SPRZ457I January 2021 – December 2024 AM2431 , AM2432 , AM2434 , AM6411 , AM6412 , AM6421 , AM6422 , AM6441 , AM6442
- 1
- 1Usage Notes and Advisories Matrices
-
2Silicon Usage Notes and Advisories
- 2.1 Silicon Usage Notes
- 2.2
Silicon Advisories
- i2049
- i2062
- i2103
- i2184
- i2189
- i2236
- i2185
- i2196
- i2207
- i2208
- i2228
- i2232
- i2244
- i2245
- i2091
- i2235
- i2303
- i2317
- i2134
- i2257
- i2277
- i2285
- i2310
- i2311
- i2313
- i2328
- i2241
- i2279
- i2307
- i2320
- i2329
- i2331
- i2243
- i2249
- i2256
- i2274
- i2278
- i2306
- i2363
- i2312
- i2371
- i2366
- i2138
- i2253
- i2259
- i2283
- i2305
- i2326
- i2368
- i2383
- i2401
- i2409
- i2291
- i2413
- i2414
- i2415
- i2417
- i2418
- i2419
- i2420
- i2422
- i2423
- i2431
- i2433
- i2434
- i2435
- Trademarks
- Revision History
i2329
MDIO: MDIO interface corruption (CPSW and PRU-ICSS)
Details:
It is possible that the MDIO interface of all instances of CPSW and PRU-ICSS peripherals (if present) returns corrupt read data on MDIO reads (e.g. returning stale or previous data), or sends incorrect data on MDIO writes. It is also possible that the MDIO interface becomes unavailable until the next peripheral reset (either by LPSC reset or global device reset with reset isolation disabled in case of CPSW).
Possible system level manifestations of this issue could be (1) erroneous ethernet PHY link down status (2) inability to properly configure an ethernet PHY over MDIO (3) incorrect PHY detection (e.g. wrong address) (4) read or write timeouts when attempting to configure PHY over MDIO.
For boot mode (only CPSW if supported), there is no workaround to guarantee the primary ethernet boot is successful. If this exception occurs during primary boot, the boot may possibly initiate retries which may or may not be successful. If the retries are unsuccessful, this would result in an eventual timeout and transition to the backup boot mode (if one is selected). If no backup boot mode is selected, then such failure will result in a timeout and force device reset via chip watchdog after which the complete boot process will restart again.
To select a backup boot option (if supported), populate the appropriate pull resistors on the boot mode pins. See boot documentation for each specific device options, but the typical timeout for primary boot attempts over ethernet is 60 seconds.
Workaround(s):
On affected devices, following workaround should be used:
MDIO manual mode: applicable for PRU-ICSS and for CPSW.
MDIO protocol can be emulated by reading and writing to the appropriate bits within the MDIO_MANUAL_IF_REG register of the MDIO peripheral to directly manipulate the MDIO clock and data pins. Refer to TRM for full details of manual mode register bits and their function.
In this case the device pin multiplexing should be configured to allow the IO to be controlled by the CPSW or PRU-ICSS peripherals (same as in normal intended operation), but the MDIO state machine must be disabled by ensuring MDIO_CONTROL_REG.ENABLE bit is 0 in the MDIO_CONTROL_REG and enable manual mode by setting MDIO_POLL_REG.MANUALMODE bit to 1.
Contact TI regarding implementation of software workaround.
In case of PRU-ICSS, the loading of the software workaround may be reduced by using the MLINK feature of MDIO to do automatic polling of link status via the MIIx_RXLINK input pin to PRU-ICSS which must be connected to a status output from the external PHY which does not toggle while the link is active. Depending on the specified behavior of the external PHY device, this PHY status output may be LED_LINK or LED_SPEED or the logic OR of LED_LINK and LED SPEED. Refer to the MDIO section of TRM for details on using the MLINK feature of MDIO. This feature is not available on the CPSW peripheral.
For EtherCAT implementation on PRU-ICSS, the software workaround will be done in RTUx/ TX_PRUx Core. The core will have to be dedicated for workaround, which means this can’t be used for other purpose. The implementation will support two user access channels for MDIO access. This provides option for R5f core and PRU core to have independent access channel. The APIs will be similar to the ones we will have in RTOS Workaround implementation.
EtherCAT will continue to use PHY fast link detection via MDIO MLINK bypassing state m/c for link status (as this path is not affected by errata). This makes sure that cable redundancy related latency requirements are still met.
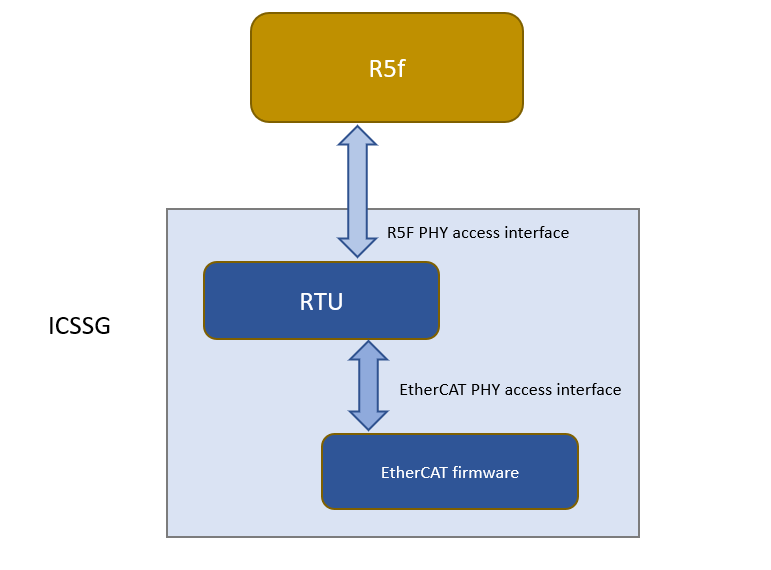 Figure 2-3 MDIO Emulation via Manual Mode using PRU Core
Figure 2-3 MDIO Emulation via Manual Mode using PRU Core