SWRS236C March 2021 – January 2024 AWR1843AOP
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison
- 5 Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Power-On Hours (POH)
- 6.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.5 Power Supply Specifications
- 6.6 Power Consumption Summary
- 6.7 RF Specification
- 6.8 CPU Specifications
- 6.9 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for FCBGA Package [ALP0180A]
- 6.10
Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 6.10.1 Antenna Radiation Patterns
- 6.10.2 Antenna Positions
- 6.10.3 Power Supply Sequencing and Reset Timing
- 6.10.4 Input Clocks and Oscillators
- 6.10.5 Multibuffered / Standard Serial Peripheral Interface (MibSPI)
- 6.10.6 LVDS Interface Configuration
- 6.10.7 General-Purpose Input/Output
- 6.10.8 Controller Area Network Interface (DCAN)
- 6.10.9 Controller Area Network - Flexible Data-rate (CAN-FD)
- 6.10.10 Serial Communication Interface (SCI)
- 6.10.11 Inter-Integrated Circuit Interface (I2C)
- 6.10.12 Quad Serial Peripheral Interface (QSPI)
- 6.10.13 ETM Trace Interface
- 6.10.14 Data Modification Module (DMM)
- 6.10.15 JTAG Interface
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Monitoring and Diagnostics
- 9 Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Revision History
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6.10.5.2.2 SPI Controller Mode Switching
Parameters (CLOCK PHASE = 0, SPICLK = output,
SPISIMO = output,
and SPISOMI = input)
| NO.(1)(2)(3) | PARAMETER | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | tc(SPC)M | Cycle time, SPICLK(4) | 25 | 256tc(VCLK) | ns | ||
| 2(4) | tw(SPCH)M | Pulse duration, SPICLK high (clock polarity = 0) | 0.5tc(SPC)M – 4 | 0.5tc(SPC)M + 4 | ns | ||
| tw(SPCL)M | Pulse duration, SPICLK low (clock polarity = 1) | 0.5tc(SPC)M – 4 | 0.5tc(SPC)M + 4 | ||||
| 3(4) | tw(SPCL)M | Pulse duration, SPICLK low (clock polarity = 0) | 0.5tc(SPC)M – 4 | 0.5tc(SPC)M + 4 | ns | ||
| tw(SPCH)M | Pulse duration, SPICLK high (clock polarity = 1) | 0.5tc(SPC)M – 4 | 0.5tc(SPC)M + 4 | ||||
| 4(4) | td(SPCH-SIMO)M | Delay time, SPISIMO valid before SPICLK low, (clock polarity = 0) | 0.5tc(SPC)M – 3 | ns | |||
| td(SPCL-SIMO)M | Delay time, SPISIMO valid before SPICLK high, (clock polarity = 1) | 0.5tc(SPC)M – 3 | |||||
| 5(4) | tv(SPCL-SIMO)M | Valid time, SPISIMO data valid after SPICLK low, (clock polarity = 0) | 0.5tc(SPC)M – 10.5 | ns | |||
| tv(SPCH-SIMO)M | Valid time, SPISIMO data valid after SPICLK high, (clock polarity = 1) | 0.5tc(SPC)M – 10.5 | |||||
| 6(5) | tC2TDELAY | Setup time CS active until SPICLK high (clock polarity = 0) |
CSHOLD = 0 | (C2TDELAY+2)*tc(VCLK) – 7.5 | (C2TDELAY+2) * tc(VCLK) + 7 | ns | |
| CSHOLD = 1 | (C2TDELAY +3) * tc(VCLK) – 7.5 | (C2TDELAY+3) * tc(VCLK) + 7 | |||||
| Setup time CS active until SPICLK
low (clock polarity = 1) |
CSHOLD = 0 | (C2TDELAY+2)*tc(VCLK) – 7.5 | (C2TDELAY+2) * tc(VCLK) + 7 | ||||
| CSHOLD = 1 | (C2TDELAY +3) * tc(VCLK) – 7.5 | (C2TDELAY+3) * tc(VCLK) + 7 | |||||
| 7(5) | tT2CDELAY | Hold time, SPICLK low until CS inactive (clock polarity = 0) | 0.5*tc(SPC)M + (T2CDELAY + 1) *tc(VCLK) – 7 | 0.5*tc(SPC)M + (T2CDELAY + 1) * tc(VCLK) + 7.5 | ns | ||
| Hold time, SPICLK high until CS inactive (clock polarity = 1) | 0.5*tc(SPC)M + (T2CDELAY + 1) *tc(VCLK) – 7 | 0.5*tc(SPC)M + (T2CDELAY + 1) * tc(VCLK) + 7.5 | |||||
| 8(4) | tsu(SOMI-SPCL)M | Setup time,
SPISOMI before SPICLK low (clock polarity = 0) |
5 | ns | |||
| tsu(SOMI-SPCH)M | Setup time,
SPISOMI before SPICLK high (clock polarity = 1) |
5 | |||||
| 9(4) | th(SPCL-SOMI)M | Hold time,
SPISOMI data valid after SPICLK low (clock polarity = 0) |
3 | ns | |||
| th(SPCH-SOMI)M | Hold time,
SPISOMI data valid after SPICLK high (clock polarity = 1) |
3 | |||||
(1) The Controller bit (SPIGCRx.0) is set and the
CLOCK PHASE bit (SPIFMTx.16) is cleared (where x= 0 or 1).
(2) tc(MSS_VCLK) = main subsystem clock
time = 1 / f(MSS_VCLK). For more details, see the Technical Reference
Manual.
(3) When the SPI is in controller mode, the
following must be true: For PS values from 1 to 255: tc(SPC)M ≥ (PS
+1)tc(MSS_VCLK) ≥ 25ns, where PS is the prescale value set in the
SPIFMTx.[15:8] register bits. For PS values of 0: tc(SPC)M =
2tc(MSS_VCLK) ≥ 25ns.
(4) The active edge of the SPICLK signal
referenced is controlled by the CLOCK POLARITY bit
(SPIFMTx.17).
(5) C2TDELAY and T2CDELAY is programmed in the
SPIDELAY register
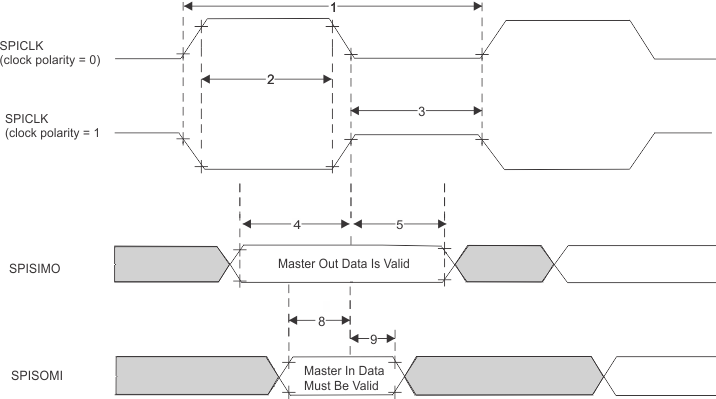 Figure 6-8 SPI Controller Mode External Timing (CLOCK
PHASE = 0)
Figure 6-8 SPI Controller Mode External Timing (CLOCK
PHASE = 0)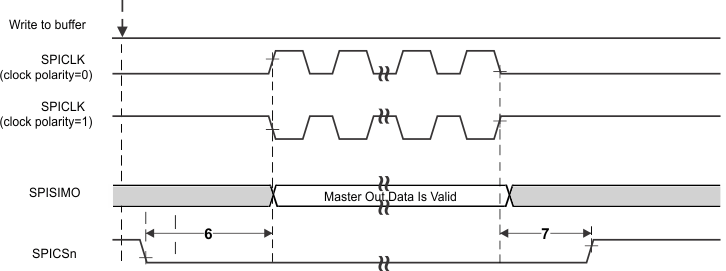 Figure 6-9 SPI Controller Mode Chip Select Timing
(CLOCK PHASE = 0)
Figure 6-9 SPI Controller Mode Chip Select Timing
(CLOCK PHASE = 0)