SPRUJ28E November 2021 – September 2024 AM68 , AM68A , TDA4AL-Q1 , TDA4VE-Q1 , TDA4VL-Q1
- 1
- Read This First
-
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Device Overview
- 1.2
Module Descriptions
- 1.2.1 Arm Cortex-A72 Subsystem
- 1.2.2 Arm Cortex-R5F Processor
- 1.2.3 C71x DSP Subsystem
- 1.2.4 Graphics Processing Unit
- 1.2.5 Video Accelerator
- 1.2.6 Vision Pre-processing Accelerator
- 1.2.7 Depth and Motion Perception Accelerator
- 1.2.8 Navigator Subsystem
- 1.2.9 Region-based Address Translation Module
- 1.2.10 Data Routing Unit
- 1.2.11 Display Subsystem
- 1.2.12 Camera Subsystem
- 1.2.13 Shared D-PHY Transmitter
- 1.2.14 Multicore Shared Memory Controller
- 1.2.15 DDR Subsystem
- 1.2.16 General Purpose Input/Output Interface
- 1.2.17 Inter-Integrated Circuit Interface
- 1.2.18 Improved Inter-Integrated Circuit Interface
- 1.2.19 Multi-channel Serial Peripheral Interface
- 1.2.20 Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter
- 1.2.21 Peripheral Component Interconnect Express Subsystem
- 1.2.22 Universal Serial Bus (USB) Subsystem
- 1.2.23 SerDes
- 1.2.24 General Purpose Memory Controller with Error Location Module
- 1.2.25 Multimedia Card/Secure Digital Interface
- 1.2.26 Enhanced Capture Module
- 1.2.27 Enhanced Pulse-Width Modulation Module
- 1.2.28 Enhanced Quadrature Encoder Pulse Module
- 1.2.29 Controller Area Network
- 1.2.30 Audio Tracking Logic
- 1.2.31 Multi-channel Audio Serial Port
- 1.2.32 Timers
- 1.2.33 Internal Diagnostics Modules
- 1.2.34 Analog-to-Digital Converter
- 1.2.35 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
- 1.2.36 Octal Serial Peripheral Interface and HyperBus Memory Controller as a Flash Subsystem
- 1.2.37 Security Management Subsystem
- 1.3 Device Identification
- 2 Memory Maps
- 3 System Interconnect
-
4 Initialization
- 4.1 Initialization Overview
- 4.2 Boot Process
- 4.3
Boot Mode Pins
- 4.3.1 MCU_BOOTMODE Pin Mapping
- 4.3.2 BOOTMODE Pin Mapping
- 4.3.3 No-boot/Dev-boot Configuration
- 4.3.4 Hyperflash Boot Device Configuration
- 4.3.5 OSPI Boot Device Configuration
- 4.3.6 QSPI Boot Device Configuration
- 4.3.7 SPI Boot Device Configuration
- 4.3.8 xSPI Boot Device Configuration
- 4.3.9 I2C Boot Device Configuration
- 4.3.10 MMC/SD Card Boot Device Configuration
- 4.3.11 eMMC Boot Device Configuration
- 4.3.12 Ethernet Boot Device Configuration
- 4.3.13 USB Boot Device Configuration
- 4.3.14 PCIe Boot Device Configuration
- 4.3.15 UART Boot Device Configuration
- 4.3.16 Serial NAND Boot Device Configuration
- 4.3.17 PLL Configuration
- 4.4
Boot Parameter Tables
- 4.4.1 Common Header
- 4.4.2 PLL Setup
- 4.4.3 PCIe Boot Parameter Table
- 4.4.4 I2C Boot Parameter Table
- 4.4.5 OSPI/QSPI/SPI Boot Parameter Table
- 4.4.6 Ethernet Boot Parameter Table
- 4.4.7 USB Boot Parameter Table
- 4.4.8 MMCSD Boot Parameter Table
- 4.4.9 UART Boot Parameter Table
- 4.4.10 Hyperflash Boot Parameter Table
- 4.4.11 Serial NAND Boot Parameter Table
- 4.5 Boot Image Format
- 4.6
Boot Modes
- 4.6.1 I2C Bootloader Operation
- 4.6.2 SPI Bootloader Operation
- 4.6.3 QSPI Bootloader Operation
- 4.6.4 OSPI Bootloader Operation
- 4.6.5 PCIe Bootloader Operation
- 4.6.6 Ethernet Bootloader Operation
- 4.6.7 USB Bootloader Operation
- 4.6.8 MMCSD Bootloader Operation
- 4.6.9 UART Bootloader Operation
- 4.7 Boot Memory Maps
-
5 Device Configuration
- 5.1
Control Module (CTRL_MMR)
- 5.1.1 CTRL_MMR Overview
- 5.1.2
CTRL_MMR Functional Description
- 5.1.2.1 Register Partitions
- 5.1.2.2 Pad Configuration Registers
- 5.1.2.3 Kick Protection Registers
- 5.1.2.4 Proxy Addressing Registers
- 5.1.2.5 CTRL_MMR Interrupts
- 5.1.2.6 Inter-processor Communication Registers
- 5.1.2.7 Timer IO Muxing Control Registers
- 5.1.2.8 EHRPWM/EQEP Control and Status Registers
- 5.1.2.9 Clock Muxing and Division Registers
- 5.1.2.10 Module Control Registers
- 5.1.2.11 DDRSS Dynamic Frequency Change Registers
- 5.1.2.12 MAC Address Registers
- 5.1.2.13 Feature Registers
- 5.1.2.14 Power and Reset Related Registers
- 5.1.2.15 I/O Debounce Control Registers
- 5.1.3 Control Module Registers
- 5.2
Power
- 5.2.1 Power Management Overview
- 5.2.2 WKUP_PSC0 Device-Specific Information
- 5.2.3
Power Management Subsystems
- 5.2.3.1 POK, PRG_PP, and POR Modules
- 5.2.3.2 Power Glitch Detect (PGD) Modules
- 5.2.3.3 Voltage and Thermal Manager (VTM)
- 5.2.4 Dynamic Power Management
- 5.3 Reset
- 5.4
Clocking
- 5.4.1 Clocking Overview
- 5.4.2 Modules Controlled by PLL
- 5.4.3 Clock Mapping
- 5.4.4 Clock Inputs
- 5.4.5 Clock Outputs
- 5.4.6 Device Oscillators
- 5.4.7
PLLs
- 5.4.7.1 WKUP and MCU Domains PLL Overview
- 5.4.7.2 MAIN Domain PLLs Overview
- 5.4.7.3 PLL Reference Clocks
- 5.4.7.4 Generic PLL Overview
- 5.4.7.5 PLLs Device-Specific Information
- 5.4.7.6 PLL and PLL Controller Connection
- 5.4.7.7 System Clocks Operating Frequency Ranges
- 5.4.7.8 Recommended Clock and Control Signal Transition Behavior
- 5.4.7.9 Interface Clock Specifications
- 5.4.7.10 PLL, PLLCTRL, and HSDIV Controllers Programming Guide
- 5.5
Module Integration
- 5.5.1 ADC
- 5.5.2 ATL
- 5.5.3 CPSW2G
- 5.5.4 CSI_RX
- 5.5.5 CSI_TX
- 5.5.6 DCC
- 5.5.7 DMTIMER (Timer)
- 5.5.8 DPHY_RX
- 5.5.9 DPHY_TX
- 5.5.10 DSS/DSI
- 5.5.11 eCAP
- 5.5.12 ePWM
- 5.5.13 ESM
- 5.5.14 FSS
- 5.5.15 GPIO
- 5.5.16 GPMC
- 5.5.17 GPU
- 5.5.18 I2C
- 5.5.19 I3C
- 5.5.20 MCAN
- 5.5.21 MMCSD
- 5.5.22 McASP
- 5.5.23 McSPI
- 5.5.24
Navigator Subsystem (NAVSS)
- 5.5.24.1 Module Allocations
- 5.5.24.2 Main Navigator SubSystem (NAVSS)
- 5.5.24.3
MCU Navigator Subsystem (MCU NAVSS)
- 5.5.24.3.1 Global Event Map
- 5.5.24.3.2 PSIL System Thread Map (All NAVSS)
- 5.5.24.3.3 MCU NAVSS VBUSM Route ID Table
- 5.5.24.3.4 MCU NAVSS Interrupt Router Configuration
- 5.5.24.3.5 MCU NAVSS UDMASS Interrupt Aggregator Configuration
- 5.5.24.3.6 MCU NAVSS UDMA Configuration
- 5.5.24.3.7 MCU NAVSS Ring Accelerator Configuration
- 5.5.24.3.8 MCU NAVSS Proxy Configuration
- 5.5.24.3.9 MCU NAVSS Secure Proxy Configuration
- 5.5.24.4 Block Copy DMA (BCDMA)
- 5.5.25 PCIE
- 5.5.26 R5FSS
- 5.5.27 RAT
- 5.5.28 RTI
- 5.5.29 UART
- 5.5.30 USBSS
- 5.5.31 Video CODEC
- 5.5.32 VPAC
- 5.1
Control Module (CTRL_MMR)
-
6 Processors and Accelerators
- 6.1 Compute Cluster
- 6.2
Dual-A72 MPU
Subsystem
- 6.2.1 A72SS Overview
- 6.2.2
A72SS Functional Description
- 6.2.2.1 A72SS Block Diagram
- 6.2.2.2 A72SS A72 Cluster
- 6.2.2.3 A72SS Interfaces and Async Bridges
- 6.2.2.4 A72SS Interrupts
- 6.2.2.5 A72SS Power Management, Clocking and Reset
- 6.2.2.6 A72SS Debug Support
- 6.2.2.7 A72SS Timestamps
- 6.2.2.8 A72SS Watchdog
- 6.2.2.9 A72SS Internal Diagnostics
- 6.2.2.10 A72SS Cache Pre-Warming
- 6.2.2.11 A72SS Boot
- 6.2.2.12 A72SS IPC with Other CPUs
- 6.3
Dual-R5F MCU Subsystem
- 6.3.1 R5FSS Overview
- 6.3.2
R5FSS Functional Description
- 6.3.2.1 R5FSS Block Diagram
- 6.3.2.2 R5FSS Cortex-R5F Core
- 6.3.2.3 R5FSS Interfaces
- 6.3.2.4 R5FSS Power, Clocking and Reset
- 6.3.2.5 R5FSS Lockstep Error Detection Logic
- 6.3.2.6 R5FSS Vectored Interrupt Manager (VIM)
- 6.3.2.7 R5FSS Region Address Translation (RAT)
- 6.3.2.8 R5FSS ECC Support
- 6.3.2.9 R5FSS Memory View
- 6.3.2.10 R5FSS Debug and Trace
- 6.3.2.11 R5FSS Boot Options
- 6.3.2.12 R5FSS Core Memory ECC Events
- 6.3.2.13 R5FSS_VIM Registers
- 6.3.2.14 R5FSS_RAT Registers
- 6.4
C71x DSP Subsystem
- 6.4.1 C71SS Overview
- 6.4.2
C71SS Functional Description
- 6.4.2.1 C71x DSP CPU
- 6.4.2.2 C71x DSP Matrix Multiply Accelerator
- 6.4.2.3 C71x DSP Cache Memory System
- 6.4.2.4 C71x DSP Streaming Engine
- 6.4.2.5 C71x DSP CorePac Memory Management Unit
- 6.4.2.6 C71x DSP ECC Support
- 6.4.2.7 C71x DSP Boot Configuration
- 6.4.2.8 C71x DSP Power-Up/Down Sequences
- 6.4.2.9 C71x DSP Interrupt Control
- 6.5 Graphics Accelerator (GPU)
- 6.6 Video Accelerator
- 6.7
Vision Pre-processing Accelerator (VPAC)
- 6.7.1 VPAC Overview
- 6.7.2
VPAC Subsystem Level
- 6.7.2.1 VPAC Subsystem Block Diagram
- 6.7.2.2 VPAC Subsystem Clocks
- 6.7.2.3 VPAC Subsystem Resets
- 6.7.2.4 VPAC Subsystem Interrupts
- 6.7.2.5 VPAC Subsystem SL2 Memory Infrastructure
- 6.7.2.6 VPAC Subsystem DMA Infrastructure
- 6.7.2.7 VPAC Subsystem Data Routing Interconnect
- 6.7.2.8 VPAC Subsystem Pipeline Flow Control and Messaging
- 6.7.2.9 VPAC Subsystem Data Formats Support
- 6.7.2.10 VPAC Subsystem Debug Features
- 6.7.2.11 VPAC Subsystem Internal Diagnostic Features
- 6.7.2.12 VPAC Subsystem Security Features
- 6.7.2.13 VPAC Subsystem Programmer’s Guide
- 6.7.3
VPAC Vision Imaging Subsystem (VISS)
- 6.7.3.1
VISS Top Level
- 6.7.3.1.1 Features Supported
- 6.7.3.1.2 VISS Block Diagram
- 6.7.3.1.3 VISS Data Flow within VPAC
- 6.7.3.1.4 Concurret Machine Vision and Human Vision Output
- 6.7.3.1.5 VISS Clocking
- 6.7.3.1.6 VISS Data Formats Support
- 6.7.3.1.7 VISS VPORT Interface
- 6.7.3.1.8 VISS Submodule Integration Specifics
- 6.7.3.1.9 VISS Stall Handling
- 6.7.3.1.10 VISS Blanking Requirements
- 6.7.3.1.11 FCP2 Sync FIFO
- 6.7.3.1.12 VISS Interrupts
- 6.7.3.1.13 VISS Error Correcting Code (ECC) Support
- 6.7.3.1.14 VISS Programmer's Guide
- 6.7.3.2
VISS RAW Frond-End (RAWFE)
- 6.7.3.2.1 RAWFE Overview
- 6.7.3.2.2 RAWFE Functional Description
- 6.7.3.2.3 RAWFE Interrupts
- 6.7.3.2.4
RAWFE Sub-Modules Details
- 6.7.3.2.4.1 RAWFE Decompanding Block
- 6.7.3.2.4.2 RAWFE WDR Merge Block
- 6.7.3.2.4.3 RAWFE Defective Pixel Correction (DPC) Block
- 6.7.3.2.4.4 RAWFE Lens Shading Correction (LSC) and Digital Gain (DG) Block
- 6.7.3.2.4.5 RAWFE Gain & Offset Block
- 6.7.3.2.4.6
RAWFE H3A
- 6.7.3.2.4.6.1 RAWFE H3A Overview
- 6.7.3.2.4.6.2 RAWFE H3A Top-Level Block Diagram
- 6.7.3.2.4.6.3 RAWFE H3A Line Framing Logic
- 6.7.3.2.4.6.4 RAWFE H3A Optional Preprocessing
- 6.7.3.2.4.6.5 RAWFE H3A Autofocus Engine
- 6.7.3.2.4.6.6 RAWFE H3A AE/AWB Engine
- 6.7.3.2.4.6.7 RAWFE H3A DMA Interface
- 6.7.3.2.4.6.8 RAWFE H3A Events and Status Checking
- 6.7.3.2.4.6.9 RAWFE H3A Interface Mux
- 6.7.3.2.4.6.10 RAWFE H3A interface to LSE
- 6.7.3.2.4.6.11 RAWFE H3A Erratas
- 6.7.3.2.5 RAWFE Programmer’s Guide
- 6.7.3.3 Chromatic Aberration Correction (CAC) Module
- 6.7.3.4 VISS Spatial Noise Filter (NSF4V)
- 6.7.3.5
VISS Global/Local Brightness and Contrast Enhancement (GLBCE) Module
- 6.7.3.5.1 GLBCE Overview
- 6.7.3.5.2 GLBCE Interface
- 6.7.3.5.3
GLBCE Core
- 6.7.3.5.3.1 GLBCE Core Key Parameters
- 6.7.3.5.3.2 GLBCE Iridix Strength Calculation
- 6.7.3.5.3.3
GLBCE Iridix Configuration Registers
- 6.7.3.5.3.3.1 GLBCE Iridix Frame Width
- 6.7.3.5.3.3.2 GLBCE Iridix Frame Height
- 6.7.3.5.3.3.3 GLBCE Iridix Control 0
- 6.7.3.5.3.3.4 GLBCE Iridix Control 1
- 6.7.3.5.3.3.5 GLBCE Iridix Strength
- 6.7.3.5.3.3.6 GLBCE Iridix Variance
- 6.7.3.5.3.3.7 GLBCE Iridix Dither
- 6.7.3.5.3.3.8 GLBCE Iridix Amplification Limit
- 6.7.3.5.3.3.9 GLBCE Iridix Slope Min and Max
- 6.7.3.5.3.3.10 GLBCE Iridix Black Level
- 6.7.3.5.3.3.11 GLBCE Iridix White Level
- 6.7.3.5.3.3.12 GLBCE Iridix Asymmetry Function Look-up-table
- 6.7.3.5.3.3.13 GLBCE Iridix Forward and Reverse Perceptual Functions Look-up-tables
- 6.7.3.5.3.3.14 GLBCE Iridix WDR Look-up-table
- 6.7.3.5.4 GLBCE Embedded Memory
- 6.7.3.5.5 GLBCE General Processing
- 6.7.3.5.6 GLBCE Continuous Frame Processing
- 6.7.3.5.7 GLBCE Single Image Processing
- 6.7.3.6
VISS Flexible Color Processing (FCP) Module
- 6.7.3.6.1 FCP Overview
- 6.7.3.6.2 FCP Functional Description
- 6.7.3.6.3
FCP Submodule Details
- 6.7.3.6.3.1 Flexible CFA / Demosaicing
- 6.7.3.6.3.2 Edge Enhancer Module Wrapper (WEE)
- 6.7.3.6.3.3 Flexible Color Conversion (CC)
- 6.7.3.6.3.4 444-422/420 Chroma Down-sampler
- 6.7.3.6.3.5 Blanking and Latency
- 6.7.3.6.4 FCP Clocking
- 6.7.3.6.5 FCP Interrupts
- 6.7.3.6.6 FCP Programmer’s Guide
- 6.7.3.7 VISS Edge Enhancer (EE)
- 6.7.3.1
VISS Top Level
- 6.7.4
VPAC Lens Distortion Correction (LDC) Module
- 6.7.4.1 LDC Overview
- 6.7.4.2
LDC Functional Description
- 6.7.4.2.1 LDC Integration in VPAC
- 6.7.4.2.2 LDC Block Diagram
- 6.7.4.2.3 LDC Clocks
- 6.7.4.2.4 LDC Interrupts
- 6.7.4.2.5 LDC Affine Transform
- 6.7.4.2.6 LDC Perspective Transformation
- 6.7.4.2.7 LDC Lens Distortion Back Mapping
- 6.7.4.2.8 LDC Pixel Interpolation
- 6.7.4.2.9 LDC Buffer Management
- 6.7.4.2.10 LDC Multi Region with Variable Block size
- 6.7.4.2.11 LDC Multi-pass Frame processing
- 6.7.4.2.12 LDC Input/Output Data Formats
- 6.7.4.2.13 LDC YUV422 to YUV420 Conversion
- 6.7.4.2.14 Independent Channel Control
- 6.7.4.2.15 LDC SL2 Interface (LSE)
- 6.7.4.2.16 LDC LUT Mapped Dual Output
- 6.7.4.2.17 LDC Band Width Controller
- 6.7.4.2.18 LDC Input Block Fetch Limit
- 6.7.4.2.19 LDC HTS Interface
- 6.7.4.2.20 LDC VBUSM Read Interface
- 6.7.4.2.21 Partial Input Frame Storage
- 6.7.4.2.22 Hybrid Addressing
- 6.7.4.3 LDC Programmers Guide
- 6.7.5
VPAC Multi-Scaler (MSC)
- 6.7.5.1 MSC Overview
- 6.7.5.2 MSC Functional Description
- 6.7.5.3 MSC Interrupt Conditions
- 6.7.5.4
MSC Submodule Details
- 6.7.5.4.1 MSC Configuration Interface (MSC_CFG)
- 6.7.5.4.2 MSC Load Store Engine (MSC_LSE)
- 6.7.5.4.3 MSC_CORE (HWA Core)
- 6.7.5.5 MSC Performance
- 6.7.5.6 MSC Clocking
- 6.7.5.7 MSC Reset
- 6.7.5.8
MSC Programmer’s Guide
- 6.7.5.8.1 Programming Model
- 6.7.5.8.2 Initialization Sequence
- 6.7.5.8.3 Real-Time Operating Requirements
- 6.7.5.8.4 Power Up/Down Sequence
- 6.7.6
VPAC Noise Filter (NF)
- 6.7.6.1 NF Overview
- 6.7.6.2 NF Functional Description
- 6.7.6.3 NF Interrupts
- 6.7.6.4 NF Submodule Details
- 6.7.6.5 NF Integration Details
- 6.7.6.6 NF Programmer’s Guide
- 6.8 Depth and Motion Perception Accelerator (DMPAC)
-
7 Interprocessor Communication
- 7.1
Mailbox
- 7.1.1 Mailbox Overview
- 7.1.2 Mailbox Integration
- 7.1.3 Mailbox Functional Description
- 7.1.4 Mailbox Programming Guide
- 7.2 Spinlock
- 7.1
Mailbox
-
8 Memory Controllers
- 8.1
Multicore Shared Memory Controller (MSMC)
- 8.1.1 MSMC Overview
- 8.1.2
MSMC Functional Description
- 8.1.2.1 MSMC Block Diagram
- 8.1.2.2 MSMC On-Chip Memory Banking
- 8.1.2.3 MSMC Snoop Filter and Data Cache
- 8.1.2.4 MSMC Access Protection Checks
- 8.1.2.5 MSMC Null Slave
- 8.1.2.6 MSMC Resource Arbitration
- 8.1.2.7 MSMC Error Detection and Correction
- 8.1.2.8 MSMC Interrupts
- 8.1.2.9 MSMC Memory Regions
- 8.1.2.10 MSMC Hardware Coherence
- 8.1.2.11 MSMC Quality-of-Service
- 8.1.2.12 MSMC Memory Regions Protection
- 8.1.2.13 MSMC Cache Tag View
- 8.1.2.14 MSMC R50+ Features
- 8.2
DDR Subsystem (DDRSS)
- 8.2.1 DDRSS Overview
- 8.2.2 DDRSS Environment
- 8.2.3
DDRSS Functional Description
- 8.2.3.1 DDRSS MSMC2DDR Bridge
- 8.2.3.2 DDRSS Interrupts
- 8.2.3.3 DDRSS Memory Regions
- 8.2.3.4 DDRSS ECC Support
- 8.2.3.5 DDRSS Dynamic Frequency Change Interface
- 8.2.3.6
DDR Controller Functional Description
- 8.2.3.6.1 DDR PHY Interface (DFI)
- 8.2.3.6.2 Command Queue
- 8.2.3.6.3 Low Power Control
- 8.2.3.6.4 Transaction Processing
- 8.2.3.6.5 BIST Engine
- 8.2.3.6.6 ECC Engine
- 8.2.3.6.7 Address Mapping
- 8.2.3.6.8 Paging Policy
- 8.2.3.6.9 DDR Controller Initialization
- 8.2.3.6.10 Programming LPDDR4 Memories
- 8.2.3.7
DDR PHY Functional Description
- 8.2.3.7.1 Data Slice
- 8.2.3.7.2 Address Slice
- 8.2.3.7.3 Address/Control Slice
- 8.2.3.7.4 Clock Slice
- 8.2.3.7.5 DDR PHY Initialization
- 8.2.3.7.6 DDR PHY Dynamic Frequency Scaling (DFS)
- 8.2.3.7.7 Chip Select and Frequency Based Register Settings
- 8.2.3.7.8 Low-Power Modes
- 8.2.3.7.9 Training Support
- 8.2.3.7.10 Data Bus Inversion (DBI)
- 8.2.3.7.11 I/O Pad Calibration
- 8.2.3.7.12 DQS Error
- 8.2.3.8 PI Functional Description
- 8.2.4 DDRSS Registers
- 8.3
Peripheral Virtualization Unit (PVU)
- 8.3.1 PVU Overview
- 8.3.2
PVU Functional Description
- 8.3.2.1 Functional Operation Overview
- 8.3.2.2 PVU Channels
- 8.3.2.3 TLB
- 8.3.2.4 TLB Entry
- 8.3.2.5 TLB Selection
- 8.3.2.6 DMA Classes
- 8.3.2.7 General virtIDs
- 8.3.2.8 TLB Lookup
- 8.3.2.9 TLB Miss
- 8.3.2.10 Multiple Matching Entries
- 8.3.2.11 TLB Disable
- 8.3.2.12 TLB Chaining
- 8.3.2.13 TLB Permissions
- 8.3.2.14 Translation
- 8.3.2.15 Memory Attributes
- 8.3.2.16 Faulted Transactions
- 8.3.2.17 Non-Virtual Transactions
- 8.3.2.18 Allowed virtIDs
- 8.3.2.19 Software Control
- 8.3.2.20 Fault Logging
- 8.3.2.21 Alignment Restrictions
- 8.4 Region-based Address Translation (RAT) Module
- 8.1
Multicore Shared Memory Controller (MSMC)
- 9 Interrupts
-
10Data Movement Architecture (DMA)
- 10.1
DMA Architecture
- 10.1.1
Overview
- 10.1.1.1 Navigator Subsystem
- 10.1.1.2 Ring Accelerator (RA)
- 10.1.1.3 Proxy
- 10.1.1.4 Secure Proxy
- 10.1.1.5 Interrupt Aggregator (INTA)
- 10.1.1.6 Interrupt Router (IR)
- 10.1.1.7 Unified DMA – Third Party Channel Controller (UDMA-C)
- 10.1.1.8 Unified Transfer Controller (UTC)
- 10.1.1.9 Data Routing Unit (DRU)
- 10.1.1.10 Unified DMA – Peripheral Root Complex (UDMA-P)
- 10.1.1.11 Peripheral DMA (PDMA)
- 10.1.1.12 Embedded DMA
- 10.1.1.13 Definition of Terms
- 10.1.2
DMA Hardware/Software Interface
- 10.1.2.1 Data Buffers
- 10.1.2.2 Descriptors
- 10.1.2.3
Transfer Request Record
- 10.1.2.3.1 Overview
- 10.1.2.3.2 Addressing Algorithm
- 10.1.2.3.3 Transfer Request Formats
- 10.1.2.3.4
Flags Field Definition
- 10.1.2.3.4.1 Type: TR Type Field
- 10.1.2.3.4.2 STATIC: Static Field Definition
- 10.1.2.3.4.3 EVENT_SIZE: Event Generation Definition
- 10.1.2.3.4.4 TRIGGER INFO: TR Triggers
- 10.1.2.3.4.5 TRIGGERX_TYPE: Trigger Type
- 10.1.2.3.4.6 TRIGGERX: Trigger Selection
- 10.1.2.3.4.7 CMD ID: Command ID Field Definition
- 10.1.2.3.4.8 Configuration Specific Flags Definition
- 10.1.2.3.5
TR Address and Size Attributes
- 10.1.2.3.5.1 ICNT0
- 10.1.2.3.5.2 ICNT1
- 10.1.2.3.5.3 ADDR
- 10.1.2.3.5.4 DIM1
- 10.1.2.3.5.5 ICNT2
- 10.1.2.3.5.6 ICNT3
- 10.1.2.3.5.7 DIM2
- 10.1.2.3.5.8 DIM3
- 10.1.2.3.5.9 DDIM1
- 10.1.2.3.5.10 DADDR
- 10.1.2.3.5.11 DDIM2
- 10.1.2.3.5.12 DDIM3
- 10.1.2.3.5.13 DICNT0
- 10.1.2.3.5.14 DICNT1
- 10.1.2.3.5.15 DICNT2
- 10.1.2.3.5.16 DICNT3
- 10.1.2.3.6
FMTFLAGS
- 10.1.2.3.6.1 AMODE: Addressing Mode Definition
- 10.1.2.3.6.2 DIR: Addressing Mode Direction Definition
- 10.1.2.3.6.3 ELTYPE: Element Type Definition
- 10.1.2.3.6.4 DFMT: Data Formatting Algorithm Definition
- 10.1.2.3.6.5 SECTR: Secondary Transfer Request Definition
- 10.1.2.3.6.6 AMODE SPECIFIC: Addressing Mode Field
- 10.1.2.3.6.7 Cache Flags
- 10.1.2.4 Transfer Response Record
- 10.1.2.5
Queues
- 10.1.2.5.1
Queue Types
- 10.1.2.5.1.1 Transmit Queues (Pass By Reference)
- 10.1.2.5.1.2 Transmit Queues (Pass By Value)
- 10.1.2.5.1.3 Transmit Completion Queues (Pass By Reference)
- 10.1.2.5.1.4 Transmit Completion Queues (Pass By Value)
- 10.1.2.5.1.5 Receive Queues
- 10.1.2.5.1.6 Free Descriptor Queues
- 10.1.2.5.1.7 Free Descriptor/Buffer Queues
- 10.1.2.5.2 Ring Accelerator Queues Implementation
- 10.1.2.5.1
Queue Types
- 10.1.3
Operational Description
- 10.1.3.1 Resource Allocation
- 10.1.3.2 Ring Accelerator Operation
- 10.1.3.3 UDMA Internal Transmit Channel Setup (All Packet Types)
- 10.1.3.4 UDMA Internal Transmit Channel Teardown (All Packet Types)
- 10.1.3.5 UDMA-P Transmit Channel Pause
- 10.1.3.6 UDMA-P Transmit Operation (Host Packet Type)
- 10.1.3.7 UDMA-P Transmit Operation (Monolithic Packet)
- 10.1.3.8 UDMA Transmit Operation (TR Packet)
- 10.1.3.9 UDMA Transmit Operation (Direct TR)
- 10.1.3.10 UDMA Transmit Error/Exception Handling
- 10.1.3.11 UDMA Receive Channel Setup (All Packet Types)
- 10.1.3.12 UDMA Receive Channel Teardown
- 10.1.3.13 UDMA-P Receive Channel Pause
- 10.1.3.14 UDMA-P Receive Free Descriptor/Buffer Queue Setup (Host Packets)
- 10.1.3.15 UDMA-P Receive FlowID Firewall Operation
- 10.1.3.16 UDMA-P Receive Operation (Host Packet)
- 10.1.3.17 UDMA-P Receive Operation (Monolithic Packet)
- 10.1.3.18 UDMA Receive Operation (TR Packet)
- 10.1.3.19 UDMA Receive Operation (Direct TR)
- 10.1.3.20 UDMA Receive Error/Exception Handling
- 10.1.3.21 UTC Operation
- 10.1.3.22 UTC Receive Error/Exception Handling
- 10.1.1
Overview
- 10.2
Navigator Subsystem (NAVSS)
- 10.2.1 Main Navigator Subsystem (NAVSS)
- 10.2.2 MCU Navigator Subsystem (MCU NAVSS)
- 10.2.3
Unified DMA Controller (UDMA)
- 10.2.3.1 UDMA Overview
- 10.2.3.2
UDMA Functional Description
- 10.2.3.2.1 Block Diagram
- 10.2.3.2.2 General Functionality
- 10.2.3.2.3 Packet Oriented Transmit Operation
- 10.2.3.2.4 Packet Oriented Receive Operation
- 10.2.3.2.5 Third Party Mode Operation
- 10.2.4
Ring Accelerator (RINGACC)
- 10.2.4.1 RINGACC Overview
- 10.2.4.2
RINGACC Functional Description
- 10.2.4.2.1
Block Diagram
- 10.2.4.2.1.1 Configuration Registers
- 10.2.4.2.1.2 Source Command FIFO
- 10.2.4.2.1.3 Source Write Data FIFO
- 10.2.4.2.1.4 Source Read Data FIFO
- 10.2.4.2.1.5 Source Write Status FIFO
- 10.2.4.2.1.6 Main State Machine
- 10.2.4.2.1.7 Destination Command FIFO
- 10.2.4.2.1.8 Destination Write Data FIFO
- 10.2.4.2.1.9 Destination Read Data FIFO
- 10.2.4.2.1.10 Destination Write Status FIFO
- 10.2.4.2.2
RINGACC Functional Operation
- 10.2.4.2.2.1 Queue Modes
- 10.2.4.2.2.2 VBUSM Slave Ring Operations
- 10.2.4.2.2.3 VBUSM Master Interface Command ID Selection
- 10.2.4.2.2.4 Ring Push Operation (VBUSM Write to Source Interface)
- 10.2.4.2.2.5 Ring Pop Operation (VBUSM Read from Source Interface)
- 10.2.4.2.2.6 Host Doorbell Access
- 10.2.4.2.2.7 Queue Push Operation (VBUSM Write to Source Interface)
- 10.2.4.2.2.8 Queue Pop Operation (VBUSM Read from Source Interface)
- 10.2.4.2.2.9 Mismatched Element Size Handling
- 10.2.4.2.3 Events
- 10.2.4.2.4 Bus Error Handling
- 10.2.4.2.5 Monitors
- 10.2.4.2.1
Block Diagram
- 10.2.5
Proxy
- 10.2.5.1 Proxy Overview
- 10.2.5.2 Proxy Functional Description
- 10.2.6
Secure Proxy
- 10.2.6.1 Secure Proxy Overview
- 10.2.6.2
Secure Proxy Functional Description
- 10.2.6.2.1 Targets
- 10.2.6.2.2 Buffers
- 10.2.6.2.3 Proxy Thread Sizes
- 10.2.6.2.4 Proxy Thread Interleaving
- 10.2.6.2.5 Proxy States
- 10.2.6.2.6 Proxy Host Access
- 10.2.6.2.7 Permission Inheritance
- 10.2.6.2.8 Resource Association
- 10.2.6.2.9 Direction
- 10.2.6.2.10 Threshold Events
- 10.2.6.2.11 Error Events
- 10.2.6.2.12 Bus Errors and Credits
- 10.2.6.2.13 Debug
- 10.2.7
Interrupt Aggregator (INTR_AGGR)
- 10.2.7.1 INTR_AGGR Overview
- 10.2.7.2
INTR_AGGR Functional Description
- 10.2.7.2.1 Submodule Descriptions
- 10.2.7.2.2
General Functionality
- 10.2.7.2.2.1 Event to Interrupt Bit Steering
- 10.2.7.2.2.2 Interrupt Status
- 10.2.7.2.2.3 Interrupt Masked Status
- 10.2.7.2.2.4 Enabling/Disabling Individual Interrupt Source Bits
- 10.2.7.2.2.5 Interrupt Output Generation
- 10.2.7.2.2.6 Global Event Counting
- 10.2.7.2.2.7 Local Event to Global Event Conversion
- 10.2.7.2.2.8 Global Event Multicast
- 10.2.8 Packet Streaming Interface Link (PSI-L)
- 10.2.9
NAVSS North Bridge (NB)
- 10.2.9.1 NB Overview
- 10.2.9.2
NB Functional Description
- 10.2.9.2.1 VBUSM Slave Interfaces
- 10.2.9.2.2 VBUSM Master Interface
- 10.2.9.2.3 VBUSM.C Interfaces
- 10.2.9.2.4 Source M2M Bridges
- 10.2.9.2.5 Destination M2M Bridge
- 10.2.9.2.6 M2C Bridge
- 10.2.9.2.7 Memory Attribute Tables
- 10.2.9.2.8 Outstanding Read Data Limiter
- 10.2.9.2.9 Ordering
- 10.2.9.2.10 Quality of Service
- 10.2.9.2.11 IDLE Behavior
- 10.2.9.2.12 Clock Power Management
- 10.3
Peripheral DMA (PDMA)
- 10.3.1
PDMA Controller
- 10.3.1.1
PDMA Overview
- 10.3.1.1.1
PDMA Features
- 10.3.1.1.1.1 MCU_PDMA0 (MCU_PDMA_MISC_G0) Features
- 10.3.1.1.1.2 MCU_PDMA1 (MCU_PDMA_MISC_G1) Features
- 10.3.1.1.1.3 MCU_PDMA2 (MCU_PDMA_MISC_G2) Features
- 10.3.1.1.1.4 MCU_PDMA3 (MCU_PDMA_ADC) Features
- 10.3.1.1.1.5 PDMA5 (PDMA_MCAN) Features
- 10.3.1.1.1.6 PDMA6 (PDMA_MCASP_G0) Features
- 10.3.1.1.1.7 PDMA9 (PDMA_SPI_G0) Features
- 10.3.1.1.1.8 PDMA10 (PDMA_SPI_G1) Features
- 10.3.1.1.1.9 PDMA13 (PDMA_USART_G0) Features
- 10.3.1.1.1.10 PDMA14 (PDMA_USART_G1) Features
- 10.3.1.1.1.11 PDMA15 (PDMA_USART_G2) Features
- 10.3.1.1.2 Peripheral DMA (PDMA) Ports
- 10.3.1.1.1
PDMA Features
- 10.3.1.2
PDMA Functional Description
- 10.3.1.2.1 PDMA Functional Blocks
- 10.3.1.2.2 PDMA General Functionality
- 10.3.1.2.3 PDMA Events and Flow Control
- 10.3.1.2.4 PDMA Transmit Operation
- 10.3.1.2.5 PDMA Receive Operation
- 10.3.1.2.6 PDMA ECC Support
- 10.3.1.3 PDMA Registers
- 10.3.1.1
PDMA Overview
- 10.3.2 PDMA Sources
- 10.3.1
PDMA Controller
- 10.4
Data Routing Unit (DRU)
- 10.4.1 DRU Overview
- 10.4.2 DRU Integration
- 10.4.3
DRU Functional Description
- 10.4.3.1 DRU Basic Functionality
- 10.4.3.2 DRU Virtualization
- 10.4.3.3 DRU Compression and Decompression
- 10.4.3.4 DRU Output Events
- 10.4.3.5 DRU Address Fetch Algorithm, TR and CR Formats
- 10.4.3.6 DRU Firewalls
- 10.4.3.7 DRU Errors
- 10.4.3.8 DRU Configurations
- 10.1
DMA Architecture
-
11Time Sync
- 11.1
Time Sync Module (CPTS)
- 11.1.1 CPTS Overview
- 11.1.2
CPTS Functional Description
- 11.1.2.1 CPTS Architecture
- 11.1.2.2 CPTS Initialization
- 11.1.2.3 32-bit Time Stamp Value
- 11.1.2.4 64-bit Time Stamp Value
- 11.1.2.5 Event FIFO
- 11.1.2.6 Timestamp Compare Output
- 11.1.2.7 Timestamp Sync Output
- 11.1.2.8 Timestamp GENF Output
- 11.1.2.9 Time Sync Events
- 11.1.2.10 Timestamp Compare Event
- 11.1.2.11 CPTS Interrupt Handling
- 11.2 Timer Manager
- 11.3 Time Sync and Compare Events
- 11.1
Time Sync Module (CPTS)
-
12Peripherals
- 12.1
General Connectivity Peripherals
- 12.1.1
Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
- 12.1.1.1 ADC Overview
- 12.1.1.2 ADC Environment
- 12.1.1.3
ADC Functional Description
- 12.1.1.3.1 ADC FSM Sequencer Functional Description
- 12.1.1.3.2 ADC AFE Functional Description
- 12.1.1.3.3 ADC FIFOs and DMA
- 12.1.1.3.4 ADC Error Correcting Code (ECC)
- 12.1.1.3.5 ADC Functional Debug Mode
- 12.1.1.4 ADC Programming Guide
- 12.1.2 General-Purpose Interface (GPIO)
- 12.1.3
Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) Interface
- 12.1.3.1 I2C Overview
- 12.1.3.2 I2C Environment
- 12.1.3.3 I2C Functional Description
- 12.1.3.4 I2C Programming Guide
- 12.1.4
Improved Inter-Integrated Circuit (I3C) Interface
- 12.1.4.1 I3C Overview
- 12.1.4.2 I3C Environment
- 12.1.4.3
I3C Functional Description
- 12.1.4.3.1 I3C Block Diagram
- 12.1.4.3.2 I3C Clock Configuration
- 12.1.4.3.3 I3C Interrupt Requests
- 12.1.4.3.4 I3C Power Configuration
- 12.1.4.3.5 I3C Dynamic Address Management
- 12.1.4.3.6 I3C Retaining Registers Space
- 12.1.4.3.7 I3C Dynamic Address Assignment Procedure
- 12.1.4.3.8 I3C Sending CCC Messages
- 12.1.4.3.9 I3C In-Band Interrupt
- 12.1.4.3.10 I3C Hot-Join Request
- 12.1.4.3.11 I3C Immediate Commands
- 12.1.4.3.12 I3C Host Commands
- 12.1.4.3.13 I3C Sending Private Data in SDR Messages
- 12.1.4.4
I3C Programming Guide
- 12.1.4.4.1 I3C Power-On Programming Model
- 12.1.4.4.2 I3C Static Devices Programming
- 12.1.4.4.3 I3C DAA Procedure Initiation
- 12.1.4.4.4 I3C SDR Write Message Programming Model
- 12.1.4.4.5 I3C SDR Read Message Programming Model
- 12.1.4.4.6 I3C DDR Write Message Programming Model
- 12.1.4.4.7 I3C DDR Read Message Programming Model
- 12.1.5
Multichannel Serial Peripheral Interface (MCSPI)
- 12.1.5.1 MCSPI Overview
- 12.1.5.2 MCSPI Environment
- 12.1.5.3
MCSPI Functional Description
- 12.1.5.3.1 SPI Block Diagram
- 12.1.5.3.2 MCSPI Reset
- 12.1.5.3.3
MCSPI Controller Mode
- 12.1.5.3.3.1 Controller Mode Features
- 12.1.5.3.3.2 Controller Transmit-and-Receive Mode (Full Duplex)
- 12.1.5.3.3.3 Controller Transmit-Only Mode (Half Duplex)
- 12.1.5.3.3.4 Controller Receive-Only Mode (Half Duplex)
- 12.1.5.3.3.5 Single-Channel Controller Mode
- 12.1.5.3.3.6 Start-Bit Mode
- 12.1.5.3.3.7 Chip-Select Timing Control
- 12.1.5.3.3.8 Programmable MCSPI Clock (SPICLK)
- 12.1.5.3.4 MCSPI Peripheral Mode
- 12.1.5.3.5 MCSPI 3-Pin or 4-Pin Mode
- 12.1.5.3.6 MCSPI FIFO Buffer Management
- 12.1.5.3.7 MCSPI Interrupts
- 12.1.5.3.8 MCSPI DMA Requests
- 12.1.5.3.9 MCSPI Power Saving Management
- 12.1.5.4
MCSPI Programming Guide
- 12.1.5.4.1
MCSPI Operational Mode Configuration
- 12.1.5.4.1.1
MCSPI Operational Modes
- 12.1.5.4.1.1.1 Common Transfer Sequence
- 12.1.5.4.1.1.2 End of Transfer Sequences
- 12.1.5.4.1.1.3 Transmit-and-Receive (Controller and Peripheral)
- 12.1.5.4.1.1.4 Transmit-Only (Controller and Peripheral)
- 12.1.5.4.1.1.5 Controller Normal Receive-Only
- 12.1.5.4.1.1.6 Controller Turbo Receive-Only
- 12.1.5.4.1.1.7 Peripheral Receive-Only
- 12.1.5.4.1.1.8
Transfer Procedures With FIFO
- 12.1.5.4.1.1.8.1 Common Transfer Sequence in FIFO Mode
- 12.1.5.4.1.1.8.2 End of Transfer Sequences in FIFO Mode
- 12.1.5.4.1.1.8.3 Transmit-and-Receive With Word Count
- 12.1.5.4.1.1.8.4 Transmit-and-Receive Without Word Count
- 12.1.5.4.1.1.8.5 Transmit-Only
- 12.1.5.4.1.1.8.6 Receive-Only With Word Count
- 12.1.5.4.1.1.8.7 Receive-Only Without Word Count
- 12.1.5.4.1.1.9 Common Transfer Procedures Without FIFO – Polling Method
- 12.1.5.4.1.1
MCSPI Operational Modes
- 12.1.5.4.1
MCSPI Operational Mode Configuration
- 12.1.6
Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART)
- 12.1.6.1 UART Overview
- 12.1.6.2 UART Environment
- 12.1.6.3
UART Functional Description
- 12.1.6.3.1 UART Block Diagram
- 12.1.6.3.2 UART Clock Configuration
- 12.1.6.3.3 UART Software Reset
- 12.1.6.3.4 UART Power Management
- 12.1.6.3.5 UART Interrupt Requests
- 12.1.6.3.6 UART FIFO Management
- 12.1.6.3.7 UART Mode Selection
- 12.1.6.3.8
UART Protocol Formatting
- 12.1.6.3.8.1
UART Mode
- 12.1.6.3.8.1.1 UART Clock Generation: Baud Rate Generation
- 12.1.6.3.8.1.2 Choosing the Appropriate Divisor Value
- 12.1.6.3.8.1.3 UART Data Formatting
- 12.1.6.3.8.2 RS-485 Mode
- 12.1.6.3.8.3
IrDA Mode
- 12.1.6.3.8.3.1 IrDA Clock Generation: Baud Generator
- 12.1.6.3.8.3.2 Choosing the Appropriate Divisor Value
- 12.1.6.3.8.3.3
IrDA Data Formatting
- 12.1.6.3.8.3.3.1 IR RX Polarity Control
- 12.1.6.3.8.3.3.2 IrDA Reception Control
- 12.1.6.3.8.3.3.3 IR Address Checking
- 12.1.6.3.8.3.3.4 Frame Closing
- 12.1.6.3.8.3.3.5 Store and Controlled Transmission
- 12.1.6.3.8.3.3.6 Error Detection
- 12.1.6.3.8.3.3.7 Underrun During Transmission
- 12.1.6.3.8.3.3.8 Overrun During Receive
- 12.1.6.3.8.3.3.9 Status FIFO
- 12.1.6.3.8.3.3.10 Multi-drop Parity Mode with Address Match
- 12.1.6.3.8.3.3.11 Time-guard
- 12.1.6.3.8.3.4 SIR Mode Data Formatting
- 12.1.6.3.8.3.5 MIR and FIR Mode Data Formatting
- 12.1.6.3.8.4 CIR Mode
- 12.1.6.3.8.1
UART Mode
- 12.1.6.4 UART Programming Guide
- 12.1.1
Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
- 12.2
High-speed Serial Interfaces
- 12.2.1 Gigabit Ethernet MAC (CPSW)
- 12.2.2
Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe) Subsystem
- 12.2.2.1 PCIe Subsystem Overview
- 12.2.2.2 PCIe Environment
- 12.2.2.3
PCIe Subsystem Functional Description
- 12.2.2.3.1 PCIe Subsystem Block Diagram
- 12.2.2.3.2 PCIe Subsystem Reset Schemes
- 12.2.2.3.3 PCIe Subsystem Power Management
- 12.2.2.3.4
PCIe Subsystem Interrupts
- 12.2.2.3.4.1 Interrupts Aggregation
- 12.2.2.3.4.2 Interrupt Generation in EP Mode
- 12.2.2.3.4.3 Interrupt Reception in EP Mode
- 12.2.2.3.4.4 Interrupt Generation in RP Mode
- 12.2.2.3.4.5 Interrupt Reception in RP Mode
- 12.2.2.3.4.6 Common Interrupt Reception in RP and EP Modes
- 12.2.2.3.4.7 ECC Aggregator Interrupts
- 12.2.2.3.4.8 CPTS Interrupt
- 12.2.2.3.5 PCIe Subsystem DMA Support
- 12.2.2.3.6 PCIe Subsystem Transactions
- 12.2.2.3.7 PCIe Subsystem Address Translation
- 12.2.2.3.8 PCIe Subsystem Virtualization Support
- 12.2.2.3.9 PCIe Subsystem Quality-of-Service (QoS)
- 12.2.2.3.10 PCIe Subsystem Precision Time Measurement (PTM)
- 12.2.2.3.11 PCIe Subsystem Loopback
- 12.2.2.3.12 PCIe Subsystem Error Handling
- 12.2.2.3.13 PCIe Subsystem Internal Diagnostics Features
- 12.2.2.3.14 LTSSM State Encoding
- 12.2.3 Universal Serial Bus (USB) Subsystem
- 12.2.4 Serializer/Deserializer (SerDes)
- 12.3
Memory Interfaces
- 12.3.1 Flash Subsystem (FSS)
- 12.3.2
Octal Serial Peripheral Interface (OSPI)
- 12.3.2.1 OSPI Overview
- 12.3.2.2 OSPI Environment
- 12.3.2.3
OSPI Functional Description
- 12.3.2.3.1 OSPI Block Diagram
- 12.3.2.3.2 OSPI Modes
- 12.3.2.3.3 OSPI Power Management
- 12.3.2.3.4 Auto HW Polling
- 12.3.2.3.5 Flash Reset
- 12.3.2.3.6 OSPI Memory Regions
- 12.3.2.3.7 OSPI Interrupt Requests
- 12.3.2.3.8 OSPI Data Interface
- 12.3.2.3.9 OSPI Direct Access Controller (DAC)
- 12.3.2.3.10 OSPI Indirect Access Controller (INDAC)
- 12.3.2.3.11 OSPI Software-Triggered Instruction Generator (STIG)
- 12.3.2.3.12 OSPI Arbitration Between Direct / Indirect Access Controller and STIG
- 12.3.2.3.13 OSPI Command Translation
- 12.3.2.3.14 Selecting the Flash Instruction Type
- 12.3.2.3.15 OSPI Data Integrity
- 12.3.2.3.16 OSPI PHY Module
- 12.3.2.4
OSPI Programming Guide
- 12.3.2.4.1 Configuring the OSPI Controller for Use After Reset
- 12.3.2.4.2 Configuring the OSPI Controller for Optimal Use
- 12.3.2.4.3 Using the Flash Command Control Register (STIG Operation)
- 12.3.2.4.4 Using SPI Legacy Mode
- 12.3.2.4.5 Entering XIP Mode from POR
- 12.3.2.4.6 Entering XIP Mode Otherwise
- 12.3.2.4.7 Exiting XIP Mode
- 12.3.3 HyperBus Interface
- 12.3.4
General-Purpose Memory Controller (GPMC)
- 12.3.4.1 GPMC Overview
- 12.3.4.2 GPMC Environment
- 12.3.4.3
GPMC Functional Description
- 12.3.4.3.1 GPMC Block Diagram
- 12.3.4.3.2 GPMC Clock Configuration
- 12.3.4.3.3 GPMC Power Management
- 12.3.4.3.4 GPMC Interrupt Requests
- 12.3.4.3.5 GPMC Interconnect Port Interface
- 12.3.4.3.6 GPMC Address and Data Bus
- 12.3.4.3.7
GPMC Address Decoder and Chip-Select Configuration
- 12.3.4.3.7.1 Chip-Select Base Address and Region Size
- 12.3.4.3.7.2 Access Protocol
- 12.3.4.3.7.3
External Signals
- 12.3.4.3.7.3.1
WAIT Pin Monitoring Control
- 12.3.4.3.7.3.1.1 Wait Monitoring During Asynchronous Read Access
- 12.3.4.3.7.3.1.2 Wait Monitoring During Asynchronous Write Access
- 12.3.4.3.7.3.1.3 Wait Monitoring During Synchronous Read Access
- 12.3.4.3.7.3.1.4 Wait Monitoring During Synchronous Write Access
- 12.3.4.3.7.3.1.5 Wait With NAND Device
- 12.3.4.3.7.3.1.6 Idle Cycle Control Between Successive Accesses
- 12.3.4.3.7.3.1.7 Slow Device Support (TIMEPARAGRANULARITY Parameter)
- 12.3.4.3.7.3.2 DIR Pin
- 12.3.4.3.7.3.3 Reset
- 12.3.4.3.7.3.4 Write Protect Signal (nWP)
- 12.3.4.3.7.3.5 Byte Enable (nBE1/nBE0)
- 12.3.4.3.7.3.1
WAIT Pin Monitoring Control
- 12.3.4.3.7.4 Error Handling
- 12.3.4.3.8
GPMC Timing Setting
- 12.3.4.3.8.1 Read Cycle Time and Write Cycle Time (RDCYCLETIME / WRCYCLETIME)
- 12.3.4.3.8.2 nCS: Chip-Select Signal Control Assertion/Deassertion Time (CSONTIME / CSRDOFFTIME / CSWROFFTIME / CSEXTRADELAY)
- 12.3.4.3.8.3 nADV/ALE: Address Valid/Address Latch Enable Signal Control Assertion/Deassertion Time (ADVONTIME / ADVRDOFFTIME / ADVWROFFTIME / ADVEXTRADELAY/ADVAADMUXONTIME/ADVAADMUXRDOFFTIME/ADVAADMUXWROFFTIME)
- 12.3.4.3.8.4 nOE/nRE: Output Enable/Read Enable Signal Control Assertion/Deassertion Time (OEONTIME / OEOFFTIME / OEEXTRADELAY / OEAADMUXONTIME / OEAADMUXOFFTIME)
- 12.3.4.3.8.5 nWE: Write Enable Signal Control Assertion/Deassertion Time (WEONTIME / WEOFFTIME / WEEXTRADELAY)
- 12.3.4.3.8.6 GPMC_CLKOUT
- 12.3.4.3.8.7 GPMC Output Clock and Control Signals Setup and Hold
- 12.3.4.3.8.8 Access Time (RDACCESSTIME / WRACCESSTIME)
- 12.3.4.3.8.9 Page Burst Access Time (PAGEBURSTACCESSTIME)
- 12.3.4.3.8.10 Bus Keeping Support
- 12.3.4.3.9
GPMC NOR Access Description
- 12.3.4.3.9.1 Asynchronous Access Description
- 12.3.4.3.9.2 Synchronous Access Description
- 12.3.4.3.9.3
Asynchronous and Synchronous Accesses in non-multiplexed Mode
- 12.3.4.3.9.3.1 Asynchronous Single-Read Operation on non-multiplexed Device
- 12.3.4.3.9.3.2 Asynchronous Single-Write Operation on non-multiplexed Device
- 12.3.4.3.9.3.3 Asynchronous Multiple (Page Mode) Read Operation on non-multiplexed Device
- 12.3.4.3.9.3.4 Synchronous Operations on a non-multiplexed Device
- 12.3.4.3.9.4 Page and Burst Support
- 12.3.4.3.9.5 System Burst vs External Device Burst Support
- 12.3.4.3.10 GPMC pSRAM Access Specificities
- 12.3.4.3.11
GPMC NAND Access Description
- 12.3.4.3.11.1
NAND Memory Device in Byte or 16-bit Word Stream Mode
- 12.3.4.3.11.1.1 Chip-Select Configuration for NAND Interfacing in Byte or Word Stream Mode
- 12.3.4.3.11.1.2 NAND Device Command and Address Phase Control
- 12.3.4.3.11.1.3 Command Latch Cycle
- 12.3.4.3.11.1.4 Address Latch Cycle
- 12.3.4.3.11.1.5 NAND Device Data Read and Write Phase Control in Stream Mode
- 12.3.4.3.11.1.6 NAND Device General Chip-Select Timing Control Requirement
- 12.3.4.3.11.1.7 Read and Write Access Size Adaptation
- 12.3.4.3.11.2 NAND Device-Ready Pin
- 12.3.4.3.11.3
ECC Calculator
- 12.3.4.3.11.3.1 Hamming Code
- 12.3.4.3.11.3.2
BCH Code
- 12.3.4.3.11.3.2.1 Requirements
- 12.3.4.3.11.3.2.2
Memory Mapping of BCH Codeword
- 3.4.3.11.3.2.2.1 Memory Mapping of Data Message
- 3.4.3.11.3.2.2.2 Memory-Mapping of the ECC
- 3.4.3.11.3.2.2.3
Wrapping Modes
- 4.3.11.3.2.2.3.1 Manual Mode (0x0)
- 4.3.11.3.2.2.3.2 Mode 0x1
- 4.3.11.3.2.2.3.3 Mode 0xA (10)
- 4.3.11.3.2.2.3.4 Mode 0x2
- 4.3.11.3.2.2.3.5 Mode 0x3
- 4.3.11.3.2.2.3.6 Mode 0x7
- 4.3.11.3.2.2.3.7 Mode 0x8
- 4.3.11.3.2.2.3.8 Mode 0x4
- 4.3.11.3.2.2.3.9 Mode 0x9
- 4.3.11.3.2.2.3.10 Mode 0x5
- 4.3.11.3.2.2.3.11 Mode 0xB (11)
- 4.3.11.3.2.2.3.12 Mode 0x6
- 12.3.4.3.11.3.2.3 Supported NAND Page Mappings and ECC Schemes
- 12.3.4.3.11.4
Prefetch and Write-Posting Engine
- 12.3.4.3.11.4.1 General Facts About the Engine Configuration
- 12.3.4.3.11.4.2 Prefetch Mode
- 12.3.4.3.11.4.3 FIFO Control in Prefetch Mode
- 12.3.4.3.11.4.4 Write-Posting Mode
- 12.3.4.3.11.4.5 FIFO Control in Write-Posting Mode
- 12.3.4.3.11.4.6 Optimizing NAND Access Using the Prefetch and Write-Posting Engine
- 12.3.4.3.11.4.7 Interleaved Accesses Between Prefetch and Write-Posting Engine and Other Chip-Selects
- 12.3.4.3.11.1
NAND Memory Device in Byte or 16-bit Word Stream Mode
- 12.3.4.3.12 GPMC Use Cases and Tips
- 12.3.4.4 GPMC Basic Programming Model
- 12.3.5 Error Location Module (ELM)
- 12.3.6
Multi-Media Card Secure Digital (MMCSD) Interface
- 12.3.6.1 MMCSD Overview
- 12.3.6.2 MMCSD Environment
- 12.3.6.3
MMCSD Functional Description
- 12.3.6.3.1 Block Diagram
- 12.3.6.3.2 Memory Regions
- 12.3.6.3.3 Interrupt Requests
- 12.3.6.3.4 ECC Support
- 12.3.6.3.5 Advanced DMA
- 12.3.6.3.6
eMMC PHY BIST
- 12.3.6.3.6.1 BIST Overview
- 12.3.6.3.6.2
BIST Modes
- 12.3.6.3.6.2.1 DS Mode
- 12.3.6.3.6.2.2 HS Mode with TXDLY using DLL
- 12.3.6.3.6.2.3 HS Mode with TXDLY using Delay Chain
- 12.3.6.3.6.2.4 DDR50 Mode with TXDLY using DLL
- 12.3.6.3.6.2.5 DDR50 Mode with TXDLY using Delay Chain
- 12.3.6.3.6.2.6 HS200 Mode with TX/RXDLY using DLL
- 12.3.6.3.6.2.7 HS200 Mode with TX/RXDLY using Delay Chain
- 12.3.6.3.6.2.8 HS400 Mode
- 12.3.6.3.6.3 BIST Functionality
- 12.3.6.3.6.4 Signal Interface
- 12.3.6.3.6.5 Programming Flow
- 12.3.6.3.6.6 HS200 BIST Result Check Procedure
- 12.3.6.4
MMCSD Programming Guide
- 12.3.6.4.1
Sequences
- 12.3.6.4.1.1 SD Card Detection
- 12.3.6.4.1.2 SD Clock Control
- 12.3.6.4.1.3 SD Bus Power Control
- 12.3.6.4.1.4 Changing Bus Width
- 12.3.6.4.1.5 Timeout Setting on DAT Line
- 12.3.6.4.1.6 Card Initialization and Identification (for SD I/F)
- 12.3.6.4.1.7 SD Transaction Generation
- 12.3.6.4.1.8 Abort Transaction
- 12.3.6.4.1.9 Changing Bus Speed Mode
- 12.3.6.4.1.10 Error Recovery
- 12.3.6.4.1.11 Wakeup Control (Optional)
- 12.3.6.4.1.12 Suspend/Resume (Optional, Not Supported from Version 4.00)
- 12.3.6.4.2 Driver Flow Sequence
- 12.3.6.4.1
Sequences
- 12.4
Industrial and Control Interfaces
- 12.4.1
Enhanced Capture (ECAP) Module
- 12.4.1.1 ECAP Overview
- 12.4.1.2 ECAP Environment
- 12.4.1.3
ECAP Functional Description
- 12.4.1.3.1
Capture and APWM Operating Modes
- 12.4.1.3.1.1
ECAP Capture Mode Description
- 12.4.1.3.1.1.1 ECAP Event Prescaler
- 12.4.1.3.1.1.2 ECAP Edge Polarity Select and Qualifier
- 12.4.1.3.1.1.3 ECAP Continuous/One-Shot Control
- 12.4.1.3.1.1.4 ECAP 32-Bit Counter and Phase Control
- 12.4.1.3.1.1.5 CAP1-CAP4 Registers
- 12.4.1.3.1.1.6 ECAP Interrupt Control
- 12.4.1.3.1.1.7 ECAP Shadow Load and Lockout Control
- 12.4.1.3.1.2 ECAP APWM Mode Operation
- 12.4.1.3.1.1
ECAP Capture Mode Description
- 12.4.1.3.2 Summary of ECAP Functional Registers
- 12.4.1.3.1
Capture and APWM Operating Modes
- 12.4.1.4
ECAP Use Cases
- 12.4.1.4.1 Absolute Time-Stamp Operation Rising Edge Trigger Example
- 12.4.1.4.2 Absolute Time-Stamp Operation Rising and Falling Edge Trigger Example
- 12.4.1.4.3 Time Difference (Delta) Operation Rising Edge Trigger Example
- 12.4.1.4.4 Time Difference (Delta) Operation Rising and Falling Edge Trigger Example
- 12.4.1.4.5 Application of the APWM Mode
- 12.4.2
Enhanced Pulse Width Modulation (EPWM) Module
- 12.4.2.1 EPWM Overview
- 12.4.2.2 ECAP Environment
- 12.4.2.3
EPWM Functional Description
- 12.4.2.3.1 EPWM Submodule Features
- 12.4.2.3.2 EPWM Time-Base (TB) Submodule
- 12.4.2.3.3 EPWM Counter-Compare (CC) Submodule
- 12.4.2.3.4 EPWM Action-Qualifier (AQ) Submodule
- 12.4.2.3.5 EPWM Dead-Band Generator (DB) Submodule
- 12.4.2.3.6 EPWM-Chopper (PC) Submodule
- 12.4.2.3.7 EPWM Trip-Zone (TZ) Submodule
- 12.4.2.3.8 EPWM Event-Trigger (ET) Submodule
- 12.4.2.3.9 EPWM High Resolution (HRPWM) Submodule
- 12.4.2.3.10 EPWM / HRPWM Functional Register Groups
- 12.4.2.3.11 Proper EPWM Interrupt Initialization Procedure
- 12.4.3
Enhanced Quadrature Encoder Pulse (EQEP) Module
- 12.4.3.1 EQEP Overview
- 12.4.3.2 EQEP Environment
- 12.4.3.3
EQEP Functional Description
- 12.4.3.3.1 EQEP Inputs
- 12.4.3.3.2 EQEP Quadrature Decoder Unit (QDU)
- 12.4.3.3.3
EQEP Position Counter and Control Unit (PCCU)
- 12.4.3.3.3.1
EQEP Position Counter Operating Modes
- 12.4.3.3.3.1.1 EQEP Position Counter Reset on Index Event (EQEP_QDEC_QEP_CTL[29-28] PCRM] = 0b00)
- 12.4.3.3.3.1.2 EQEP Position Counter Reset on Maximum Position (EQEP_QDEC_QEP_CTL[29-28] PCRM=0b01)
- 12.4.3.3.3.1.3 Position Counter Reset on the First Index Event (EQEP_QDEC_QEP_CTL[29-28] PCRM = 0b10)
- 12.4.3.3.3.1.4 Position Counter Reset on Unit Time out Event (EQEP_QDEC_QEP_CTL[29-28] PCRM = 0b11)
- 12.4.3.3.3.2 EQEP Position Counter Latch
- 12.4.3.3.3.3 EQEP Position Counter Initialization
- 12.4.3.3.3.4 EQEP Position-Compare Unit
- 12.4.3.3.3.1
EQEP Position Counter Operating Modes
- 12.4.3.3.4 EQEP Edge Capture Unit
- 12.4.3.3.5 EQEP Watchdog
- 12.4.3.3.6 Unit Timer Base
- 12.4.3.3.7 EQEP Interrupt Structure
- 12.4.3.3.8 Summary of EQEP Functional Registers
- 12.4.4
Controller Area Network (MCAN)
- 12.4.4.1 MCAN Overview
- 12.4.4.2 MCAN Environment
- 12.4.4.3
MCAN Functional Description
- 12.4.4.3.1 Module Clocking Requirements
- 12.4.4.3.2 Interrupt and DMA Requests
- 12.4.4.3.3
Operating Modes
- 12.4.4.3.3.1 Software Initialization
- 12.4.4.3.3.2 Normal Operation
- 12.4.4.3.3.3 CAN FD Operation
- 12.4.4.3.3.4 Transmitter Delay Compensation
- 12.4.4.3.3.5 Restricted Operation Mode
- 12.4.4.3.3.6 Bus Monitoring Mode
- 12.4.4.3.3.7 Disabled Automatic Retransmission (DAR) Mode
- 12.4.4.3.3.8 Power Down (Sleep Mode)
- 12.4.4.3.3.9 Test Modes
- 12.4.4.3.4 Timestamp Generation
- 12.4.4.3.5 Timeout Counter
- 12.4.4.3.6 ECC Support
- 12.4.4.3.7 Rx Handling
- 12.4.4.3.8 Tx Handling
- 12.4.4.3.9 FIFO Acknowledge Handling
- 12.4.4.3.10 Message RAM
- 12.4.1
Enhanced Capture (ECAP) Module
- 12.5
Audio Interfaces
- 12.5.1 Audio Tracking Logic (ATL)
- 12.5.2
Multichannel Audio Serial Port (MCASP)
- 12.5.2.1 MCASP Overview
- 12.5.2.2 MCASP Environment
- 12.5.2.3
MCASP Functional Description
- 12.5.2.3.1 MCASP Block Diagram
- 12.5.2.3.2 MCASP Clock and Frame-Sync Configurations
- 12.5.2.3.3 MCASP Frame Sync Feedback for Cross Synchronization
- 12.5.2.3.4 MCASP Serializers
- 12.5.2.3.5 MCASP Format Units
- 12.5.2.3.6 MCASP State-Machines
- 12.5.2.3.7 MCASP TDM Sequencers
- 12.5.2.3.8 MCASP Software Reset
- 12.5.2.3.9 MCASP Power Management
- 12.5.2.3.10 MCASP Transfer Modes
- 12.5.2.3.11 MCASP Data Transmission and Reception
- 12.5.2.3.12 MCASP Audio FIFO (AFIFO)
- 12.5.2.3.13 MCASP Events and Interrupt Requests
- 12.5.2.3.14 MCASP DMA Requests
- 12.5.2.3.15 MCASP Loopback Modes
- 12.5.2.3.16 MCASP Error Reporting
- 12.5.2.4 MCASP Programming Guide
- 12.6
Display Subsystem (DSS) and Peripherals
- 12.6.1 DSS Overview
- 12.6.2 DSS Environment
- 12.6.3
Display Subsystem Controller (DISPC) with Frame Buffer Decompression Core (FBDC)
- 12.6.3.1 DISPC Overview
- 12.6.3.2 DISPC Clocks
- 12.6.3.3 DISPC Resets
- 12.6.3.4 DISPC Power Management
- 12.6.3.5 DISPC Interrupt Requests
- 12.6.3.6
DISPC DMA Controller
- 12.6.3.6.1 DISPC DMA Addressing and Bursts
- 12.6.3.6.2 DISPC Read DMA Buffers
- 12.6.3.6.3 DISPC Write DMA Buffer
- 12.6.3.6.4 DISPC Flip/Mirror Support
- 12.6.3.6.5 DISPC DMA Predecimation
- 12.6.3.6.6 DISPC DMA Buffer Sharing
- 12.6.3.6.7 DISPC DMA MFLAG Mechanism
- 12.6.3.6.8 DISPC DMA Priority Requests Control
- 12.6.3.6.9 DISPC DMA Arbitration
- 12.6.3.6.10 DISPC DMA Ultra-Low Power Mode
- 12.6.3.6.11 DISPC Compressed Data Format Support
- 12.6.3.7 DISPC Pixel Data Formats
- 12.6.3.8
DISPC Video Pipeline
- 12.6.3.8.1 DISPC VID Replication Logic
- 12.6.3.8.2 DISPC VID VC-1 Range Mapping Unit
- 12.6.3.8.3 DISPC VID Color Look-Up Table (CLUT)
- 12.6.3.8.4 DISPC VID Chrominance Resampling
- 12.6.3.8.5 DISPC VID Scaler Unit
- 12.6.3.8.6 DISPC VID Color Space Conversion YUV to RGB
- 12.6.3.8.7 DISPC VID Brightness/Contrast/Saturation/Hue Control
- 12.6.3.8.8 DISPC VID Luma Key Support
- 12.6.3.8.9 DISPC VID Cropping Support
- 12.6.3.9 DISPC Write-Back Pipeline
- 12.6.3.10 DISPC Overlay Manager
- 12.6.3.11
DISPC Video Port Output
- 12.6.3.11.1 DISPC VP Gamma Correction Unit
- 12.6.3.11.2 DISPC VP Color Phase Rotation Unit
- 12.6.3.11.3 DISPC VP Color Space Conversion - RGB to YUV
- 12.6.3.11.4 DISPC VP BT.656 and BT.1120 Modes
- 12.6.3.11.5 DISPC VP Spatial/Temporal Dithering
- 12.6.3.11.6 DISPC VP Multiple Cycle Output Format (TDM)
- 12.6.3.11.7 DISPC VP Stall Mode
- 12.6.3.11.8 DISPC VP Timing Generator and Display Panel Settings
- 12.6.3.11.9 DISPC VP Merge-Split-Sync (MSS) Module
- 12.6.3.12 DISPC Internal Diagnostic Features
- 12.6.3.13 DISPC Security Management
- 12.6.3.14 DISPC Resources Sharing
- 12.6.3.15 DISPC Shadow Mechanism for Registers
- 12.6.4
MIPI Display Serial Interface (DSI) Controller
- 12.6.4.1 DSI Block Diagram
- 12.6.4.2 DSI Clocking
- 12.6.4.3 DSI Reset
- 12.6.4.4 DSI Power Management
- 12.6.4.5 DSI Interrupts
- 12.6.4.6 DSI Internal Interfaces
- 12.6.4.7
DSI Programming Guide
- 12.6.4.7.1 Application Guidelines
- 12.6.4.7.2 Application Considerations
- 12.6.4.7.3 Start-up Procedure
- 12.6.4.7.4 Interrupt Management
- 12.6.4.7.5
Direct Command Usage
- 12.6.4.7.5.1 Trigger Mapping Information
- 12.6.4.7.5.2 Command Mode Settings
- 12.6.4.7.5.3 Bus Turnaround Sequence
- 12.6.4.7.5.4 Tearing Effect Control
- 12.6.4.7.5.5 Tearing Effect Control on Panels with Frame Buffer
- 12.6.4.7.5.6 Return Path Operation
- 12.6.4.7.5.7 EoT Packet Management
- 12.6.4.7.5.8 ECC Correction
- 12.6.4.7.5.9 LP Transmission and BTA
- 12.6.4.7.6 Low-power Management
- 12.6.4.7.7 Video Mode Settings
- 12.6.4.7.8 DPI To DSI Programming
- 12.6.4.7.9 Programming the DSITX Controller to Match the Incoming DPI Stream
- 12.6.4.7.10 DSITX Video Stream Variable Refresh
- 12.6.5
Embedded DisplayPort (еDP) Transmitter
- 12.6.5.1 EDP Block Diagram
- 12.6.5.2 EDP Wrapper Functions
- 12.6.5.3 EDP Transmitter Controller Subsystem (MHDPTX_TOP)
- 12.6.5.4 EDP AUX_PHY Interface
- 12.6.5.5 EDP Clocks
- 12.6.5.6 EDP Resets
- 12.6.5.7 EDP Interrupt Requests
- 12.6.5.8 EDP Embedded Memories
- 12.6.5.9
EDP Programmer's Guide
- 12.6.5.9.1
EDP Controller Programming
- 12.6.5.9.1.1 MHDPTX Register/Memory Regions
- 12.6.5.9.1.2 Boot Sequence
- 12.6.5.9.1.3 Setting Core Clock Frequency
- 12.6.5.9.1.4 Loading Firmware
- 12.6.5.9.1.5 FW Running indication
- 12.6.5.9.1.6 Software Events Handling
- 12.6.5.9.1.7 DisplayPort Source (TX) Sequence
- 12.6.5.9.1.8 HDCP
- 12.6.5.9.1.9 HD Display TX Controller
- 12.6.5.9.1.10 DPTX TX Controller
- 12.6.5.9.2 EDP PHY Wrapper Initialization
- 12.6.5.9.3 EDP PHY Programming
- 12.6.5.9.1
EDP Controller Programming
- 12.7
Camera Subsystem
- 12.7.1
Camera Streaming Interface Receiver (CSI_RX_IF)
- 12.7.1.1 CSI_RX_IF Overview
- 12.7.1.2 CSI_RX_IF Environment
- 12.7.1.3
CSI_RX_IF Functional Description
- 12.7.1.3.1 CSI_RX_IF Block Diagram
- 12.7.1.3.2 CSI_RX_IF Hardware and Software Reset
- 12.7.1.3.3 CSI_RX_IF Clock Configuration
- 12.7.1.3.4 CSI_RX_IF Interrupt Events
- 12.7.1.3.5 CSI_RX_IF Data Memory Organization Details
- 12.7.1.3.6 CSI_RX_IF PSI_L (DMA) Interface
- 12.7.1.3.7 CSI_RX_IF ECC Protection Support
- 12.7.1.3.8
CSI_RX_IF Programming Guide
- 12.7.1.3.8.1 Overview
- 12.7.1.3.8.2 Controller Configuration
- 12.7.1.3.8.3 Power on Configuration
- 12.7.1.3.8.4 Stream Start and Stop
- 12.7.1.3.8.5 Error Control With Soft Resets
- 12.7.1.3.8.6 Stream Error Detected – No Error Bypass Mode
- 12.7.1.3.8.7 Stream Error Detected – Error Bypass Mode
- 12.7.1.3.8.8 Stream Error Detected – Soft Reset Recovery
- 12.7.1.3.8.9 Stream Monitor Configuration
- 12.7.1.3.8.10 Stream Monitor Frame Capture Control
- 12.7.1.3.8.11 Stream Monitor Timer interrupt
- 12.7.1.3.8.12 Stream Monitor Line/Byte Counters Interrupt
- 12.7.1.3.8.13 Example Controller Programming Sequence (Single Stream Operation)
- 12.7.1.3.8.14 CSI_RX_IF Programming Restrictions
- 12.7.1.3.8.15 CSI_RX_IF Real-time operating requirements
- 12.7.2
MIPI D-PHY Receiver (DPHY_RX)
- 12.7.2.1 DPHY_RX Overview
- 12.7.2.2 DPHY_RX Environment
- 12.7.2.3
DPHY_RX Functional Description
- 12.7.2.3.1
DPHY_RX Programming Guide
- 12.7.2.3.1.1 Overview
- 12.7.2.3.1.2 Initial Configuration Programming
- 12.7.2.3.1.3 Common Configuration
- 12.7.2.3.1.4 Lane Configuration
- 12.7.2.3.1.5 Procedure: Clock Lane Low Power Analog Receiver Functions Test
- 12.7.2.3.1.6 Procedure: Data Lane Low Power Analog Receiver Functions Test
- 12.7.2.3.1.7 Procedure: Clock and Data Lane High Speed Receiver BIST Functions Test
- 12.7.2.3.1
DPHY_RX Programming Guide
- 12.7.3
Camera Streaming Interface Transmitter (CSI_TX_IF)
- 12.7.3.1 CSI_TX_IF Overview
- 12.7.3.2 CSI_TX_IF Features
- 12.7.3.3 CSI_TX_IF Environment
- 12.7.3.4
CSI_TX_IF Functional Description
- 12.7.3.4.1 CSI_TX_IF Block Diagram
- 12.7.3.4.2 CSI_TX_IF Hardware and Software Reset
- 12.7.3.4.3 CSI_TX_IF Clock Configuration
- 12.7.3.4.4 CSI_TX_IF Interrupt Events
- 12.7.3.4.5 CSI_TX_IF Data Memory Organization Details
- 12.7.3.4.6 CSI_TX_IF PSI_L (DMA) Interface
- 12.7.3.4.7 CSI_TX_IF ECC Protection Support
- 12.7.3.5
CSI_TX_IF Programming Guide
- 12.7.3.5.1 CSI_TX_IF Programming (Configuration Mode)
- 12.7.3.5.2 CSI_TX_IF System Initialization Programming
- 12.7.3.5.3 CSI_TX_IF Lane Control Programming
- 12.7.3.5.4 CSI_TX_IF Virtual Channel and Data Type Management
- 12.7.3.5.5 CSI_TX_IF Line Control
- 12.7.3.5.6 CSI_TX_IF Lane Manager FSM
- 12.7.3.5.7 CSI_TX_IF Data Lane Control FSM
- 12.7.3.5.8 CSI_TX_IF Application Examples
- 12.7.3.5.9 CSI_TX_IF DPHY_TX Status
- 12.7.3.5.10 CSI_TX_IF ULPS Operation
- 12.7.3.5.11 CSI_TX_IF System Frame Rate Measurement
- 12.7.3.5.12 CSI_TX_IF Configuration for PSI_L
- 12.7.3.5.13 CSI_TX_IF Configuration for Color Bar
- 12.7.3.5.14 CSI_TX_IF Error Recovery
- 12.7.3.5.15 CSI_TX_IF Power up/down Sequence
- 12.7.1
Camera Streaming Interface Receiver (CSI_RX_IF)
- 12.8 Shared MIPI D-PHY Transmitter (DPHY_TX)
- 12.9
Timer Modules
- 12.9.1 Global Timebase Counter (GTC)
- 12.9.2 Windowed Watchdog Timer (WWDT)
- 12.9.3
Timers
- 12.9.3.1 Timers Overview
- 12.9.3.2 Timers Environment
- 12.9.3.3
Timers Functional Description
- 12.9.3.3.1 Timer Block Diagram
- 12.9.3.3.2 Timer Power Management
- 12.9.3.3.3 Timer Software Reset
- 12.9.3.3.4 Timer Interrupts
- 12.9.3.3.5 Timer Mode Functionality
- 12.9.3.3.6 Timer Capture Mode Functionality
- 12.9.3.3.7 Timer Compare Mode Functionality
- 12.9.3.3.8 Timer Prescaler Functionality
- 12.9.3.3.9 Timer Pulse-Width Modulation
- 12.9.3.3.10 Timer Counting Rate
- 12.9.3.3.11 Timer Under Emulation
- 12.9.3.3.12 Accessing Timer Registers
- 12.9.3.3.13 Timer Posted Mode Selection
- 12.9.3.4 Timers Low-Level Programming Models
- 12.10
Internal Diagnostics Modules
- 12.10.1
Dual Clock Comparator (DCC)
- 12.10.1.1 DCC Overview
- 12.10.1.2
DCC Functional Description
- 12.10.1.2.1 DCC Counter Operation
- 12.10.1.2.2 DCC Low Power Mode Operation
- 12.10.1.2.3 DCC Suspend Mode Behavior
- 12.10.1.2.4 DCC Single-Shot Mode
- 12.10.1.2.5 DCC Continuous mode
- 12.10.1.2.6 DCC Control and count hand-off across clock domains
- 12.10.1.2.7 DCC Error Trajectory record
- 12.10.1.2.8 DCC Count read registers
- 12.10.2
Error Signaling Module (ESM)
- 12.10.2.1 ESM Overview
- 12.10.2.2 ESM Environment
- 12.10.2.3
ESM Functional Description
- 12.10.2.3.1 ESM Interrupt Requests
- 12.10.2.3.2 ESM Error Event Inputs
- 12.10.2.3.3 ESM Error Pin Output
- 12.10.2.3.4 PWM Mode
- 12.10.2.3.5 ESM Minimum Time Interval
- 12.10.2.3.6 ESM Protection for Registers
- 12.10.2.3.7 ESM Clock Stop
- 12.10.3
Memory Cyclic Redundancy Check (MCRC) Controller
- 12.10.3.1 MCRC Overview
- 12.10.3.2
MCRC Functional Description
- 12.10.3.2.1 MCRC Block Diagram
- 12.10.3.2.2 MCRC General Operation
- 12.10.3.2.3 MCRC Modes of Operation
- 12.10.3.2.4 PSA Signature Register
- 12.10.3.2.5 PSA Sector Signature Register
- 12.10.3.2.6 CRC Value Register
- 12.10.3.2.7 Raw Data Register
- 12.10.3.2.8 Example DMA Controller Setup
- 12.10.3.2.9 Pattern Count Register
- 12.10.3.2.10 Sector Count Register/Current Sector Register
- 12.10.3.2.11 Interrupts
- 12.10.3.2.12 Power Down Mode
- 12.10.3.2.13 Emulation
- 12.10.3.3 MCRC Programming Examples
- 12.10.4
ECC Aggregator
- 12.10.4.1 ECC Aggregator Overview
- 12.10.4.2
ECC Aggregator Functional Description
- 12.10.4.2.1 ECC Aggregator Block Diagram
- 12.10.4.2.2 ECC Aggregator Register Groups
- 12.10.4.2.3 Read Access to the ECC Control and Status Registers
- 12.10.4.2.4 Serial Write Operation
- 12.10.4.2.5 Interrupts
- 12.10.4.2.6 Inject Only Mode
- 12.10.4.2.7 ECC Error Injection Sequence
- 12.10.4.3 ECC Aggregator Registers
- 12.10.1
Dual Clock Comparator (DCC)
- 12.1
General Connectivity Peripherals
- 13On-Chip Debug
- 14Revision History
A time-base synchronization scheme connects all of the EPWM modules on a device. Each EPWM module has a synchronization input (EPWMxSYNCI) and a synchronization output (EPWMxSYNCO). The input synchronization for the first instance (EPWM0) comes from an external pin. For the device EPWM environment sync pin details refer to EPWM Environment. The possible synchronization connections for the remaining EPWM modules is shown in Figure 12-180.
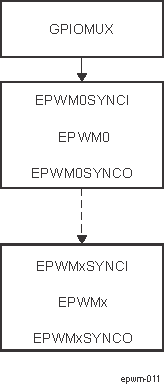 Figure 12-180 EPWM Time-Base Counter Synchronization Scheme 1
Figure 12-180 EPWM Time-Base Counter Synchronization Scheme 1Each EPWM module can be configured to use or ignore the synchronization input. If the EPWM_TBCTL[2] PHSEN bit is set, then the time-base counter (TBCNT) of the EPWM module (EPWM_TBCNT register) will be automatically loaded with the phase register (EPWM_TBPHS) contents when one of the following conditions occur:
- EPWMxSYNCI: Synchronization Input Pulse: The value of the phase register is loaded into the counter register when an input synchronization pulse is detected (EPWM_TBPHS → EPWM_TBCNT). This operation occurs on the next valid time-base clock (TBCLK) edge.
- Software Forced Synchronization Pulse: Writing a 1h to the EPWM_TBCTL[6] SWFSYNC control bit invokes a software forced synchronization. This pulse is ORed with the synchronization input signal, and therefore has the same effect as a pulse on EPWMxSYNCI.
This feature enables the EPWM module to be automatically synchronized to the time base of another EPWM module. Lead or lag phase control can be added to the waveforms generated by different EPWM modules to synchronize them. In up-down-count mode, the EPWM_TBCTL[13] PHSDIR bit configures the direction of the time-base counter immediately after a synchronization event. The new direction is independent of the direction prior to the synchronization event. The TBPHS bit is ignored in count-up or count-down modes. See Figure 12-181 through Figure 12-184 for examples.
Clearing the EPWM_TBCTL[2] PHSEN bit configures the EPWM to ignore the synchronization input pulse. The synchronization pulse can still be allowed to flow-through to the EPWMxSYNCO and be used to synchronize other EPWM modules. In this way, a controller time-base (for example, EPWM1) and downstream modules (EPWM2–EPWMx) can be set and they may select to run in synchronization with the controller.