SSZTD41 June 2024 DRV7308
Today’s market for major household appliances is strongly intertwined with energy efficiency and associated branding such as Energy Star certification. Consumers expect end equipment in this category – refrigerators or heating, ventilation and air-conditioning (HVAC) systems – to have high levels of power efficiency and product reliability. So in this article, we’ll explore how the intersection of gallium nitride (GaN) and brushless-DC (BLDC) motor systems can help enhance the lives of consumers.
Figure 1 shows typical home appliances where energy efficiency plays a big role.
 Figure 1 Line-powered home appliance
and HVAC motor-driver applications
Figure 1 Line-powered home appliance
and HVAC motor-driver applicationsTaking refrigerator compressors and HVAC furnace blowers as typical examples of household appliances that contribute significantly to household electricity usage, these types of end equipment use a motor system to control the flow of air and liquids for heating and cooling applications. When designing these systems, it’s vital to optimize how the motor converts electrical power into mechanical movement. Motor system designers will often modify the physical design of the motor assembly, adjusting properties to achieve a specific rated voltage and speed. The system’s electrical design will also need to have the right printed circuit board (PCB) layout, and electronics components capable of achieving the proper signals for motor commutation and power delivery.
Table 1 lists some appliance motor system requirements, and why they matter.
| System requirement | Performance impact | Technical challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Power output and performance | Achieve intended motion Optimize speed Output high torque |
Faster slew rate and switching Higher voltage Higher current |
| Thermal management and power efficiency | System efficiency Minimize wear and tear Extended use without overheating |
Losses in system conduction and reverse recovery Space constraints Heat-sink effects |
| Size and cost | Market competitiveness Convenience |
Integration of features Integrated circuit packaging technology |
| Electromagnetic interference (EMI) and acoustics | Electrical interference Audible noise for consumers |
Slew-rate control Accurate and responsive timing |
| Reliability and safety | Consumer hazards Cost to repair Brand reputation for quality |
Electrical ratings Protection and monitoring features Manufacturing quality |
Having the right components for the task at hand simplifies the development process. For example, TI has integrated its three-layer-metal e-mode GaN technology into a new motor-driver product to meet specialized requirements. Capable of supporting 650V and hosting nearly all of the features necessary to operate a three-phase BLDC motor, the DRV7308 is housed in a small-enough package such that you can design your system to an especially small size. You may not even need a thermal heat sink if you are operating below 250W of power. For more information, download the white paper, “How three-phase integrated GaN technology maximizes motor-drive performance.”
The DRV7308 targets 250W home appliance applications such as HVAC compressors. Figure 2 is a block diagram of this system with our GaN intelligent power module (IPM). These line-powered systems usually include an AC/DC stage, EMI filter, motor-inverter stage and motor.
 Figure 2 BLDC motor-driver system block
diagram
Figure 2 BLDC motor-driver system block
diagramA high-voltage system such as the one shown in Figure 2 has major cost components, including the PCB, heat sink and its assembly, passive components, and motor. TI’s GaN IPM technology offers cost advantages across all of these major components, and ultimately can enable energy cost savings over a system’s lifetime.
There are currently two options when designing a 250W HVAC compressor motor-inverter stage: using metal-oxide semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) or insulated-gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) IPMs, or choosing a discrete implementation. Both solutions’ maximum motor-inverter stage efficiency is 96% or 97%, with typical power losses of 6W to 7.5W. These low levels of efficiency require cooling components such as heat sinks, larger PCBs to dissipate heat, and more expensive motors to reach a specific system efficiency. The DRV7308 GaN IPM can help reduce power losses 50% or more in a smaller package, which translates to more than 99% motor-inverter efficiency, as shown in Figure 3.
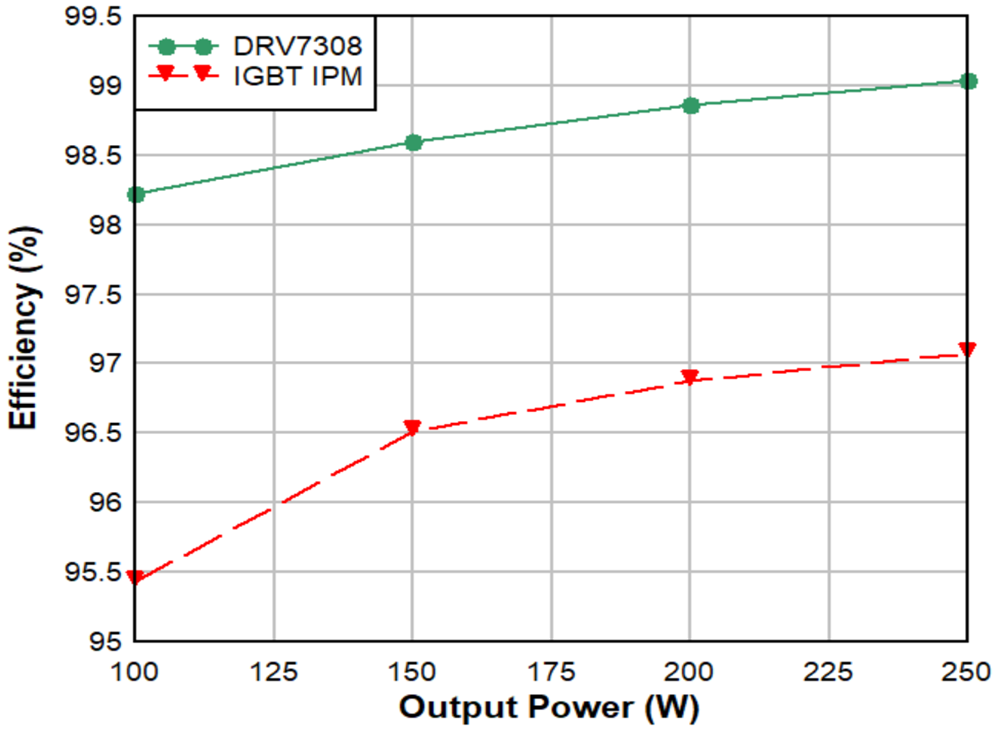 Figure 3 Efficiency comparison between
DRV7308 GaN IPM and IGBT IPM in a 250W system
Figure 3 Efficiency comparison between
DRV7308 GaN IPM and IGBT IPM in a 250W systemThe DRV7308 can enable 2x reduction in power losses given GaN’s intrinsic technological advantages: no reverse-recovery losses, low output capacitance, no tail current, higher slew-rate capability, and a low drain-to-source on-resistance of 205mΩ. The 50% reduction or more in power losses eliminates the need for a heat sink to dissipate heat created from power losses.
The DRV7308 comes in a 12mm-by-12mm package, which is 55% smaller than competing 250W IPMs; see Figure 4 for comparison. Ultimately, these GaN IPM advantages and small package size enable you to shrink PCB size by more than 65%, reducing the cost of the PCB and cooling components. Table 2 lists the savings when using the DRV7308 in a 250W system.
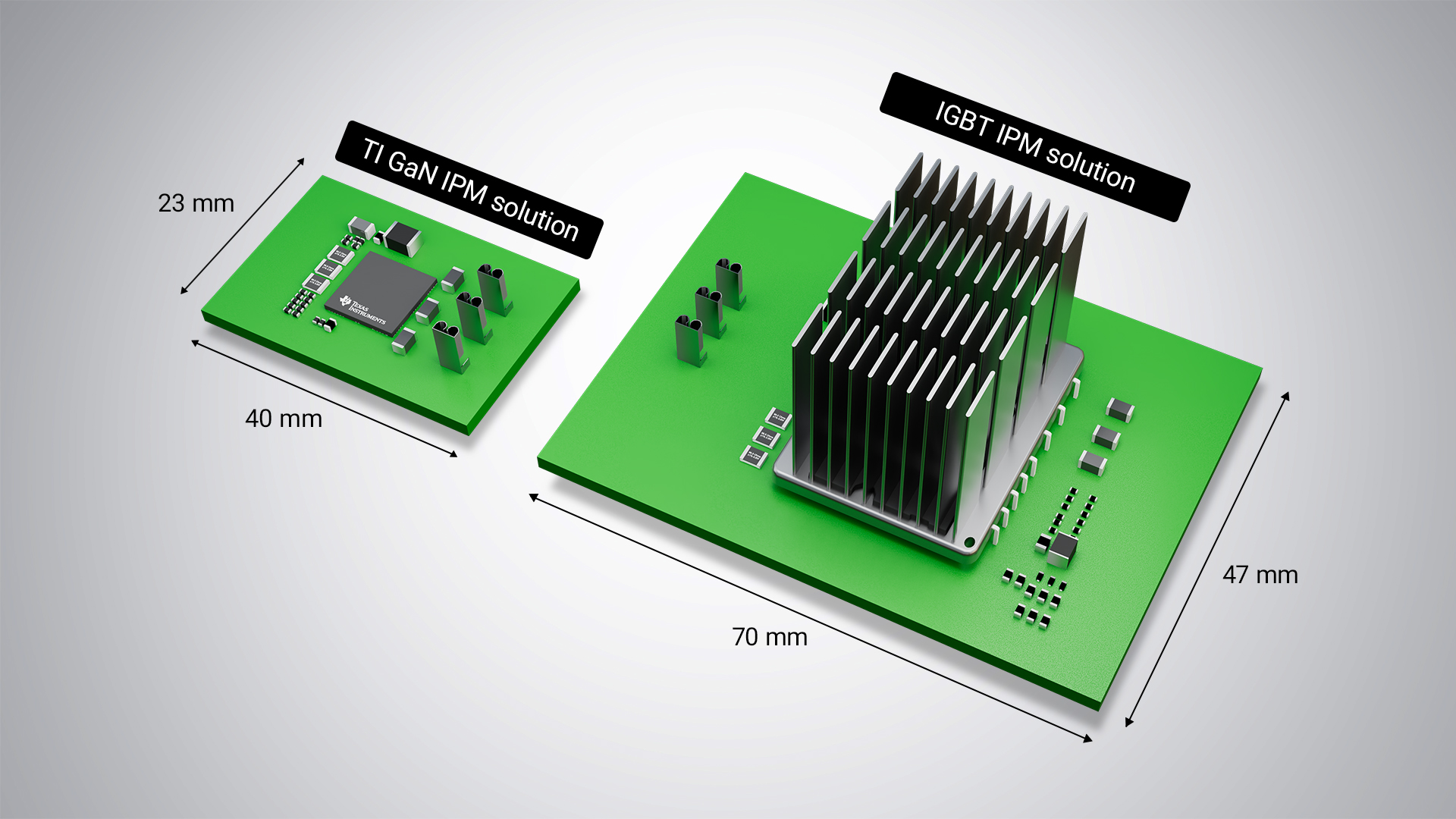 Figure 4 The DRV7308 board compared to
an 250W IGBT solution
Figure 4 The DRV7308 board compared to
an 250W IGBT solution>$2 in system cost savings at 250W
| Value | Cost savings |
|---|---|
| Heat-sink elimination (cost + assembly) | $1.00 |
| Reduction in motor costs by meeting system efficiency standards with more efficient motor | $0.90 |
| Integrated single-shunt operational amplifier Fewer discrete components PCB size savings: 12mm by 12mm vs. 32mm by 12.5mm |
$0.10 |
The design of the motor in these applications sometimes plays a major role in overall system costs. The 2023 seasonal energy-efficient rating (SEER) of 14 for HVAC systems requires 85% efficiency, a 5% increase. The >99% efficiency possible with the DRV7308 exceeds the 85% efficiency requirement without increasing motor costs.
In HVAC motor manufacturing, every 1% improvement in motor efficiency saves an estimated $0.35 because of windings and thicker copper gauge wire; therefore, we estimate up to $0.63 in motor copper savings with the DRV7308. See Table 3.
| Motor output power (W) | Motor efficiency (%) | IPM efficiency (%) | System efficiency (%) | Comments | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IGBT | 250 | 85.0% | 97.0% | 80.8% | Existing solution for SEER rating of 13 (Current) |
| IGBT | 250 | 89.4% | 97.0% | 85.0% | IGBT solution with SEER of 13 (2023 onwards) |
| DRV7308 | 250 | 87.6% | 99.0% | 85.0% | GaN-based solution with SEER of 14 (2023 onwards) |
| DRV7308 can help meet SEER rating of 14 with lower efficient motor | (1) | ||||
- Assumed 98% efficiency of other components in system.
Conclusion
New appliance and HVAC systems continue to hit the market with greater efficiency and reliability. The DRV7308 addresses long-standing challenges in motor inverters for these types of products, helping further push the boundaries for better power density and reliability and less audible noise.
Trademarks
All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.