SSZTAE9 february 2017 CSD17571Q2 , TPD6E05U06 , TPS25923 , TS3A226AE , TS5USBA224 , TUSB320LAI
As USB Type-C ports continue to rise in popularity in laptops, tablets and smartphones, so do the number of failures that early adopters experience. These failures are frequently due to the new USB Type-C cables, many of which are not compliant with the official USB 3.1 specification.
With previous USB implementations (common ones shown in Figure 1 below), most systems were able to withstand the <10W applied by noncompliant cables. Now, with up to 100W of charging available through USB Type-C, properly protecting systems has become much more complicated.
 Figure 1 Today’s popular USB connectors
from left to right: Type A, Mini B and Micro B
Figure 1 Today’s popular USB connectors
from left to right: Type A, Mini B and Micro BNot All USB Type-C Cables Are Created Equal
 Figure 2 The Next Generation of Connectors: USB 3.1, Otherwise Known as USB Type-C
Figure 2 The Next Generation of Connectors: USB 3.1, Otherwise Known as USB Type-CThe Benefits of Implementing USB Type-C Protection
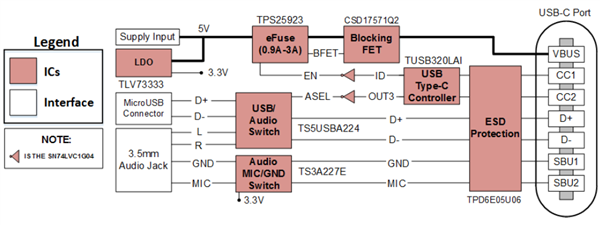 Figure 3 USB Type-C Power-Path Protection with Audio Accessory Support Reference Design Block Diagram
Figure 3 USB Type-C Power-Path Protection with Audio Accessory Support Reference Design Block DiagramThere are multiple levels of protection required for USB Type-C ports, specifically power-path and signal-path protection. In this reference design, the TPD6E05U06 handles signal-path protection on the CC1, CC2, D+, D-, SBU1 and SBU2 pins. This device integrates six ultra-low loading-capacitance transient voltage suppression (TVS) diodes into a single chip, providing International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) 61000-4-2 Level 4 electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection. The TPS25923 eFuse and CSD17571Q2 power MOSFET together provide up to 30V of overvoltage protection, current limiting and block reverse current for the power-path. Last but certainly not least, the TUSB320LAI, TS5USBA224 and TS3A226AE manage the USB cable orientation (don’t forget that USB Type-C is a reversible connector), acting role (DFP, UFP, DRP) and cable attach/detach.
Additionally, these devices provide support for analog audio accessories, allowing for power or audio delivery over a single USB Type-C port. Download the USB Type-C Power Path Protection with Audio Accessory Support Reference Design today to add the proper protection to your next USB Type-C design.
Additional Resources
- Read the blog posts, “USB Type-C audio: Do I need to buy a new pair of headphones?” and “Upgrading USB chargers from Type-A to Type-C.”
- Download the white papers, “Low-cost implementation of USB Type-C™” and “A primer on USB Type-C and Power Delivery applications and requirements.”
- Read the “USB Type-C Power Path Protection with Audio Accessory Support Reference Design” user guide to learn more.