SSZT387 october 2019 TLV320AIC3104-Q1 , TLV320AIC3106-Q1 , TLV320AIC3109-Q1
In the cost-driven automotive industry, reducing bill-of-materials (BOM) costs by sharing resources across multiple subsystems (when possible) can give manufacturers an edge. Traditional automotive end-equipments often use independent hardware to control specific functions of the car, and chances to combine functions may be overlooked.
Sharing microphones between different automotive audio subsystems not only saves automakers the cost of a microphone – it eliminates the cost associated with microphone plastic enclosures, wiring and installation. These costs likely outweigh the cost of a microphone or a codec. In this article, I’ll discuss an effective way to share hands-free voice command recognition and eCall microphones using TI’s automotive-grade TLV320AIC3109-Q1, TLV320AIC3104-Q1 and TLV320AIC3106-Q1 audio codecs.
A typical application of microphones in vehicles
As shown in Figure 1-1, a typical telematics system with eCall has one dedicated microphone for direct audio communication between the car and local emergency services in an emergency. The microphone signal is digitized using an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) inside a codec, and is eventually transmitted to emergency operators through a connectivity module.
Therefore, most vehicles use at least two dedicated microphones: one for eCall applications and another for voice command recognition and hands-free telecommunication applications.
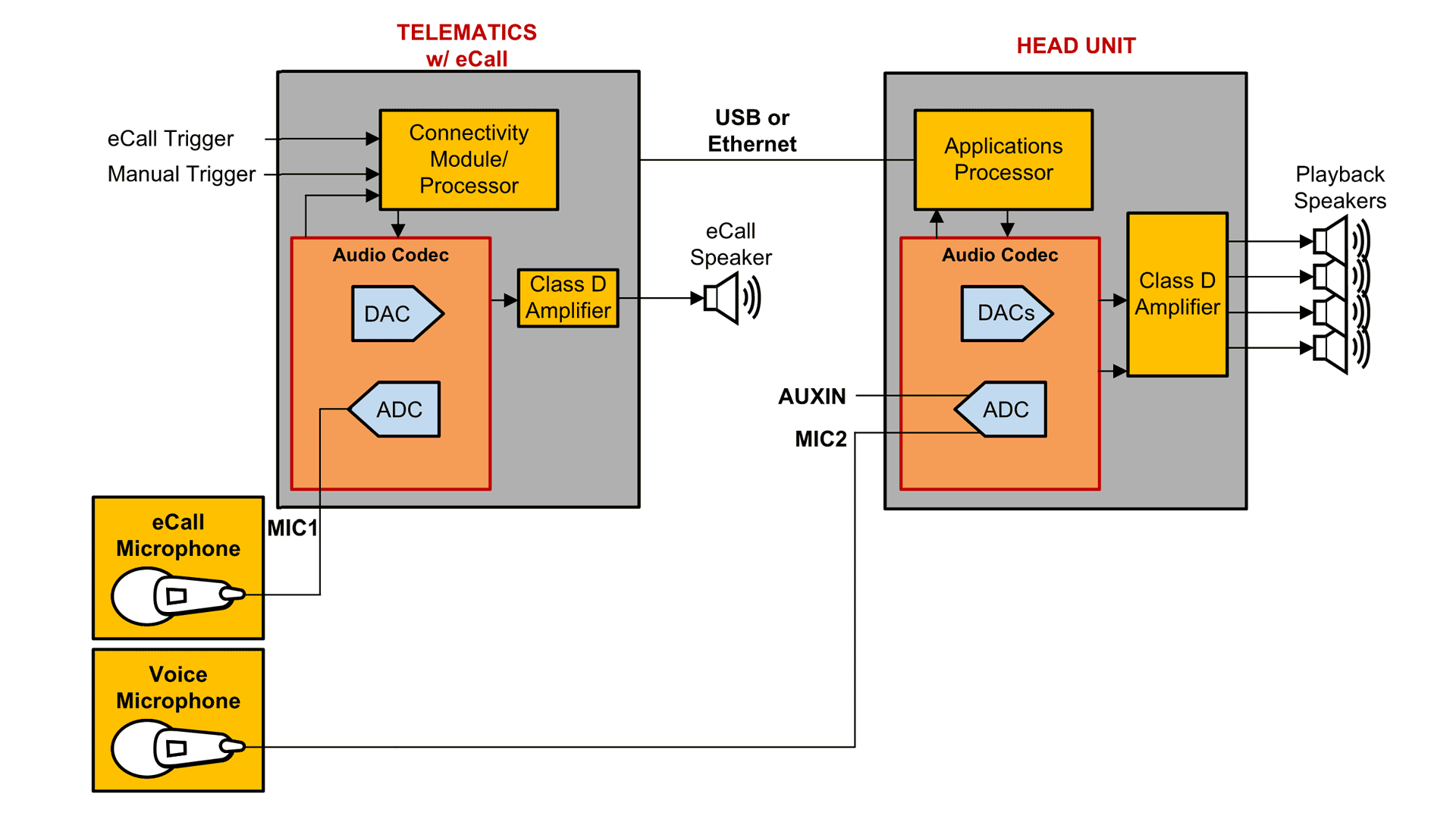 Figure 1-1 A Typical Application Using Dedicated eCall and Voice Microphones
Figure 1-1 A Typical Application Using Dedicated eCall and Voice MicrophonesSharing a microphone for eCall and voice command recognition
TI’s automotive-grade TLV320AIC3109-Q1, TLV320AIC3104-Q1 and TLV320AIC3106-Q1 audio codecs offer two special modes that allow the microphone signal to be routed to the ADC of the codec for eCall and also to the head unit for voice command recognition:
- Passive direct bypass mode establishes a direct connection from microphone input to line output, in addition to the regular ADC path. This mode allows the microphone signal to be bypassed directly to the line output passively, without any amplification.
- Active PGA bypass mode establishes a buffered connection from microphone input to analog output through a PGA and a mixer, in addition to the regular ADC path. This mode allows the amplification of the microphone signal (if necessary) before the signal is routed to the line or headphone output.
As shown in Figure 1-2, these modes enable you to eliminate one microphone from the system altogether, resulting in reduced cost and space associated with the second microphone, along with reduced cable routing and microphone installation costs.
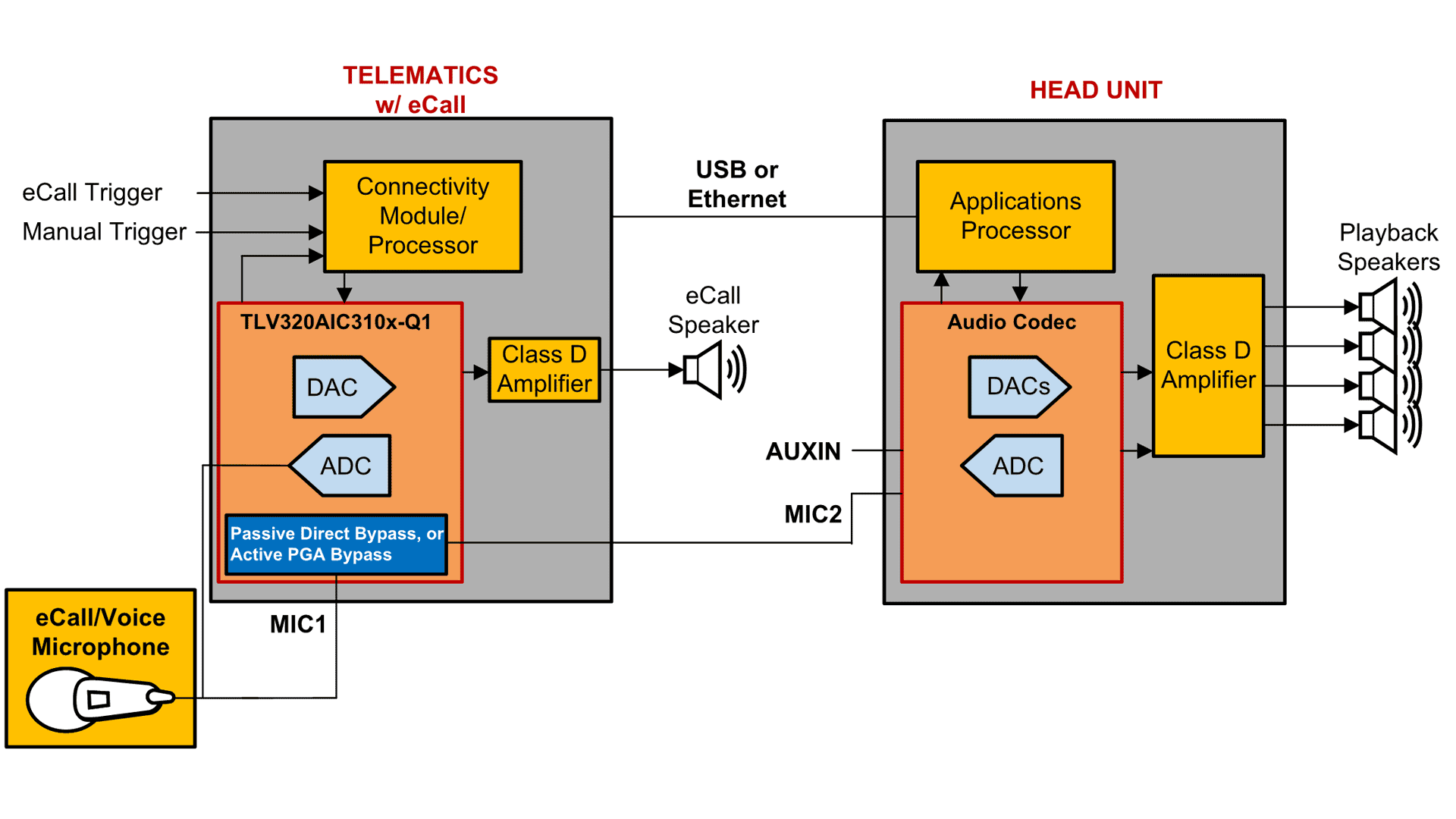 Figure 1-2 Sharing eCall and Voice Microphones Using TLV320AIC310x-Q1 Devices
Figure 1-2 Sharing eCall and Voice Microphones Using TLV320AIC310x-Q1 DevicesThe application note, “Different Configurations in TLV320AIC310x-Q1 Codec Family to Enable Sharing eCall and Hands-Free Voice Microphones in Vehicles,” explains the different possible configurations, along with example pseudo-code, in both passive direct bypass and active PGA bypass modes.
Additional resources
- Explore TI’s portfolio of low-power, high-performing audio converters.
- Learn more about automotive infotainment.