SWRA679 January 2021 CC3200 , CC3220R , CC3220S , CC3220SF , CC3230S , CC3230SF , CC3235S , CC3235SF
2.1.1.1 Extra Current Draw
The equivalent resistance of R1 + R2 in series draws a current of Vcc/(R1 + R2) = 3.3V/370K ~= 9 μA. If the current draw is a concern, you may be tempted to simply increase the resistor values. However, this slows down the re-charging of the capacitor Cext after the pin is disconnected from the ADC.
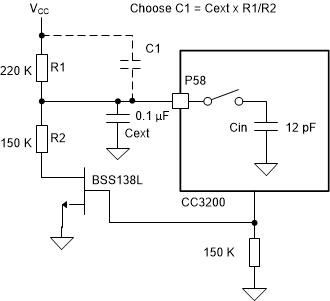 Figure 2-2 Reducing Resistive Current
Draw
Figure 2-2 Reducing Resistive Current
DrawAn alternative is to disconnect R2 from the circuit by using an NMOS transistor controlled by the CC32xx device. This circuit is shown in Figure 2-2. In this circuit, an additional optional capacitor is shown (C1) that can be used to improve the overall frequency response and speed up the charging time. This capacitor, along with R1, R2, and Cext, work as a compensated attenuator. Note that this arrangement will not offer any noise filtering and should be used with caution.