-
How to Avoid the Pain of a Discharged Device SSZT425 august 2019 TPS25830-Q1 , TPS25830A-Q1 , TPS25831-Q1
-
How to Avoid the Pain of a Discharged Device
How to Avoid the Pain of a Discharged Device
Jim Bird

Frustration caused by a dead mobile device battery is not limited to adults with phones. Children too young to read can transform from charming angels to noisy demons when their tablet battery dies.
This can be especially painful when it occurs during a long car ride. I have seen this happen, and recommend taking all reasonable steps to avoid it.
How did we get here?
Before mobile devices, automotive cigarette lighters were populated with cigarette lighters, and sometimes radar detectors or CB radios. These sockets provide considerable power and are typically fused at 15 A or 20 A. Today they are commonly occupied by an adapter for charging mobile devices. Almost all of these adapters have one or more USB ports as an output.
More recently, automakers have been integrating USB charge ports into vehicles at the factory. These USB ports are either in the head unit (aka the radio), the console, or in a rear-seat charging hub. Initially, automakers installed only one or two ports and each port only had to supply 1.0-1.5 A. The DC/DC converter used to create 5 V for these ports had to deliver a modest 5-15 W, and a reasonably thoughtful thermal design could provide reliable operation.
Such is not the case today.
As mobile devices and USB evolved, charging current demands increased to 2 A, then 2.4 A, and now, with USB Type-C™, each port may require 3 A. This significant growth in USB power demand has driven many automakers to move USB charging power conversion and management out of the head unit and into hubs or consoles. This allows greater thermal, mechanical and electrical design flexibility than a location in the head unit.
 Figure 1 Typical Console USB
Port
Figure 1 Typical Console USB
PortGetting integrated with the TPS25830-Q1 and TPS25831-Q1
A complete charge port design includes compliance with power, performance, safety and self-protection standards. Some of these standards require:
- A wide input voltage (VIN) DC/DC converter to provide 5 V at up to 3 A with 8 V < VIN < 40 V.
- A current-limiting USB power switch to prevent excessive current in an overload condition.
- Electrostatic discharge protection for sensitive circuitry.
- Short-to-battery/ground protection to protect data and power against connector pin mishaps.
- USB charge port control – USB Battery Charging (BC) Revision 1.2 and/or USB Type-C handshake capability to enable the maximum charging current.
Historically, this required multichip solutions, but today it is possible to satisfy all of these functions with a single 5-mm-by-5mm 32-pin quad flat no-lead device that has 94% efficiency at a 12-V VIN. The TPS25830-Q1 and TPS25831-Q1 USB charge port converters are simple to use and integrate a DC/DC converter to minimize solution size and cost.
These devices enable maximum charging rates in divider mode and BC1.2 devices, along with USB Type-C handshaking. Cable compensation counteracts voltage droop across USB cables and provides 5 V at the USB connector over the full range of load current.
Smart thermal management on the TPS25831-Q1 prevents thermal shutdown due to overheating by progressively reducing load current as the system temperature approaches the overtemperature threshold.
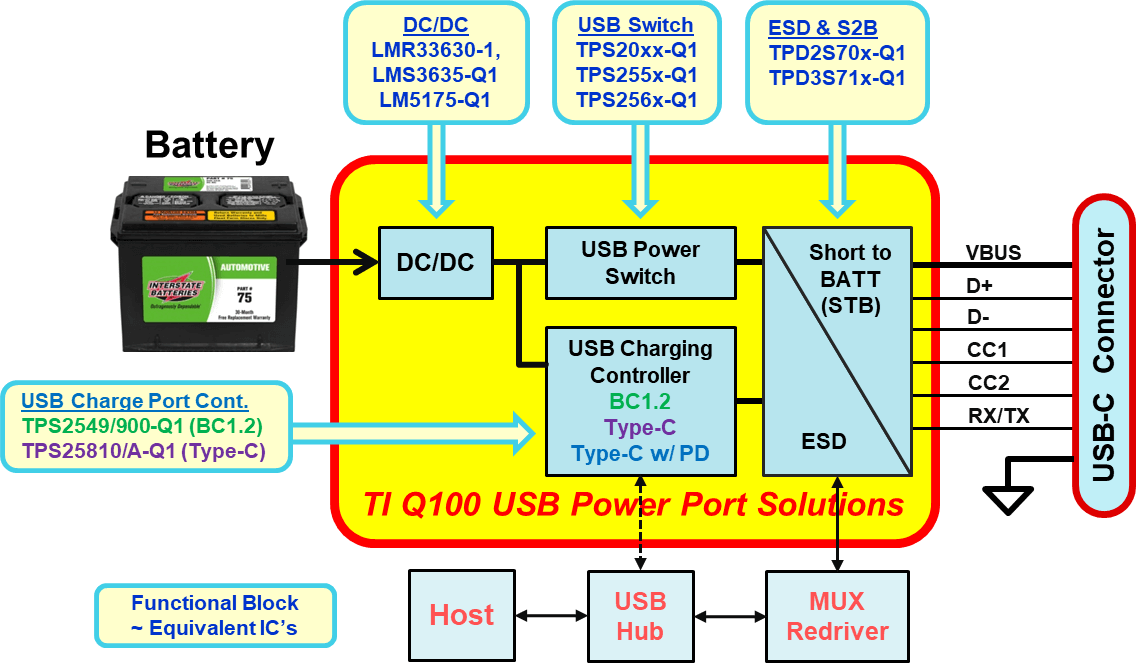 Figure 2 Equivalent functions of TPS25830-Q1 and TPS25831-Q1 devices
Figure 2 Equivalent functions of TPS25830-Q1 and TPS25831-Q1 devicesIf your automotive USB charge port design calls for high efficiency and small size – and low noise from back-seat occupants – check out the TPS25830-Q1 and TPS25831-Q1 and order an evaluation module today.
Additional Resources
- Consider this TI design for a dual port USB Type-C charger.
- Jump start your design with the TPS25830-Q1 USB Type-C and BC1.2 synchronous buck with cable compensation and current limit or TPS25831-Q1 USB Type-C and BC1.2 synchronous buck with cable compensation and current limit evaluation modules.