SWRU619A July 2024 – December 2024
- 1
- Description
- Applications
- Get Started
- Features
- 6
- 1Evaluation Module Overview
-
2Hardware
- 2.1 xWRL1432BOOST-BSD Antenna
- 2.2 EVM Mux Block Diagram
- 2.3 Switch Settings
- 2.4 LEDs
- 2.5 Connectors
- 2.6 USB Connector
- 2.7 DCA1000 HD Connector
- 2.8 Booster Pack Connector for the LaunchPad Connectivity
- 2.9 SPI-CAN Driver
- 2.10 CAN-FD Connector
- 2.11 LIN PHY Connection
- 2.12 I2C Connections
- 2.13 XDS110 Interface
- 2.14 Flashing the Board
- 2.15 DCA1000EVM Mode
- 2.16 PCB Storage and Handling Recommendations:
- 3Software
- 4Hardware Design Files
- 5Additional Information
- 6References
- Revision History
2.9 SPI-CAN Driver
The SPI-CAN driver allows for the radar device to communicate to the CAN bus using SPI connectivity. This functionality comes from TI's TCAN4550 family of TCAN drivers. This driver can be selected by turning on (closing) S4.4. This routes the SPI connection from the DCA, LP, and FTDI to the TCAN bus. This TCAN bus can be accessed using J10. The driver can be woken up by pressing S6. A 12V supply must be connected to J7 DC jack.
 Figure 2-16 SPI-CAN Connector
Figure 2-16 SPI-CAN Connector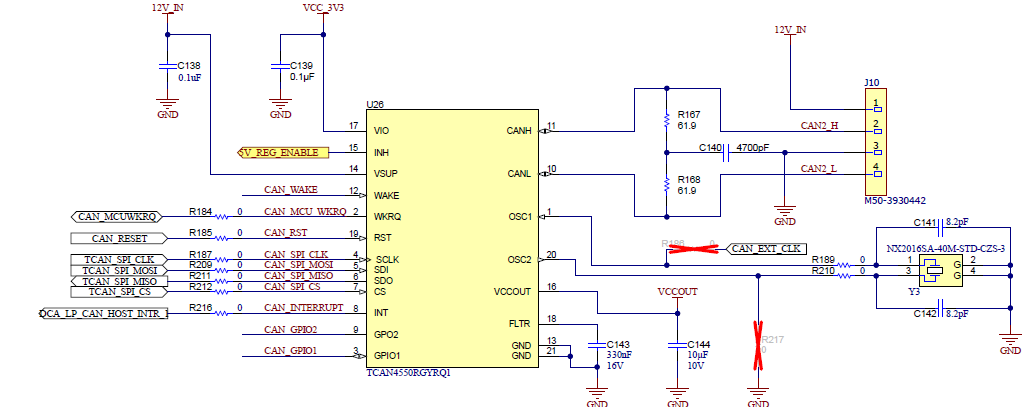 Figure 2-17 SPI-CAN Interface
Figure 2-17 SPI-CAN Interface