examples
- 8.6.1.1 CLA arcsine(x) using a lookup table (cla_asin_cpu01)
- 8.6.1.2 CLA arcsine(x) using a lookup table (cla_asin_cpu01) - C28X_DUAL
- 8.6.1.3 CLA Arcsine Example. - C28X_DUAL
- 8.6.1.4 CLA arctangent(x) using a lookup table (cla_atan_cpu01)
- 8.6.1.5 CLA 2 Pole 2 Zero Infinite Impulse Response Filter (cla_iir2p2z_cpu01) - C28X_DUAL
- 8.6.1.6 CLA 2-pole 2-zero IIR Filter Example for F2837xD. - C28X_DUAL
- 8.6.1.7 CLA background nesting task
- 8.6.1.8 Controlling PWM output using CLA
- 8.6.1.9 Just-in-time ADC sampling with CLA
- 8.6.1.10 Optimal offloading of control algorithms to CLA
- 8.6.1.11 Handling shared resources across C28x and CLA
- 8.6.1
CLA Examples
- 8.7
Instruction Set
- 8.7.1 Instruction Descriptions
- 8.7.2 Addressing Modes and Encoding
- 8.7.3
Instructions
- MABSF32 MRa, MRb
- MADD32 MRa, MRb, MRc
- MADDF32 MRa, #16FHi, MRb
- MADDF32 MRa, MRb, #16FHi
- MADDF32 MRa, MRb, MRc
- MADDF32 MRd, MRe, MRf||MMOV32 mem32, MRa
- MADDF32 MRd, MRe, MRf ||MMOV32 MRa, mem32
- MAND32 MRa, MRb, MRc
- MASR32 MRa, #SHIFT
- MBCNDD 16BitDest [, CNDF]
- MCCNDD 16BitDest [, CNDF]
- MCLRC BGINTM
- MCMP32 MRa, MRb
- MCMPF32 MRa, MRb
- MCMPF32 MRa, #16FHi
- MDEBUGSTOP
- MDEBUGSTOP1
- MEALLOW
- MEDIS
- MEINVF32 MRa, MRb
- MEISQRTF32 MRa, MRb
- MF32TOI16 MRa, MRb
- MF32TOI16R MRa, MRb
- MF32TOI32 MRa, MRb
- MF32TOUI16 MRa, MRb
- MF32TOUI16R MRa, MRb
- MF32TOUI32 MRa, MRb
- MFRACF32 MRa, MRb
- MI16TOF32 MRa, MRb
- MI16TOF32 MRa, mem16
- MI32TOF32 MRa, mem32
- MI32TOF32 MRa, MRb
- MLSL32 MRa, #SHIFT
- MLSR32 MRa, #SHIFT
- MMACF32 MR3, MR2, MRd, MRe, MRf ||MMOV32 MRa, mem32
- MMAXF32 MRa, MRb
- MMAXF32 MRa, #16FHi
- MMINF32 MRa, MRb
- MMINF32 MRa, #16FHi
- MMOV16 MARx, MRa, #16I
- MMOV16 MARx, mem16
- MMOV16 mem16, MARx
- MMOV16 mem16, MRa
- MMOV32 mem32, MRa
- MMOV32 mem32, MSTF
- MMOV32 MRa, mem32 [, CNDF]
- MMOV32 MRa, MRb [, CNDF]
- MMOV32 MSTF, mem32
- MMOVD32 MRa, mem32
- MMOVF32 MRa, #32F
- MMOVI16 MARx, #16I
- MMOVI32 MRa, #32FHex
- MMOVIZ MRa, #16FHi
- MMOVZ16 MRa, mem16
- MMOVXI MRa, #16FLoHex
- MMPYF32 MRa, MRb, MRc
- MMPYF32 MRa, #16FHi, MRb
- MMPYF32 MRa, MRb, #16FHi
- MMPYF32 MRa, MRb, MRc||MADDF32 MRd, MRe, MRf
- MMPYF32 MRd, MRe, MRf ||MMOV32 MRa, mem32
- MMPYF32 MRd, MRe, MRf ||MMOV32 mem32, MRa
- MMPYF32 MRa, MRb, MRc ||MSUBF32 MRd, MRe, MRf
- MNEGF32 MRa, MRb[, CNDF]
- MNOP
- MOR32 MRa, MRb, MRc
- MRCNDD [CNDF]
- MSETC BGINTM
- MSETFLG FLAG, VALUE
- MSTOP
- MSUB32 MRa, MRb, MRc
- MSUBF32 MRa, MRb, MRc
- MSUBF32 MRa, #16FHi, MRb
- MSUBF32 MRd, MRe, MRf ||MMOV32 MRa, mem32
- MSUBF32 MRd, MRe, MRf ||MMOV32 mem32, MRa
- MSWAPF MRa, MRb [, CNDF]
- MTESTTF CNDF
- MUI16TOF32 MRa, mem16
- MUI16TOF32 MRa, MRb
- MUI32TOF32 MRa, mem32
- MUI32TOF32 MRa, MRb
- MXOR32 MRa, MRb, MRc
- 8.8 CLA Registers
-
9 Configurable Logic Block (CLB)
- 9.1 Introduction
- 9.2 Description
- 9.3 CLB Input/Output Connection
- 9.4 CLB Tile
- 9.5 CPU Interface
- 9.6 DMA Access
- 9.7 CLB Data Export Through SPI RX Buffer
- 9.8 CLB Pipeline Mode
- 9.9
Software
- 9.9.1
CLB Examples
- 9.9.1.1 CLB Empty Project
- 9.9.1.2 CLB Combinational Logic
- 9.9.1.3 CLB GPIO Input Filter
- 9.9.1.4 CLB Auxilary PWM
- 9.9.1.5 CLB PWM Protection
- 9.9.1.6 CLB Event Window
- 9.9.1.7 CLB Signal Generator
- 9.9.1.8 CLB State Machine
- 9.9.1.9 CLB External Signal AND Gate
- 9.9.1.10 CLB Timer
- 9.9.1.11 CLB Timer Two States
- 9.9.1.12 CLB Interrupt Tag
- 9.9.1.13 CLB Output Intersect
- 9.9.1.14 CLB PUSH PULL
- 9.9.1.15 CLB Multi Tile
- 9.9.1.16 CLB Tile to Tile Delay
- 9.9.1.17 CLB based One-shot PWM
- 9.9.1.18 CLB AOC Control
- 9.9.1.19 CLB AOC Release Control
- 9.9.1.20 CLB XBARs
- 9.9.1.21 CLB AOC Control
- 9.9.1.22 CLB Serializer
- 9.9.1.23 CLB LFSR
- 9.9.1.24 CLB Lock Output Mask
- 9.9.1.25 CLB INPUT Pipeline Mode
- 9.9.1.26 CLB Clocking and PIPELINE Mode
- 9.9.1.27 CLB SPI Data Export
- 9.9.1.28 CLB SPI Data Export DMA
- 9.9.1.29 CLB Trip Zone Timestamp
- 9.9.1.30 CLB CRC
- 9.9.1
CLB Examples
- 9.10 CLB Registers
- 10Dual-Clock Comparator (DCC)
- 11Direct Memory Access (DMA)
-
12External Memory Interface (EMIF)
- 12.1 Introduction
- 12.2
EMIF Module Architecture
- 12.2.1 EMIF Clock Control
- 12.2.2 EMIF Requests
- 12.2.3 EMIF Signal Descriptions
- 12.2.4 EMIF Signal Multiplexing Control
- 12.2.5
SDRAM Controller and Interface
- 12.2.5.1 SDRAM Commands
- 12.2.5.2 Interfacing to SDRAM
- 12.2.5.3 SDRAM Configuration Registers
- 12.2.5.4 SDRAM Auto-Initialization Sequence
- 12.2.5.5 SDRAM Configuration Procedure
- 12.2.5.6 EMIF Refresh Controller
- 12.2.5.7 Self-Refresh Mode
- 12.2.5.8 Power-Down Mode
- 12.2.5.9 SDRAM Read Operation
- 12.2.5.10 SDRAM Write Operations
- 12.2.5.11 Mapping from Logical Address to EMIF Pins
- 12.2.6 Asynchronous Controller and Interface
- 12.2.7 Data Bus Parking
- 12.2.8 Reset and Initialization Considerations
- 12.2.9 Interrupt Support
- 12.2.10 DMA Event Support
- 12.2.11 EMIF Signal Multiplexing
- 12.2.12 Memory Map
- 12.2.13 Priority and Arbitration
- 12.2.14 System Considerations
- 12.2.15 Power Management
- 12.2.16 Emulation Considerations
- 12.3
Example Configuration
- 12.3.1 Hardware Interface
- 12.3.2
Software Configuration
- 12.3.2.1
Configuring the SDRAM Interface
- 12.3.2.1.1 PLL Programming for EMIF to K4S641632H-TC(L)70 Interface
- 12.3.2.1.2 SDRAM Timing Register (SDRAM_TR) Settings for EMIF to K4S641632H-TC(L)70 Interface
- 12.3.2.1.3 SDRAM Self Refresh Exit Timing Register (SDR_EXT_TMNG) Settings for EMIF to K4S641632H-TC(L)70 Interface
- 12.3.2.1.4 SDRAM Refresh Control Register (SDRAM_RCR) Settings for EMIF to K4S641632H-TC(L)70 Interface
- 12.3.2.1.5 SDRAM Configuration Register (SDRAM_CR) Settings for EMIF to K4S641632H-TC(L)70 Interface
- 12.3.2.2 Configuring the Flash Interface
- 12.3.2.1
Configuring the SDRAM Interface
- 12.4
Software
- 12.4.1
EMIF Examples
- 12.4.1.1 Pin setup for EMIF module accessing ASRAM.
- 12.4.1.2 EMIF1 ASYNC module accessing 16bit ASRAM.
- 12.4.1.3 EMIF1 ASYNC module accessing 16bit ASRAM through CPU1 and CPU2. - C28X_DUAL
- 12.4.1.4 EMIF1 ASYNC module accessing 16bit ASRAM trhough CPU1 and CPU2. - C28X_DUAL
- 12.4.1.5 EMIF1 module accessing 16bit ASRAM as code memory.
- 12.4.1.6 EMIF1 module accessing 16bit SDRAM using memcpy_fast_far().
- 12.4.1.7 EMIF1 module accessing 16bit SDRAM then puts into Self Refresh mode before entering Low Power Mode.
- 12.4.1.8 EMIF1 module accessing 32bit SDRAM using DMA.
- 12.4.1.9 EMIF1 module accessing 16bit SDRAM using alternate address mapping.
- 12.4.1.10 EMIF1 ASYNC module accessing 16bit ASRAM HIC FSI
- 12.4.1.11 EMIF1 ASYNC module accessing 8bit HIC controller.
- 12.4.1
EMIF Examples
- 12.5 EMIF Registers
-
13Flash Module
- 13.1 Introduction to Flash and OTP Memory
- 13.2 Flash Bank, OTP, and Pump
- 13.3 Flash Module Controller (FMC)
- 13.4 Flash and OTP Memory Power-Down Modes and Wakeup
- 13.5 Active Grace Period
- 13.6 Flash and OTP Memory Performance
- 13.7 Flash Read Interface
- 13.8 Flash Erase and Program
- 13.9 Error Correction Code (ECC) Protection
- 13.10 Reserved Locations Within Flash and OTP Memory
- 13.11 Migrating an Application from RAM to Flash
- 13.12 Procedure to Change the Flash Control Registers
- 13.13 Flash Pump Ownership Semaphore
- 13.14 Software
- 13.15
Flash Registers
- 13.15.1 FLASH Base Address Table (C28)
- 13.15.2 CM FLASH Base Address Table (CM)
- 13.15.3 FLASH_CTRL_REGS Registers
- 13.15.4 FLASH_ECC_REGS Registers
- 13.15.5 CM_FLASH_CTRL_REGS Registers
- 13.15.6 CM_FLASH_ECC_REGS Registers
- 13.15.7 FLASH_PUMP_SEMAPHORE_REGS Registers
- 13.15.8 FLASH Registers to Driverlib Functions
-
14Embedded Real-time Analysis and Diagnostic (ERAD)
- 14.1 Introduction
- 14.2 Enhanced Bus Comparator Unit
- 14.3 System Event Counter Unit
- 14.4 ERAD Ownership, Initialization and Reset
- 14.5 ERAD Programming Sequence
- 14.6 Cyclic Redundancy Check Unit
- 14.7 Program Counter Trace
- 14.8
Software
- 14.8.1
ERAD Examples
- 14.8.1.1 ERAD Profiling Interrupts
- 14.8.1.2 ERAD Profile Function
- 14.8.1.3 ERAD Profile Function
- 14.8.1.4 ERAD HWBP Monitor Program Counter
- 14.8.1.5 ERAD HWBP Monitor Program Counter
- 14.8.1.6 ERAD Profile Function
- 14.8.1.7 ERAD HWBP Stack Overflow Detection
- 14.8.1.8 ERAD HWBP Stack Overflow Detection
- 14.8.1.9 ERAD Stack Overflow
- 14.8.1.10 ERAD Profile Interrupts CLA
- 14.8.1.11 ERAD Profiling Interrupts
- 14.8.1.12 ERAD Profiling Interrupts
- 14.8.1.13 ERAD MEMORY ACCESS RESTRICT
- 14.8.1.14 ERAD INTERRUPT ORDER
- 14.8.1.15 ERAD AND CLB
- 14.8.1.16 ERAD PWM PROTECTION
- 14.8.1
ERAD Examples
- 14.9 ERAD Registers
-
15General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
- 15.1 Introduction
- 15.2 Configuration Overview
- 15.3 Digital General-Purpose I/O Control
- 15.4 Input Qualification
- 15.5 USB Signals
- 15.6 SPI Signals
- 15.7 GPIO and Peripheral Muxing
- 15.8 Internal Pullup Configuration Requirements
- 15.9 Software
- 15.10
GPIO Registers
- 15.10.1 GPIO Base Address Table (C28)
- 15.10.2 CM GPIO Base Address Table (CM)
- 15.10.3 GPIO_CTRL_REGS Registers
- 15.10.4 GPIO_DATA_REGS Registers
- 15.10.5 GPIO_DATA_READ_REGS Registers
- 15.10.6 CM_GPIO_DATA_REGS Registers
- 15.10.7 CM_GPIO_DATA_READ_REGS Registers
- 15.10.8 GPIO Registers to Driverlib Functions
-
16Interprocessor Communication (IPC)
- 16.1 Introduction
- 16.2 Message RAMs
- 16.3 IPC Flags and Interrupts
- 16.4 IPC Command Registers
- 16.5 Free-Running Counter
- 16.6 IPC Communication Protocol
- 16.7
Software
- 16.7.1
IPC Examples
- 16.7.1.1 IPC basic message passing example with interrupt - C28X_CM
- 16.7.1.2 IPC basic message passing example with interrupt - C28X_CM
- 16.7.1.3 IPC basic message passing example with interrupt - C28X_DUAL
- 16.7.1.4 IPC basic message passing example with interrupt - C28X_DUAL
- 16.7.1.5 IPC message passing example with interrupt and message queue - C28X_CM
- 16.7.1.6 IPC message passing example with interrupt and message queue - C28X_CM
- 16.7.1.7 IPC message passing example with interrupt and message queue - C28X_DUAL
- 16.7.1.8 IPC message passing example with interrupt and message queue - C28X_DUAL
- 16.7.1.9 IPC basic message passing example with interrupt - C28X_DUAL
- 16.7.1.10 IPC basic message passing example with interrupt - C28X_DUAL
- 16.7.1.11 IPC message passing example with interrupt and message queue - C28X_DUAL
- 16.7.1.12 IPC message passing example with interrupt and message queue - C28X_DUAL
- 16.7.1
IPC Examples
- 16.8
IPC Registers
- 16.8.1 IPC Base Address Table (C28)
- 16.8.2 CM IPC Base Address Table (CM)
- 16.8.3 CPU1TOCPU2_IPC_REGS_CPU1VIEW Registers
- 16.8.4 CPU1TOCPU2_IPC_REGS_CPU2VIEW Registers
- 16.8.5 CPU1TOCM_IPC_REGS_CPU1VIEW Registers
- 16.8.6 CPU1TOCM_IPC_REGS_CMVIEW Registers
- 16.8.7 CPU2TOCM_IPC_REGS_CPU2VIEW Registers
- 16.8.8 CPU2TOCM_IPC_REGS_CMVIEW Registers
- 16.8.9 IPC Registers to Driverlib Functions
-
17Crossbar (X-BAR)
- 17.1 Input X-BAR and CLB Input X-BAR
- 17.2 ePWM, CLB, and GPIO Output X-BAR
- 17.3 XBAR Registers
- 18► ANALOG PERIPHERALS
- 19Analog Subsystem
-
20Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
- 20.1 Introduction
- 20.2 ADC Configurability
- 20.3 SOC Principle of Operation
- 20.4 SOC Configuration Examples
- 20.5 ADC Conversion Priority
- 20.6 Burst Mode
- 20.7 EOC and Interrupt Operation
- 20.8 Post-Processing Blocks
- 20.9 Opens/Shorts Detection Circuit (OSDETECT)
- 20.10 Power-Up Sequence
- 20.11 ADC Calibration
- 20.12 ADC Timings
- 20.13 Additional Information
- 20.14
Software
- 20.14.1
ADC Examples
- 20.14.1.1 ADC Software Triggering
- 20.14.1.2 ADC ePWM Triggering
- 20.14.1.3 ADC Temperature Sensor Conversion
- 20.14.1.4 ADC Synchronous SOC Software Force (adc_soc_software_sync)
- 20.14.1.5 ADC Continuous Triggering (adc_soc_continuous)
- 20.14.1.6 ADC Continuous Conversions Read by DMA (adc_soc_continuous_dma)
- 20.14.1.7 ADC PPB Offset (adc_ppb_offset)
- 20.14.1.8 ADC PPB Limits (adc_ppb_limits)
- 20.14.1.9 ADC PPB Delay Capture (adc_ppb_delay)
- 20.14.1.10 ADC ePWM Triggering Multiple SOC
- 20.14.1.11 ADC Burst Mode
- 20.14.1.12 ADC Burst Mode Oversampling
- 20.14.1.13 ADC SOC Oversampling
- 20.14.1.14 ADC PPB PWM trip (adc_ppb_pwm_trip)
- 20.14.1.15 ADC High Priority SOC (adc_high_priority_soc)
- 20.14.1.16 ADC Interleaved Averaging in Software
- 20.14.1.17 ADC Open Shorts Detection (adc_open_shorts_detection)
- 20.14.1
ADC Examples
- 20.15 ADC Registers
- 21Buffered Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC)
- 22Comparator Subsystem (CMPSS)
- 23► CONTROL PERIPHERALS
-
24Enhanced Capture (eCAP)
- 24.1 Introduction
- 24.2 Description
- 24.3 Configuring Device Pins for the eCAP
- 24.4 Capture and APWM Operating Mode
- 24.5
Capture Mode Description
- 24.5.1 Event Prescaler
- 24.5.2 Edge Polarity Select and Qualifier
- 24.5.3 Continuous/One-Shot Control
- 24.5.4 32-Bit Counter and Phase Control
- 24.5.5 CAP1-CAP4 Registers
- 24.5.6 eCAP Synchronization
- 24.5.7 Interrupt Control
- 24.5.8 DMA Interrupt
- 24.5.9 Shadow Load and Lockout Control
- 24.5.10 APWM Mode Operation
- 24.6
Application of the eCAP Module
- 24.6.1 Example 1 - Absolute Time-Stamp Operation Rising-Edge Trigger
- 24.6.2 Example 2 - Absolute Time-Stamp Operation Rising- and Falling-Edge Trigger
- 24.6.3 Example 3 - Time Difference (Delta) Operation Rising-Edge Trigger
- 24.6.4 Example 4 - Time Difference (Delta) Operation Rising- and Falling-Edge Trigger
- 24.7 Application of the APWM Mode
- 24.8 Software
- 24.9 eCAP Registers
- 25High Resolution Capture (HRCAP)
-
26Enhanced Pulse Width Modulator (ePWM)
- 26.1 Introduction
- 26.2 Configuring Device Pins
- 26.3 ePWM Modules Overview
- 26.4
Time-Base (TB) Submodule
- 26.4.1 Purpose of the Time-Base Submodule
- 26.4.2 Controlling and Monitoring the Time-Base Submodule
- 26.4.3 Calculating PWM Period and Frequency
- 26.4.4 Phase Locking the Time-Base Clocks of Multiple ePWM Modules
- 26.4.5 Simultaneous Writes to TBPRD and CMPx Registers Between ePWM Modules
- 26.4.6 Time-Base Counter Modes and Timing Waveforms
- 26.4.7 Global Load
- 26.5 Counter-Compare (CC) Submodule
- 26.6 Action-Qualifier (AQ) Submodule
- 26.7 Dead-Band Generator (DB) Submodule
- 26.8 PWM Chopper (PC) Submodule
- 26.9 Trip-Zone (TZ) Submodule
- 26.10 Event-Trigger (ET) Submodule
- 26.11 Digital Compare (DC) Submodule
- 26.12 ePWM Crossbar (X-BAR)
- 26.13
Applications to Power Topologies
- 26.13.1 Overview of Multiple Modules
- 26.13.2 Key Configuration Capabilities
- 26.13.3 Controlling Multiple Buck Converters With Independent Frequencies
- 26.13.4 Controlling Multiple Buck Converters With Same Frequencies
- 26.13.5 Controlling Multiple Half H-Bridge (HHB) Converters
- 26.13.6 Controlling Dual 3-Phase Inverters for Motors (ACI and PMSM)
- 26.13.7 Practical Applications Using Phase Control Between PWM Modules
- 26.13.8 Controlling a 3-Phase Interleaved DC/DC Converter
- 26.13.9 Controlling Zero Voltage Switched Full Bridge (ZVSFB) Converter
- 26.13.10 Controlling a Peak Current Mode Controlled Buck Module
- 26.13.11 Controlling H-Bridge LLC Resonant Converter
- 26.14 Register Lock Protection
- 26.15
High-Resolution Pulse Width Modulator (HRPWM)
- 26.15.1
Operational Description of HRPWM
- 26.15.1.1 Controlling the HRPWM Capabilities
- 26.15.1.2 HRPWM Source Clock
- 26.15.1.3 Configuring the HRPWM
- 26.15.1.4 Configuring High-Resolution in Deadband Rising-Edge and Falling-Edge Delay
- 26.15.1.5 Principle of Operation
- 26.15.1.6 Deadband High-Resolution Operation
- 26.15.1.7 Scale Factor Optimizing Software (SFO)
- 26.15.1.8 HRPWM Examples Using Optimized Assembly Code
- 26.15.2 SFO Library Software - SFO_TI_Build_V8.lib
- 26.15.1
Operational Description of HRPWM
- 26.16
Software
- 26.16.1
EPWM Examples
- 26.16.1.1 ePWM Trip Zone
- 26.16.1.2 ePWM Up Down Count Action Qualifier
- 26.16.1.3 ePWM Synchronization
- 26.16.1.4 ePWM Digital Compare
- 26.16.1.5 ePWM Digital Compare Event Filter Blanking Window
- 26.16.1.6 ePWM Valley Switching
- 26.16.1.7 ePWM Digital Compare Edge Filter
- 26.16.1.8 ePWM Deadband
- 26.16.1.9 ePWM DMA
- 26.16.1.10 ePWM Chopper
- 26.16.1.11 EPWM Configure Signal
- 26.16.1.12 Realization of Monoshot mode
- 26.16.1.13 EPWM Action Qualifier (epwm_up_aq)
- 26.16.2 HRPWM Examples
- 26.16.1
EPWM Examples
- 26.17 ePWM Registers
-
27Enhanced Quadrature
Encoder Pulse (eQEP)
- 27.1 Introduction
- 27.2 Configuring Device Pins
- 27.3 Description
- 27.4 Quadrature Decoder Unit (QDU)
- 27.5 Position Counter and Control Unit (PCCU)
- 27.6 eQEP Edge Capture Unit
- 27.7 eQEP Watchdog
- 27.8 eQEP Unit Timer Base
- 27.9 QMA Module
- 27.10 eQEP Interrupt Structure
- 27.11
Software
- 27.11.1
EQEP Examples
- 27.11.1.1 Frequency Measurement Using eQEP
- 27.11.1.2 Position and Speed Measurement Using eQEP
- 27.11.1.3 ePWM frequency Measurement Using eQEP via xbar connection
- 27.11.1.4 Frequency Measurement Using eQEP via unit timeout interrupt
- 27.11.1.5 Motor speed and direction measurement using eQEP via unit timeout interrupt
- 27.11.1
EQEP Examples
- 27.12 eQEP Registers
-
28Sigma Delta Filter Module
(SDFM)
- 28.1 Introduction
- 28.2 Configuring Device Pins
- 28.3 Input Qualification
- 28.4 Input Control Unit
- 28.5 SDFM Clock Control
- 28.6 Sinc Filter
- 28.7 Data (Primary) Filter Unit
- 28.8 Comparator (Secondary) Filter Unit
- 28.9 Theoretical SDFM Filter Output
- 28.10 Interrupt Unit
- 28.11 Software
- 28.12 SDFM Registers
- 29► COMMUNICATION PERIPHERALS
-
30Controller Area Network (CAN)
- 30.1 Introduction
- 30.2 Functional Description
- 30.3 Operating Modes
- 30.4 Multiple Clock Source
- 30.5 Interrupt Functionality
- 30.6 DMA Functionality
- 30.7 Parity Check Mechanism
- 30.8 Debug Mode
- 30.9 Module Initialization
- 30.10 Configuration of Message Objects
- 30.11
Message Handling
- 30.11.1 Message Handler Overview
- 30.11.2 Receive/Transmit Priority
- 30.11.3 Transmission of Messages in Event Driven CAN Communication
- 30.11.4 Updating a Transmit Object
- 30.11.5 Changing a Transmit Object
- 30.11.6 Acceptance Filtering of Received Messages
- 30.11.7 Reception of Data Frames
- 30.11.8 Reception of Remote Frames
- 30.11.9 Reading Received Messages
- 30.11.10 Requesting New Data for a Receive Object
- 30.11.11 Storing Received Messages in FIFO Buffers
- 30.11.12 Reading from a FIFO Buffer
- 30.12 CAN Bit Timing
- 30.13 Message Interface Register Sets
- 30.14 Message RAM
- 30.15
Software
- 30.15.1
CAN Examples
- 30.15.1.1 NMI handling - C28X_DUAL
- 30.15.1.2 CAN External Loopback
- 30.15.1.3 Watchdog Reset - C28X_DUAL
- 30.15.1.4 CAN Loopback - CM
- 30.15.1.5 CAN External Loopback with Interrupts
- 30.15.1.6 CAN External Loopback with Interrupts - C28X_DUAL
- 30.15.1.7 CAN External Loopback with Interrupts - CM
- 30.15.1.8 CAN-A to CAN-B External Transmit
- 30.15.1.9 CAN-A to CAN-B External Transmit - CM
- 30.15.1.10 CAN External Loopback with DMA
- 30.15.1.11 CAN Transmit and Receive Configurations - CM
- 30.15.1.12 CAN Transmit and Receive Configurations
- 30.15.1.13 CAN Error Generation Example
- 30.15.1.14 CAN Remote Request Loopback
- 30.15.1.15 CAN example that illustrates the usage of Mask registers
- 30.15.1
CAN Examples
- 30.16 CAN Registers
-
31EtherCAT®
Slave Controller
(ESC)
- 31.1
Introduction
- 31.1.1 ECAT Related Collateral
- 31.1.2 ESC Features
- 31.1.3 ESC Subsystem Integrated Features
- 31.1.4 F2838x ESC versus Beckhoff ET1100
- 31.1.5 EtherCAT IP Block Diagram
- 31.1.6
ESC Functional Blocks
- 31.1.6.1 Interface to EtherCAT Master
- 31.1.6.2 Process Data Interface
- 31.1.6.3 General-Purpose Inputs and Outputs
- 31.1.6.4 EtherCAT Processing Unit (EPU)
- 31.1.6.5 Fieldbus Memory Management Unit (FMMU)
- 31.1.6.6 Sync Manager
- 31.1.6.7 Monitoring
- 31.1.6.8 Reset Controller
- 31.1.6.9 PHY Management
- 31.1.6.10 Distributed Clock (DC)
- 31.1.6.11 EEPROM
- 31.1.6.12 Status / LEDs
- 31.1.7 EtherCAT Physical Layer
- 31.1.8 EtherCAT Protocol
- 31.1.9 EtherCAT State Machine (ESM)
- 31.1.10 More Information on EtherCAT
- 31.1.11 Beckhoff® Automation EtherCAT IP Errata
- 31.2
ESC and ESCSS Description
- 31.2.1 ESC RAM Parity and Memory Address Maps
- 31.2.2 Local Host Communication
- 31.2.3 Debug Emulation Mode Operation
- 31.2.4 ESC SubSystem
- 31.2.5 Interrupts and Interrupt Mapping
- 31.2.6 Power, Clocks, and Resets
- 31.2.7 LED Controls
- 31.2.8 Slave Node Configuration and EEPROM
- 31.2.9 General-Purpose Inputs and Outputs
- 31.2.10 Distributed Clocks – Sync and Latch
- 31.3 Software Initialization Sequence and Allocating Ownership
- 31.4 ESC Configuration Constants
- 31.5 EtherCAT IP Registers
- 31.1
Introduction
-
32Fast Serial Interface
(FSI)
- 32.1 Introduction
- 32.2 System-level Integration
- 32.3
FSI Functional Description
- 32.3.1 Introduction to Operation
- 32.3.2 FSI Transmitter Module
- 32.3.3
FSI Receiver Module
- 32.3.3.1 Initialization
- 32.3.3.2 FSI_RX Clocking
- 32.3.3.3 Receiving Frames
- 32.3.3.4 Ping Frame Watchdog
- 32.3.3.5 Frame Watchdog
- 32.3.3.6 Delay Line Control
- 32.3.3.7 Buffer Management
- 32.3.3.8 CRC Submodule
- 32.3.3.9 Using the Zero Bits of the Receiver Tag Registers
- 32.3.3.10 Conditions in Which the Receiver Must Undergo a Soft Reset
- 32.3.3.11 FSI_RX Reset
- 32.3.4 Frame Format
- 32.3.5 Flush Sequence
- 32.3.6 Internal Loopback
- 32.3.7 CRC Generation
- 32.3.8 ECC Module
- 32.3.9 Tag Matching
- 32.3.10 TDM Configurations
- 32.3.11 FSI-SPI Compatibility Mode
- 32.4 FSI Programing Guide
- 32.5
Software
- 32.5.1
FSI Examples
- 32.5.1.1 FSI Multi-Rx Tag-Match - C28X_DUAL
- 32.5.1.2 FSI Loopback:CPU Control
- 32.5.1.3 FSI Multi-Rx Tag-Match - C28X_DUAL
- 32.5.1.4 FSI Loopback CLA control
- 32.5.1.5 FSI DMA frame transfers:DMA Control
- 32.5.1.6 FSI data transfer by external trigger
- 32.5.1.7 FSI data transfers upon CPU Timer event
- 32.5.1.8 FSI and SPI communication(fsi_ex6_spi_main_tx)
- 32.5.1.9 FSI and SPI communication(fsi_ex7_spi_remote_rx)
- 32.5.1.10 FSI P2Point Connection:Rx Side
- 32.5.1.11 FSI P2Point Connection:Tx Side
- 32.5.1.12 FSI star connection topology example. FSI communication using CPU control
- 32.5.1.13 FSI daisy chain topology, lead device example
- 32.5.1.14 FSI daisy chain topology, node device example
- 32.5.1
FSI Examples
- 32.6 FSI Registers
-
33Inter-Integrated Circuit Module (I2C)
- 33.1 Introduction
- 33.2 Configuring Device Pins
- 33.3
I2C Module Operational Details
- 33.3.1 Input and Output Voltage Levels
- 33.3.2 Selecting Pullup Resistors
- 33.3.3 Data Validity
- 33.3.4 Operating Modes
- 33.3.5 I2C Module START and STOP Conditions
- 33.3.6 Non-repeat Mode versus Repeat Mode
- 33.3.7 Serial Data Formats
- 33.3.8 Clock Synchronization
- 33.3.9 Arbitration
- 33.3.10 Digital Loopback Mode
- 33.3.11 NACK Bit Generation
- 33.4 Interrupt Requests Generated by the I2C Module
- 33.5 Resetting or Disabling the I2C Module
- 33.6
Software
- 33.6.1
I2C Examples
- 33.6.1.1 C28x-I2C Library source file for FIFO interrupts
- 33.6.1.2 C28x-I2C Library source file for FIFO using polling
- 33.6.1.3 C28x-I2C Library source file for FIFO interrupts
- 33.6.1.4 I2C Loopback with Slave Receive Interrupt - CM
- 33.6.1.5 I2C Digital Loopback with FIFO Interrupts
- 33.6.1.6 I2C EEPROM
- 33.6.1.7 I2C Digital External Loopback with FIFO Interrupts
- 33.6.1.8 I2C EEPROM
- 33.6.1.9 I2C controller target communication using FIFO interrupts
- 33.6.1.10 I2C EEPROM
- 33.6.1
I2C Examples
- 33.7 I2C Registers
-
34Multichannel Buffered Serial Port (McBSP)
- 34.1 Introduction
- 34.2 Configuring Device Pins
- 34.3
McBSP Operation
- 34.3.1 Data Transfer Process of McBSPs
- 34.3.2 Companding (Compressing and Expanding) Data
- 34.3.3 Clocking and Framing Data
- 34.3.4 Frame Phases
- 34.3.5 McBSP Reception
- 34.3.6 McBSP Transmission
- 34.3.7 Interrupts and DMA Events Generated by a McBSP
- 34.4 McBSP Sample Rate Generator
- 34.5 McBSP Exception/Error Conditions
- 34.6
Multichannel Selection Modes
- 34.6.1 Channels, Blocks, and Partitions
- 34.6.2 Multichannel Selection
- 34.6.3 Configuring a Frame for Multichannel Selection
- 34.6.4 Using Two Partitions
- 34.6.5 Using Eight Partitions
- 34.6.6 Receive Multichannel Selection Mode
- 34.6.7 Transmit Multichannel Selection Modes
- 34.6.8 Using Interrupts Between Block Transfers
- 34.7 SPI Operation Using the Clock Stop Mode
- 34.8
Receiver Configuration
- 34.8.1 Programming the McBSP Registers for the Desired Receiver Operation
- 34.8.2 Resetting and Enabling the Receiver
- 34.8.3 Set the Receiver Pins to Operate as McBSP Pins
- 34.8.4 Digital Loopback Mode
- 34.8.5 Clock Stop Mode
- 34.8.6 Receive Multichannel Selection Mode
- 34.8.7 Receive Frame Phases
- 34.8.8 Receive Word Lengths
- 34.8.9 Receive Frame Length
- 34.8.10 Receive Frame-Synchronization Ignore Function
- 34.8.11 Receive Companding Mode
- 34.8.12 Receive Data Delay
- 34.8.13 Receive Sign-Extension and Justification Mode
- 34.8.14 Receive Interrupt Mode
- 34.8.15 Receive Frame-Synchronization Mode
- 34.8.16 Receive Frame-Synchronization Polarity
- 34.8.17 Receive Clock Mode
- 34.8.18 Receive Clock Polarity
- 34.8.19 SRG Clock Divide-Down Value
- 34.8.20 SRG Clock Synchronization Mode
- 34.8.21 SRG Clock Mode (Choose an Input Clock)
- 34.8.22 SRG Input Clock Polarity
- 34.9
Transmitter Configuration
- 34.9.1 Programming the McBSP Registers for the Desired Transmitter Operation
- 34.9.2 Resetting and Enabling the Transmitter
- 34.9.3 Set the Transmitter Pins to Operate as McBSP Pins
- 34.9.4 Digital Loopback Mode
- 34.9.5 Clock Stop Mode
- 34.9.6 Transmit Multichannel Selection Mode
- 34.9.7 XCERs Used in the Transmit Multichannel Selection Mode
- 34.9.8 Transmit Frame Phases
- 34.9.9 Transmit Word Lengths
- 34.9.10 Transmit Frame Length
- 34.9.11 Enable/Disable the Transmit Frame-Synchronization Ignore Function
- 34.9.12 Transmit Companding Mode
- 34.9.13 Transmit Data Delay
- 34.9.14 Transmit DXENA Mode
- 34.9.15 Transmit Interrupt Mode
- 34.9.16 Transmit Frame-Synchronization Mode
- 34.9.17 Transmit Frame-Synchronization Polarity
- 34.9.18 SRG Frame-Synchronization Period and Pulse Width
- 34.9.19 Transmit Clock Mode
- 34.9.20 Transmit Clock Polarity
- 34.10
Emulation and Reset Considerations
- 34.10.1 McBSP Emulation Mode
- 34.10.2 Resetting and Initializing McBSPs
- 34.11 Data Packing Examples
- 34.12 Interrupt Generation
- 34.13 McBSP Modes
- 34.14 Special Case: External Device is the Transmit Frame Master
- 34.15
Software
- 34.15.1
MCBSP Examples
- 34.15.1.1 Pin Setup for McBSP module
- 34.15.1.2 McBSP loopback example
- 34.15.1.3 McBSP loopback with DMA example.
- 34.15.1.4 McBSP loopback with interrupts example
- 34.15.1.5 McBSP loopback with interrupts example
- 34.15.1.6 McBSP loopback example using SPI mode
- 34.15.1.7 McBSP external loopback example
- 34.15.1.8 McBSP external loopback example using SPI mode
- 34.15.1.9 McBSP TDM-8 Test
- 34.15.1
MCBSP Examples
- 34.16 McBSP Registers
-
35Power Management Bus Module (PMBus)
- 35.1 Introduction
- 35.2 Configuring Device Pins
- 35.3
Slave Mode
Operation
- 35.3.1 Configuration
- 35.3.2
Message Handling
- 35.3.2.1 Quick Command
- 35.3.2.2 Send Byte
- 35.3.2.3 Receive Byte
- 35.3.2.4 Write Byte and Write Word
- 35.3.2.5 Read Byte and Read Word
- 35.3.2.6 Process Call
- 35.3.2.7 Block Write
- 35.3.2.8 Block Read
- 35.3.2.9 Block Write-Block Read Process Call
- 35.3.2.10 Alert Response
- 35.3.2.11 Extended Command
- 35.3.2.12 Group Command
- 35.4
Master Mode
Operation
- 35.4.1 Configuration
- 35.4.2
Message Handling
- 35.4.2.1 Quick Command
- 35.4.2.2 Send Byte
- 35.4.2.3 Receive Byte
- 35.4.2.4 Write Byte and Write Word
- 35.4.2.5 Read Byte and Read Word
- 35.4.2.6 Process Call
- 35.4.2.7 Block Write
- 35.4.2.8 Block Read
- 35.4.2.9 Block Write-Block Read Process Call
- 35.4.2.10 Alert Response
- 35.4.2.11 Extended Command
- 35.4.2.12 Group Command
- 35.5 PMBus Registers
-
36Serial Communications Interface (SCI)
- 36.1 Introduction
- 36.2 Architecture
- 36.3 SCI Module Signal Summary
- 36.4 Configuring Device Pins
- 36.5 Multiprocessor and Asynchronous Communication Modes
- 36.6 SCI Programmable Data Format
- 36.7 SCI Multiprocessor Communication
- 36.8 Idle-Line Multiprocessor Mode
- 36.9 Address-Bit Multiprocessor Mode
- 36.10 SCI Communication Format
- 36.11 SCI Port Interrupts
- 36.12 SCI Baud Rate Calculations
- 36.13 SCI Enhanced Features
- 36.14 Software
- 36.15 SCI Registers
-
37Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
- 37.1 Introduction
- 37.2 System-Level Integration
- 37.3 SPI Operation
- 37.4 Programming Procedure
- 37.5 Software
- 37.6 SPI Registers
-
38Universal Serial Bus (USB) Controller
- 38.1 Introduction
- 38.2 Functional Description
- 38.3 Initialization and Configuration
- 38.4 USB Global Interrupts
- 38.5
Software
- 38.5.1
USB Examples
- 38.5.1.1 Wrapper for interrupt functions and USB support pins. - CM
- 38.5.1.2 USB CDC serial example
- 38.5.1.3 USB Composite Serial Device (usb_dev_cserial) - CM
- 38.5.1.4 USB HID Mouse Device
- 38.5.1.5 USB HID Mouse Device - CM
- 38.5.1.6 Data structures defining the USB mouse device. - CM
- 38.5.1.7 USB Device Keyboard
- 38.5.1.8 USB HID Keyboard Device (usb_dev_keyboard) - CM
- 38.5.1.9 Data structures defining the USB keyboard device. - CM
- 38.5.1.10 Data structures defining this bulk USB device. - CM
- 38.5.1.11 USB Generic Bulk Device (usb_dev_bulk) - CM
- 38.5.1.12 USB Generic Bulk Device
- 38.5.1.13 USB HID Mouse Host
- 38.5.1.14 USB HID Mouse Host (usb_host_mouse) - CM
- 38.5.1.15 USB HID Keyboard Host (usb_host_keyboard) - CM
- 38.5.1.16 USB HID Keyboard Host
- 38.5.1.17 USB Mass Storage Class Host
- 38.5.1.18 USB Mass Storage Class Host (usb_host_msc) - CM
- 38.5.1.19 USB Dual Detect
- 38.5.1.20 Data structures defining this bulk USB device. - CM
- 38.5.1.21 USB Throughput Bulk Device Example (usb_ex9_throughput_dev_bulk) - CM
- 38.5.1.22 USB HUB Host example - CM
- 38.5.1.23 USB Throughput Bulk Device Example (usb_ex9_throughput_dev_bulk)
- 38.5.1.24 USB HUB Host example
- 38.5.1
USB Examples
- 38.6 USB Registers
- 39► CONNECTIVITY MANAGER (CM)
- 40Connectivity Manager Subsystem
-
41Connectivity
Manager System Control and Interrupts
- 41.1 Introduction
- 41.2 Reset
- 41.3 CM Clocking
- 41.4 SysTick
- 41.5 Watchdog Timer
- 41.6 Exceptions and NMI
- 41.7 Nested Vectored Interrupt Controller (NVIC)
- 41.8 32-Bit CM CPU Timers 0/1/2
- 41.9 Memory Controller Module
- 41.10 Memory Protection Unit (MPU)
- 41.11 Debug and Trace
- 41.12
CM-SysCtrl Registers
- 41.12.1 CM System Control Base Addresses
- 41.12.2 CM_MEMCFG_REGS Registers
- 41.12.3 CM_MEMORYDIAGERROR_REGS Registers
- 41.12.4 CM_MEMORYERROR_REGS Registers
- 41.12.5 CMSYSCTL_REGS Registers
- 41.12.6 CM_CPUTIMER_REGS Registers
- 41.12.7 MPU_REGS Registers
- 41.12.8 CM_NMI_INTRUPT_REGS Registers
- 41.12.9 NVIC Registers
- 41.12.10 SCB Registers
- 41.12.11 CSFR Registers
- 41.12.12 SYSTICK Registers
- 41.12.13 MPU Registers
- 41.12.14 CM_WD_REGS Registers
- 42Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) Accelerator
-
43Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC)
- 43.1 Introduction
- 43.2 System Level Integration
- 43.3
Features
- 43.3.1 Multiple Channels and Queues Support
- 43.3.2
IEEE 1588 Timestamp Support
- 43.3.2.1
Feature Description
- 43.3.2.1.1 Clock Types
- 43.3.2.1.2 Maximum PTP Clock Frequency
- 43.3.2.1.3 Minimum PTP Clock Frequency
- 43.3.2.1.4 PTP Processing and Control
- 43.3.2.1.5 PTP Packets Over IPv4
- 43.3.2.1.6 PTP Frames Over IPv6
- 43.3.2.1.7 PTP Packets Over Ethernet
- 43.3.2.1.8 Transmit Path Functions
- 43.3.2.1.9 Receive Path Functions
- 43.3.2.2 IEEE 1588 System Time Source
- 43.3.2.3 IEEE 1588 Higher Word Register
- 43.3.2.4 IEEE 1588 Auxillary Snapshot
- 43.3.2.5 Flexible Pulse-Per-Second Output
- 43.3.2.1
Feature Description
- 43.3.3 Packet Filtering
- 43.3.4 VLAN Support
- 43.3.5
TCP/IP Offloading Features
- 43.3.5.1 Transmit Checksum Offload Engine
- 43.3.5.2 Receive Checksum Offload Engine
- 43.3.5.3 TCP/IP Segmentation Offload (TSO) Engine
- 43.3.5.4 Segmentation Versus Fragmentation
- 43.3.5.5 Using the IPv4 ARP Offload Engine
- 43.3.5.6 Energy Efficient Ethernet (EEE) Support
- 43.3.5.7 Automated Entry/Exit of LPI Mode in Transmit Path
- 43.3.5.8 Receive Path Functions
- 43.3.6 Loopback Mode
- 43.3.7 Reverse Media Independent Interface (RevMII)
- 43.4
Descriptors
- 43.4.1 Descriptor Structure
- 43.4.2 Transmit Descriptor
- 43.4.3 Receive Descriptor
- 43.5
Programming
- 43.5.1 Initializing DMA
- 43.5.2 Initializing MTL Registers
- 43.5.3 Initializing MAC
- 43.5.4 Performing Normal Receive and Transmit Operation
- 43.5.5 Stopping and Starting Transmission
- 43.5.6
Programming Guidelines for Multi-Channel Multi-Queuing
- 43.5.6.1 Transmit
- 43.5.6.2 Receive
- 43.5.6.3 Programming Guidelines for Recovering from DMA Channel Failure
- 43.5.6.4 Programming Guidelines for IEEE 1588 Timestamping
- 43.5.6.5 Programming Guidelines for Energy Efficient Ethernet
- 43.5.6.6 Programming Guidelines for Flexible Pulse-Per-Second Output
- 43.5.6.7 Programming Guidelines for TSO
- 43.6
Software
- 43.6.1
ETHERNET Examples
- 43.6.1.1 Ethernet + IPC basic message passing example with interrupt - C28X_CM
- 43.6.1.2 Ethernet + IPC basic message passing example with interrupt - C28X_CM
- 43.6.1.3 Ethernet MAC Internal Loopback - CM
- 43.6.1.4 Ethernet Basic Transmit and Receive PHY Loopback - CM
- 43.6.1.5 Ethernet Threshold mode with level PHY loopback - CM
- 43.6.1.6 Ethernet PTP Basic Master - CM
- 43.6.1.7 Ethernet PTP Basic Slave - CM
- 43.6.1.8 Ethernet PTP Offload Master - CM
- 43.6.1.9 Ethernet PTP Offload Slave - CM
- 43.6.1.10 Ethernet MAC CRC and Checksum Offload - CM
- 43.6.1.11 Ethernet Transmit Segmentation Offload - CM
- 43.6.1.12 Ethernet MAC Internal Loopback - CM
- 43.6.1.13 Ethernet RevMII Example MII side - CM
- 43.6.1.14 Ethernet RevMII Example RevMII side - CM
- 43.6.1.15 Ethernet Low Latency Interrupt - CM
- 43.6.1
ETHERNET Examples
- 43.7 Ethernet Registers
- 44Generic Cyclic Redundancy Check (GCRC)
-
45Modular Controller Area Network (MCAN)
- 45.1 MCAN Introduction
- 45.2 MCAN Environment
- 45.3 CAN Network Basics
- 45.4 MCAN Integration
- 45.5
MCAN Functional Description
- 45.5.1 Module Clocking Requirements
- 45.5.2 Interrupt Requests
- 45.5.3 Operating Modes
- 45.5.4 Transmitter Delay Compensation
- 45.5.5 Restricted Operation Mode
- 45.5.6 Bus Monitoring Mode
- 45.5.7 Disabled Automatic Retransmission (DAR) Mode
- 45.5.8 Clock Stop Mode
- 45.5.9 Test Modes
- 45.5.10 Timestamp Generation
- 45.5.11 Timeout Counter
- 45.5.12 Safety
- 45.5.13 Rx Handling
- 45.5.14 Tx Handling
- 45.5.15 FIFO Acknowledge Handling
- 45.5.16 Message RAM
- 45.6
Software
- 45.6.1
MCAN Examples
- 45.6.1.1 MCAN Internal Loopback with Interrupt - CM
- 45.6.1.2 MCAN Internal Loopback with Interrupt
- 45.6.1.3 MCAN External Loopback with Interrupt - CM
- 45.6.1.4 MCAN Loopback with Interrupts Example Using SYSCONFIG Tool
- 45.6.1.5 MCAN receive using Rx Buffer
- 45.6.1.6 MCAN External Reception (with mask filter) into RX-FIFO1
- 45.6.1.7 MCAN Classic frames transmission using Tx Buffer
- 45.6.1.8 MCAN External Reception (with RANGE filter) into RX-FIFO1
- 45.6.1.9 MCAN External Transmit using Tx Buffer
- 45.6.1.10 MCAN receive using Rx Buffer
- 45.6.1.11 MCAN Internal Loopback with Interrupt
- 45.6.1.12 MCAN External Transmit using Tx Buffer
- 45.6.1
MCAN Examples
- 45.7 MCAN Registers
-
46Connectivity Manager
Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) Module
- 46.1 Introduction
- 46.2
Functional Description
- 46.2.1
I2C Bus Functional Overview
- 46.2.1.1 START and STOP Conditions
- 46.2.1.2 Data Format With 7-Bit Address
- 46.2.1.3 Data Validity
- 46.2.1.4 Acknowledge
- 46.2.1.5 Repeated START
- 46.2.1.6 Clock Low Time-out (CLTO)
- 46.2.1.7 Dual Address
- 46.2.1.8 Arbitration
- 46.2.1.9 Glitch Suppression in Multi-Master Configuration
- 46.2.1.10 SMBus Operation
- 46.2.2 Available Speed Modes
- 46.2.3 Interrupts
- 46.2.4 Loopback Operation
- 46.2.5 FIFO and µDMA Operation
- 46.2.6 Command Sequence Flow Charts
- 46.2.1
I2C Bus Functional Overview
- 46.3 Initialization and Configuration
- 46.4 CM I2C Registers
-
47Synchronous Serial Interface
(SSI)
- 47.1 Introduction
- 47.2
Functional Description
- 47.2.1 Bit Rate Generation
- 47.2.2 FIFO Operation
- 47.2.3 SSInFSS Function
- 47.2.4 Interrupts
- 47.2.5 Frame Formats
- 47.2.6 DMA Operation
- 47.3 Initialization and Configuration
- 47.4 Software
- 47.5 SSI Registers
- 48Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART)
-
49Micro Direct Memory Access (µDMA)
- 49.1 Introduction
- 49.2 Functional Description
- 49.3 Initialization and Configuration
- 49.4 Software
- 49.5 µDMA Registers
- 50Revision History
43.3.2.1.1.1 Peer-to-Peer Transparent Clock (P2PTC) Message Support
The IEEE 1588-2008 supports peer-to-peer PTP (Pdelay) message in addition to the SYNC, Delay Request, Follow-up, and Delay Response messages.
The IEEE 1588-2008 supports peer-to-peer PTP (Pdelay) message in addition to the SYNC, Delay Request, Follow-up, and Delay Response messages. Figure 43-11 shows the method to calculate the propagation delay in clocks supporting peer-to-peer path correction.
- Port 1 issues a Pdelay_Req message and generates a timestamp (t1) for the Pdelay_Req message.
- Port 2 receives the Pdelay_Req message and generates a timestamp (t2) for this message.
- Port 2 returns a Pdelay_Resp message and generates a timestamp (t3) for this message. To minimize errors because of any frequency offset between the two ports, Port 2 returns the Pdelay_Resp message as quickly as possible after the receipt of the Pdelay_Req message. Port 2 returns any one of the following:
- Difference between the timestamps t2 and t3 in the Pdelay_Resp message
- Difference between the timestamps t2 and t3 in the Pdelay_Resp_Follow_Up message
- Timestamps t2 and t3 in the Pdelay_Resp and Pdelay_Resp_Follow_Up messages, respectively
- Port 1 generates a timestamp (t4) on receiving the Pdelay_Resp message.
- Port 1 uses all four timestamps to compute the mean link delay.
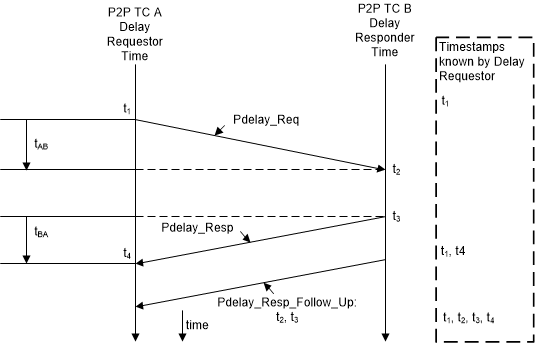 Figure 43-11 Propagation Delay Calculation in Clocks Supporting Peer-to-Peer Path Correction
Figure 43-11 Propagation Delay Calculation in Clocks Supporting Peer-to-Peer Path Correction