SPRUJ93 august 2023
- 1
- Description
- Features
- 4
- 1Evaluation Module Overview
-
2Hardware
- 2.1 Functional Block Diagram
- 2.2 Component Identification
- 2.3 Power Requirements
- 2.4 Reset
- 2.5 Clock
- 2.6 Boot Mode Selection
- 2.7 JTAG Path Selection
- 2.8 Header Information
- 2.9 GPIO Mapping
- 2.10 Push Buttons
- 2.11 Test Points
- 2.12 Interfaces
- 2.13 HSEC Pinout and Pinmux Mapping
- 3Software
- 4Hardware Design Files
- 5Additional Information
- 6References
2.6 Boot Mode Selection
The bootmode for the AM263x is selected by either the DIP switch (SW3) or the test automation header. The test automation header uses an I2C IO expansion buffer to drive the bootmode when PORz is toggled. The supported boot modes are as shown in Supported Boot Modes.
Table 2-4 Supported Boot Modes
| Boot Mode/Peripheral | Boot Media/Host | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| QSPI (4S) - Quad Read Mode | QSPI Flash | Download and boot SBL from QSPI flash in quad read mode. Attempt Primary SBL, followed by Secondary SBL if primary loading fails. |
| UART | External Host | Download and boot SBL from UART. Device is expected to get SBL from UART. Device supports the XMODEM protocol for download over UART. |
| QSPI (1S) - Single Read Mode | QSPI Flash | Download and boot SBL from QSPI flash in single read mode. Attempt Primary SBL, followed by Secondary SBL if primary loading fails. |
| QSPI (4S) - Quad Read UART Fallback Mode | QSPI Flash / External Host | Download and boot SBL from QSPI flash in quad read mode. Attempt Primary SBL, followed by Secondary SBL if primary loading fails. If Secondary SBL also fails then boot from external host via UART interface. |
| QSPI (1S) - Single Read UART Fallback Mode | QSPI Flash / External Host | Download and boot SBL from QSPI flash in single read mode. Attempt Primary SBL, followed by Secondary SBL if primary loading fails. If Secondary SBL also fails then boot from external host via UART interface. |
| DevBoot | N/A | No SBL. Used for development purposes only. |
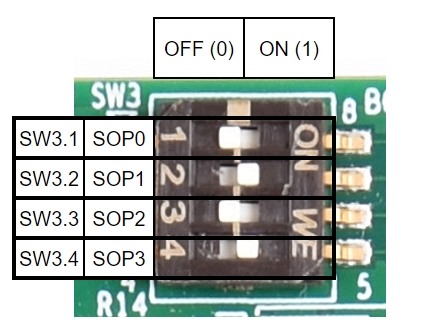 Figure 2-14 SW3 Switch Positions
Figure 2-14 SW3 Switch PositionsTable 2-5 Boot-Mode Selection
Table
| Boot Mode | SPI0_D0_pad (SOP3) | SPI0_CLK_pad (SOP2) | QSPI_D1 (SOP1) | QSPI_D0 (SOP0) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| QSPI (4S) - Quad Read Mode | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| UART | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| QSPI (1S) - Single Read Mode | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| QSPI (4S) - Quad Read UART Fallback Mode | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| QSPI (1S) - Single Read UART Fallback Mode | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| DevBoot | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Unsupported Boot Mode | All other combinations not defined above | |||