SWCU185G January 2018 – June 2024 CC1312PSIP , CC1312R , CC1352P , CC1352R , CC2642R , CC2642R-Q1 , CC2652P , CC2652PSIP , CC2652R , CC2652RB , CC2652RSIP , CC2662R-Q1
- 1
- Read This First
-
2 Architectural Overview
- 2.1 Target Applications
- 2.2 Overview
- 2.3
Functional Overview
- 2.3.1 Arm® Cortex®-M4F
- 2.3.2 On-Chip Memory
- 2.3.3 Radio
- 2.3.4 Security Core
- 2.3.5 General-Purpose Timers
- 2.3.6 Direct Memory Access
- 2.3.7 System Control and Clock
- 2.3.8 Serial Communication Peripherals
- 2.3.9 Programmable I/Os
- 2.3.10 Sensor Controller
- 2.3.11 Random Number Generator
- 2.3.12 cJTAG and JTAG
- 2.3.13 Power Supply System
-
3 Arm® Cortex®-M4F Processor
- 3.1 Arm® Cortex®-M4F Processor Introduction
- 3.2 Block Diagram
- 3.3 Overview
- 3.4 Programming Model
- 3.5
Arm® Cortex®-M4F Core Registers
- 3.5.1 Core Register Map
- 3.5.2
Core Register Descriptions
- 3.5.2.1 Cortex®General-Purpose Register 0 (R0)
- 3.5.2.2 Cortex® General-Purpose Register 1 (R1)
- 3.5.2.3 Cortex® General-Purpose Register 2 (R2)
- 3.5.2.4 Cortex® General-Purpose Register 3 (R3)
- 3.5.2.5 Cortex® General-Purpose Register 4 (R4)
- 3.5.2.6 Cortex® General-Purpose Register 5 (R5)
- 3.5.2.7 Cortex® General-Purpose Register 6 (R6)
- 3.5.2.8 Cortex® General-Purpose Register 7 (R7)
- 3.5.2.9 Cortex® General-Purpose Register 8 (R8)
- 3.5.2.10 Cortex® General-Purpose Register 9 (R9)
- 3.5.2.11 Cortex® General-Purpose Register 10 (R10)
- 3.5.2.12 Cortex® General-Purpose Register 11 (R11)
- 3.5.2.13 Cortex® General-Purpose Register 12 (R12)
- 3.5.2.14 Stack Pointer (SP)
- 3.5.2.15 Link Register (LR)
- 3.5.2.16 Program Counter (PC)
- 3.5.2.17 Program Status Register (PSR)
- 3.5.2.18 Priority Mask Register (PRIMASK)
- 3.5.2.19 Fault Mask Register (FAULTMASK)
- 3.5.2.20 Base Priority Mask Register (BASEPRI)
- 3.5.2.21 Control Register (CONTROL)
- 3.6 Instruction Set Summary
- 3.7
Floating Point Unit (FPU)
- 3.7.1 About the FPU
- 3.7.2 FPU Functional Description
- 3.7.3 FPU Programmers Model
- 3.8 Memory Protection Unit (MPU)
- 3.9 Arm® Cortex®-M4F Processor Registers
- 4 Memory Map
- 5 Arm® Cortex®-M4F Peripherals
- 6 Interrupts and Events
-
7 JTAG Interface
- 7.1 Top-Level Debug System
- 7.2 cJTAG
- 7.3 ICEPick
- 7.4 ICEMelter
- 7.5 Serial Wire Viewer (SWV)
- 7.6 Halt In Boot (HIB)
- 7.7 Debug and Shutdown
- 7.8 Debug Features Supported Through WUC TAP
- 7.9 Profiler Register
- 7.10 Boundary Scan
- 8 Power, Reset, and Clock Management (PRCM)
- 9 Versatile Instruction Memory System (VIMS)
- 10SRAM
-
11Bootloader
- 11.1 Bootloader Functionality
- 11.2
Bootloader Interfaces
- 11.2.1 Packet Handling
- 11.2.2 Transport Layer
- 11.2.3
Serial Bus Commands
- 11.2.3.1 COMMAND_PING
- 11.2.3.2 COMMAND_DOWNLOAD
- 11.2.3.3 COMMAND_SEND_DATA
- 11.2.3.4 COMMAND_SECTOR_ERASE
- 11.2.3.5 COMMAND_GET_STATUS
- 11.2.3.6 COMMAND_RESET
- 11.2.3.7 COMMAND_GET_CHIP_ID
- 11.2.3.8 COMMAND_CRC32
- 11.2.3.9 COMMAND_BANK_ERASE
- 11.2.3.10 COMMAND_MEMORY_READ
- 11.2.3.11 COMMAND_MEMORY_WRITE
- 11.2.3.12 COMMAND_SET_CCFG
- 11.2.3.13 COMMAND_DOWNLOAD_CRC
- 12Device Configuration
-
13Cryptography
- 13.1 AES and Hash Cryptoprocessor Introduction
- 13.2 Functional Description
- 13.3 Power Management and Sleep Modes
- 13.4 Hardware Description
- 13.5 Module Description
- 13.6 AES Module Performance
- 13.7
Programming Guidelines
- 13.7.1 One-Time Initialization After a Reset
- 13.7.2 DMAC and Master Control
- 13.7.3 Hashing
- 13.7.4 Encryption and Decryption
- 13.7.5
Exceptions Handling
- 13.7.5.1 Soft Reset
- 13.7.5.2 External Port Errors
- 13.7.5.3 Key Store Errors
- 13.8 Conventions and Compliances
- 13.9 Cryptography Registers
- 14I/O Controller (IOC)
-
15Micro Direct Memory Access (µDMA)
- 15.1 μDMA Introduction
- 15.2 Block Diagram
- 15.3 Functional Description
- 15.4 Initialization and Configuration
- 15.5 µDMA Registers
- 16Timers
- 17Real-Time Clock (RTC)
- 18Watchdog Timer (WDT)
- 19True Random Number Generator (TRNG)
-
20AUX Domain Sensor Controller and Peripherals
- 20.1 Introduction
- 20.2 Power and Clock Management
- 20.3
Sensor Controller
- 20.3.1 Sensor Controller Studio
- 20.3.2 Sensor Controller Engine (SCE)
- 20.4
Digital Peripheral Modules
- 20.4.1 Overview
- 20.4.2 AIODIO
- 20.4.3 SMPH
- 20.4.4 SPIM
- 20.4.5 Time-to-Digital Converter (TDC)
- 20.4.6 Timer01
- 20.4.7
Timer2
- 20.4.7.1 Introduction
- 20.4.7.2
Functional Description
- 20.4.7.2.1 Clock Source
- 20.4.7.2.2 Clock Prescaler
- 20.4.7.2.3 Counter
- 20.4.7.2.4 Event Outputs
- 20.4.7.2.5 Channel Actions
- 20.4.7.2.6 Asynchronous Bus Bridge
- 20.5
Analog Peripheral Modules
- 20.5.1 Overview
- 20.5.2 Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
- 20.5.3 COMPA
- 20.5.4 COMPB
- 20.5.5 Reference DAC
- 20.5.6 ISRC
- 20.6 Event Routing and Usage
- 20.7 Sensor Controller Alias Register Space
- 20.8
AUX Domain Sensor Controller and Peripherals Registers
- 20.8.1 ADI_4_AUX Registers
- 20.8.2 AUX_AIODIO Registers
- 20.8.3 AUX_EVCTL Registers
- 20.8.4 AUX_SMPH Registers
- 20.8.5 AUX_TDC Registers
- 20.8.6 AUX_TIMER01 Registers
- 20.8.7 AUX_TIMER2 Registers
- 20.8.8 AUX_ANAIF Registers
- 20.8.9 AUX_SYSIF Registers
- 20.8.10 AUX_SPIM Registers
- 20.8.11 AUX_MAC Registers
- 20.8.12 AUX_SCE Registers
- 21Battery Monitor and Temperature Sensor (BATMON)
-
22Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART)
- 22.1 Introduction
- 22.2 Block Diagram
- 22.3 Signal Description
- 22.4 Functional Description
- 22.5 Interface to DMA
- 22.6 Initialization and Configuration
- 22.7 UART Registers
-
23Synchronous Serial Interface (SSI)
- 23.1 Introduction
- 23.2 Block Diagram
- 23.3 Signal Description
- 23.4
Functional Description
- 23.4.1 Bit Rate Generation
- 23.4.2 FIFO Operation
- 23.4.3 Interrupts
- 23.4.4
Frame Formats
- 23.4.4.1 Texas Instruments Synchronous Serial Frame Format
- 23.4.4.2 Motorola SPI Frame Format
- 23.4.4.3 Motorola SPI Frame Format With SPO = 0 and SPH = 0
- 23.4.4.4 Motorola SPI Frame Format With SPO = 0 and SPH = 1
- 23.4.4.5 Motorola SPI Frame Format With SPO = 1 and SPH = 0
- 23.4.4.6 Motorola SPI Frame Format With SPO = 1 and SPH = 1
- 23.4.4.7 MICROWIRE Frame Format
- 23.5 DMA Operation
- 23.6 Initialization and Configuration
- 23.7 SSI Registers
- 24Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C)
-
25Inter-IC Sound (I2S)
- 25.1 Introduction
- 25.2 Block Diagram
- 25.3 Signal Description
- 25.4 Functional Description
- 25.5 Memory Interface
- 25.6 Samplestamp Generator
- 25.7 Error Detection
- 25.8 Usage
- 25.9 I2S Registers
-
26Radio
- 26.1 RF Core
- 26.2 Radio Doorbell
- 26.3
RF Core HAL
- 26.3.1 Hardware Support
- 26.3.2 Firmware Support
- 26.3.3
Command Definitions
- 26.3.3.1
Protocol-Independent Radio Operation Commands
- 26.3.3.1.1 CMD_NOP: No Operation Command
- 26.3.3.1.2 CMD_RADIO_SETUP: Set Up Radio Settings Command
- 26.3.3.1.3 CMD_FS_POWERUP: Power Up Frequency Synthesizer
- 26.3.3.1.4 CMD_FS_POWERDOWN: Power Down Frequency Synthesizer
- 26.3.3.1.5 CMD_FS: Frequency Synthesizer Controls Command
- 26.3.3.1.6 CMD_FS_OFF: Turn Off Frequency Synthesizer
- 26.3.3.1.7 CMD_RX_TEST: Receiver Test Command
- 26.3.3.1.8 CMD_TX_TEST: Transmitter Test Command
- 26.3.3.1.9 CMD_SYNC_STOP_RAT: Synchronize and Stop Radio Timer Command
- 26.3.3.1.10 CMD_SYNC_START_RAT: Synchronously Start Radio Timer Command
- 26.3.3.1.11 CMD_COUNT: Counter Command
- 26.3.3.1.12 CMD_SCH_IMM: Run Immediate Command as Radio Operation
- 26.3.3.1.13 CMD_COUNT_BRANCH: Counter Command With Branch of Command Chain
- 26.3.3.1.14 CMD_PATTERN_CHECK: Check a Value in Memory Against a Pattern
- 26.3.3.2
Protocol-Independent Direct and Immediate Commands
- 26.3.3.2.1 CMD_ABORT: ABORT Command
- 26.3.3.2.2 CMD_STOP: Stop Command
- 26.3.3.2.3 CMD_GET_RSSI: Read RSSI Command
- 26.3.3.2.4 CMD_UPDATE_RADIO_SETUP: Update Radio Settings Command
- 26.3.3.2.5 CMD_TRIGGER: Generate Command Trigger
- 26.3.3.2.6 CMD_GET_FW_INFO: Request Information on the Firmware Being Run
- 26.3.3.2.7 CMD_START_RAT: Asynchronously Start Radio Timer Command
- 26.3.3.2.8 CMD_PING: Respond With Interrupt
- 26.3.3.2.9 CMD_READ_RFREG: Read RF Core Register
- 26.3.3.2.10 CMD_SET_RAT_CMP: Set RAT Channel to Compare Mode
- 26.3.3.2.11 CMD_SET_RAT_CPT: Set RAT Channel to Capture Mode
- 26.3.3.2.12 CMD_DISABLE_RAT_CH: Disable RAT Channel
- 26.3.3.2.13 CMD_SET_RAT_OUTPUT: Set RAT Output to a Specified Mode
- 26.3.3.2.14 CMD_ARM_RAT_CH: Arm RAT Channel
- 26.3.3.2.15 CMD_DISARM_RAT_CH: Disarm RAT Channel
- 26.3.3.2.16 CMD_SET_TX_POWER: Set Transmit Power
- 26.3.3.2.17 CMD_SET_TX20_POWER: Set Transmit Power of the 20 dBm PA
- 26.3.3.2.18 CMD_UPDATE_FS: Set New Synthesizer Frequency Without Recalibration (Depricated)
- 26.3.3.2.19 CMD_MODIFY_FS: Set New Synthesizer Frequency Without Recalibration
- 26.3.3.2.20 CMD_BUS_REQUEST: Request System BUS Available for RF Core
- 26.3.3.1
Protocol-Independent Radio Operation Commands
- 26.3.4 Immediate Commands for Data Queue Manipulation
- 26.4
Data Queue Usage
- 26.4.1
Operations on Data Queues Available Only for Internal Radio CPU Operations
- 26.4.1.1 PROC_ALLOCATE_TX: Allocate TX Entry for Reading
- 26.4.1.2 PROC_FREE_DATA_ENTRY: Free Allocated Data Entry
- 26.4.1.3 PROC_FINISH_DATA_ENTRY: Finish Use of First Data Entry From Queue
- 26.4.1.4 PROC_ALLOCATE_RX: Allocate RX Buffer for Storing Data
- 26.4.1.5 PROC_FINISH_RX: Commit Received Data to RX Data Entry
- 26.4.2 Radio CPU Usage Model
- 26.4.1
Operations on Data Queues Available Only for Internal Radio CPU Operations
- 26.5
IEEE 802.15.4
- 26.5.1 IEEE 802.15.4 Commands
- 26.5.2 Interrupts
- 26.5.3 Data Handling
- 26.5.4 Radio Operation Commands
- 26.5.5 Immediate Commands
- 26.6 Bluetooth® low energy
- 26.7 Data Handling
- 26.8
Radio Operation Command Descriptions
- 26.8.1 Bluetooth® 5 Radio Setup Command
- 26.8.2 Radio Operation Commands for Bluetooth® low energy Packet Transfer
- 26.8.3 Coding Selection for Coded PHY
- 26.8.4 Parameter Override
- 26.8.5 Link Layer Connection
- 26.8.6 Slave Command
- 26.8.7 Master Command
- 26.8.8 Legacy Advertiser
- 26.8.9 Bluetooth® 5 Advertiser Commands
- 26.8.10 Scanner Commands
- 26.8.11
Initiator Command
- 26.8.11.1 Initiator Receiving Legacy Advertising Packets on Primary Channel
- 26.8.11.2 Initiator Receiving Extended Advertising Packets on Primary Channel
- 26.8.11.3 Initiator Receiving Extended Advertising Packets on Secondary Channel
- 26.8.11.4 Automatic Window Offset Insertion
- 26.8.11.5 End of Initiator Commands
- 26.8.12 Generic Receiver Command
- 26.8.13 PHY Test Transmit Command
- 26.8.14 Whitelist Processing
- 26.8.15 Backoff Procedure
- 26.8.16 AUX Pointer Processing
- 26.8.17 Dynamic Change of Device Address
- 26.9 Immediate Commands
- 26.10
Proprietary Radio
- 26.10.1 Packet Formats
- 26.10.2 Commands
- 26.10.3 Interrupts
- 26.10.4 Data Handling
- 26.10.5 Radio Operation Command Descriptions
- 26.10.6 Immediate Commands
- 26.11 Radio Registers
- 27Revision History
24.3.1.2 Data Format With 7-Bit Address
Data transfers follow the format shown in Figure 24-4. After the Start condition, a slave address is transmitted. This address is 7 bits long followed by an eighth bit, which is a data direction bit (the R/S bit in the I2C:MSA register). If the RS bit is clear, it indicates a transmit operation (send), and if it is set, it indicates a request for data (receive). A data transfer is always terminated by a Stop condition generated by the master; however, a master can initiate communications with another device on the bus, by generating a Repeated Start condition and addressing another slave without first generating a Stop condition. Various combinations of receive and transmit formats are then possible within a single transfer.
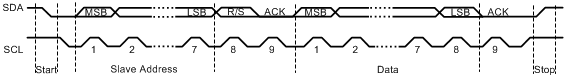 Figure 24-4 Complete Data Transfer With a 7-Bit Address
Figure 24-4 Complete Data Transfer With a 7-Bit AddressThe first 7 bits of the first byte comprise the slave address (see Figure 24-5). The eighth bit determines the direction of the message. A 0 in the R/S position of the first byte means that the master transmits (sends) data to the selected slave, and a 1 in this position means that the master receives data from the slave.
 Figure 24-5 R/S Bit in First Byte
Figure 24-5 R/S Bit in First Byte