SPRUIR8B april 2020 – july 2023
- 1
- CLB Tool
- Trademarks
- 1Introduction
- 2Getting Started
- 3Using the CLB Tool
-
4Examples
- 4.1
Foundational Examples
- 4.1.1 CLB Empty Project
- 4.1.2 Example 3 – PWM Generation
- 4.1.3 Example 7 – State Machine
- 4.1.4 Example 13 – PUSH-PULL Interface
- 4.1.5 Example 14 – Multi-Tile
- 4.1.6 Example 15 – Tile to Tile Delay
- 4.1.7 Example 16 - Glue Logic
- 4.1.8 Exampe 18 - AOC
- 4.1.9 Example 19 - AOC Release Control
- 4.1.10 Example 20 - CLB XBARs
- 4.2
Getting Started Examples
- 4.2.1 Example 1 – Combinatorial Logic
- 4.2.2 Example 2 – GPIO Input Filter
- 4.2.3 Example 4 – PWM Protection
- 4.2.4 Example 5 – Event Window
- 4.2.5 Example 6 – Signal Generation and Check
- 4.2.6 Example 8 – External AND Gate
- 4.2.7 Example 9 – Timer
- 4.2.8 Example 10 – Timer With Two States
- 4.2.9 Example 11 – Interrupt Tag
- 4.2.10 Example 12 – Output Intersect
- 4.2.11 Example 17 – One-Shot PWM Generation
- 4.2.12 Example 21 - Clock Prescaler and NMI
- 4.2.13 Example 22 - Serializer
- 4.2.14 Example 23 - LFSR
- 4.2.15 Example 24 - Lock Output Mask
- 4.2.16 Example 25 - Input Pipeline Mode
- 4.2.17 Example 26 - Clocking Pipeline Mode
- 4.3 Expert Examples
- 4.1
Foundational Examples
- 5Enabling CLB Tool in Existing DriverLib Projects
- 6Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 7Revision History
2.3.1 Installation to Compile SystemC
To allow the simulation source file clb_sim.cpp to compile for Windows:
- Download “tdm-gcc” version 5.1.0-2 from SourceForge.
- Open the downloaded file.
- Uncheck the "Check for updated files on the TDM-GCC server" option.
- Select “Create” from the setup wizard.
 Figure 2-1 TDM Compiler
Installation Wizard
Figure 2-1 TDM Compiler
Installation Wizard - If the
wizard shows this information regarding license changes, select "Next".
 Figure 2-2 TDM License
Change
Figure 2-2 TDM License
Change - Select the installation directory as C:\TDM-GCC-64 and click
“Next”.
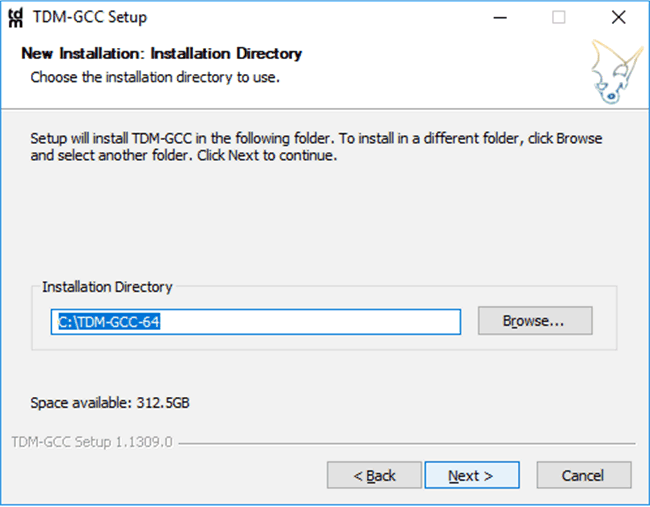 Figure 2-3 TDM Compiler
Path
Figure 2-3 TDM Compiler
Path - Verify
that the proper components are selected before clicking "Install".
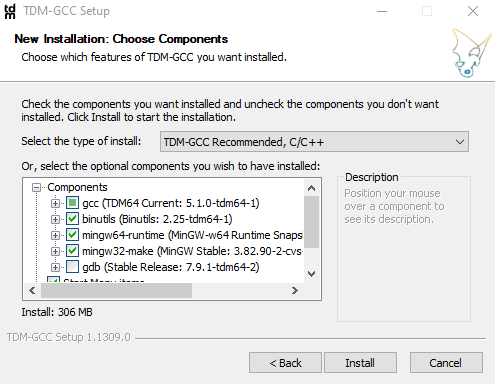 Figure 2-4 TDM Components
Figure 2-4 TDM Components - Once the installation completes, select "Next" and "Finish".
For Mac or Linux, the SystemC library needs to be installed, but the G++ compiler does not. Verify that the G++ compiler is up-to-date before proceeding. To install SystemC for Mac or Linux:
- Open the terminal.
- Run
sudo apt-get install build-essential. - Install SystemC 2.3.3 from Accelera and extract it by
running
tar -xvf systemc-2.3.3.tar.gzin the terminal. - Copy this extracted folder into
the "/usr/bin" directory by doing
sudo cp -r systemc-2.3.3 /usr/bin. Go to the directory created by the tar command (not in "/usr/bin") and create a directory called "objdir".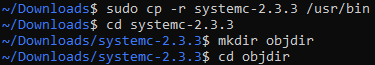 Figure 2-5 SystemC Directory
Creation
Figure 2-5 SystemC Directory
Creation - Run
sudo ../configure --prefix=/usr/bin/systemc-2.3.3/.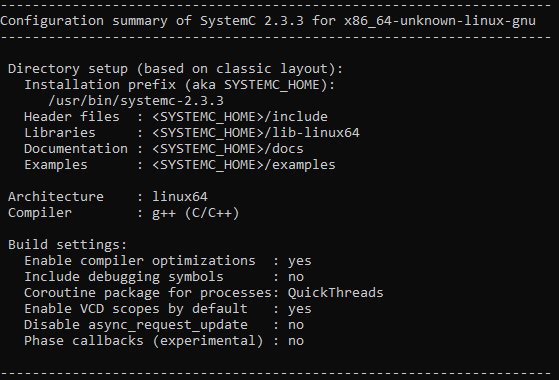 Figure 2-6 SystemC Configuration
Output
Figure 2-6 SystemC Configuration
Output - Run
sudo make.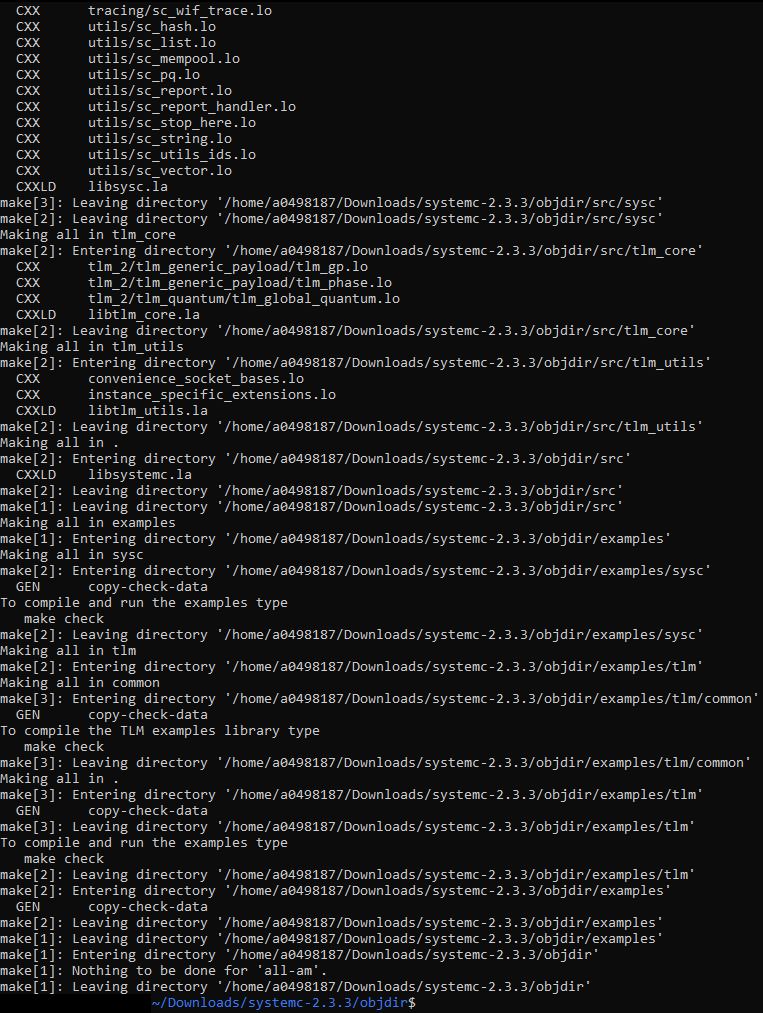 Figure 2-7 Make Output
Figure 2-7 Make Output - Run
sudo make install.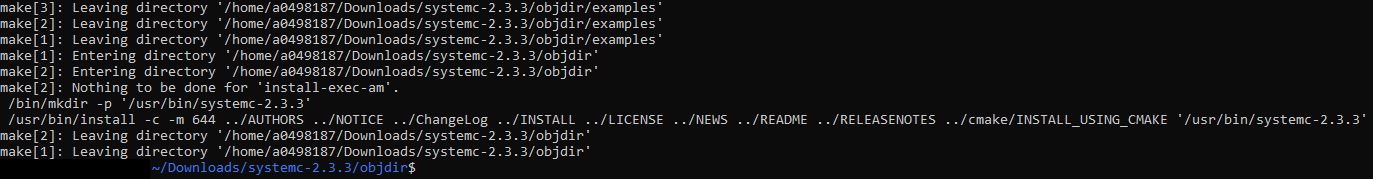 Figure 2-8 Make Install
Output
Figure 2-8 Make Install
Output