TIDT222 April 2021
4.3 Load Transients
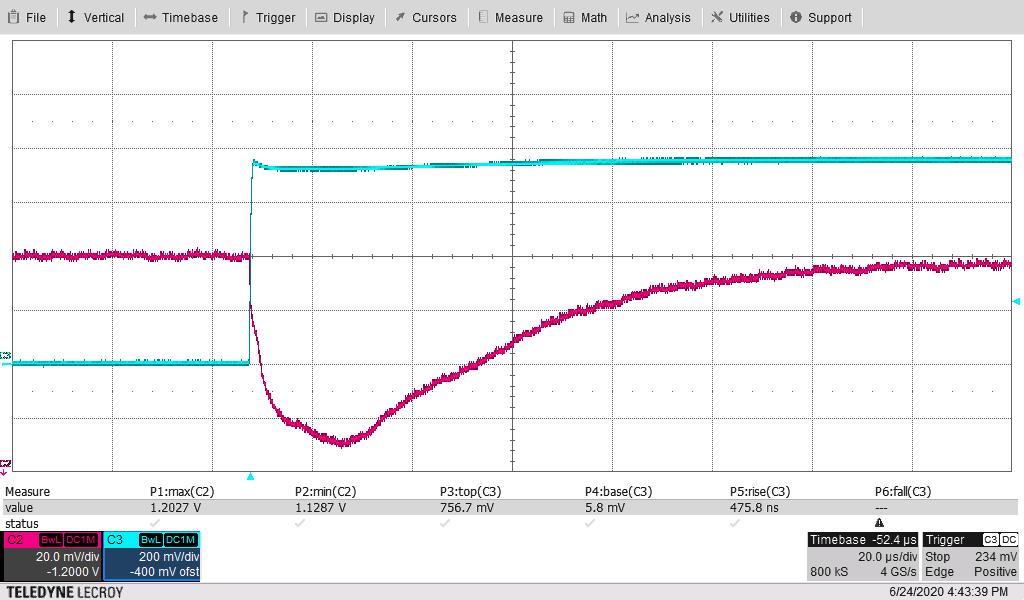
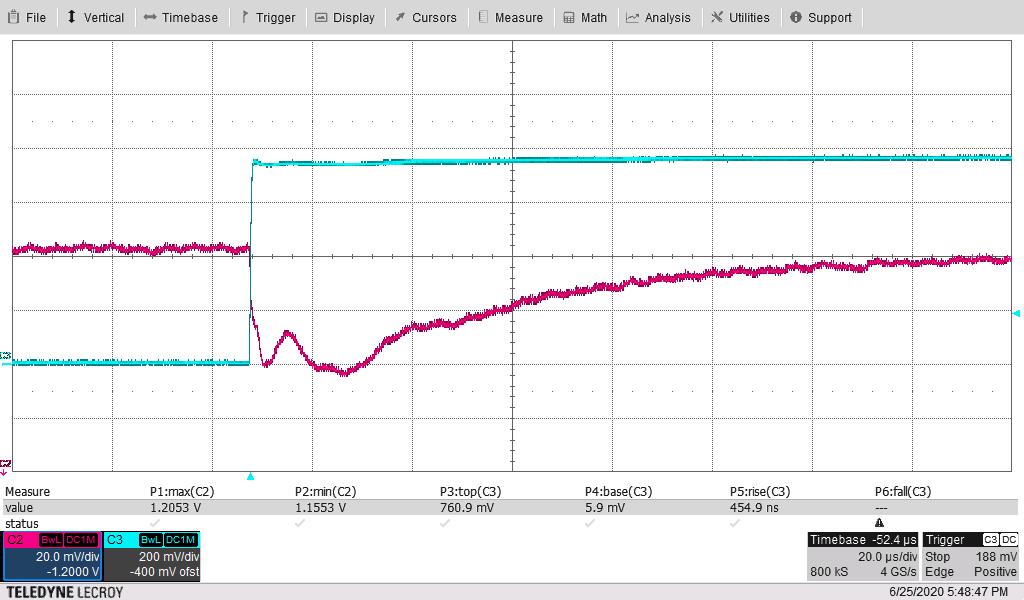
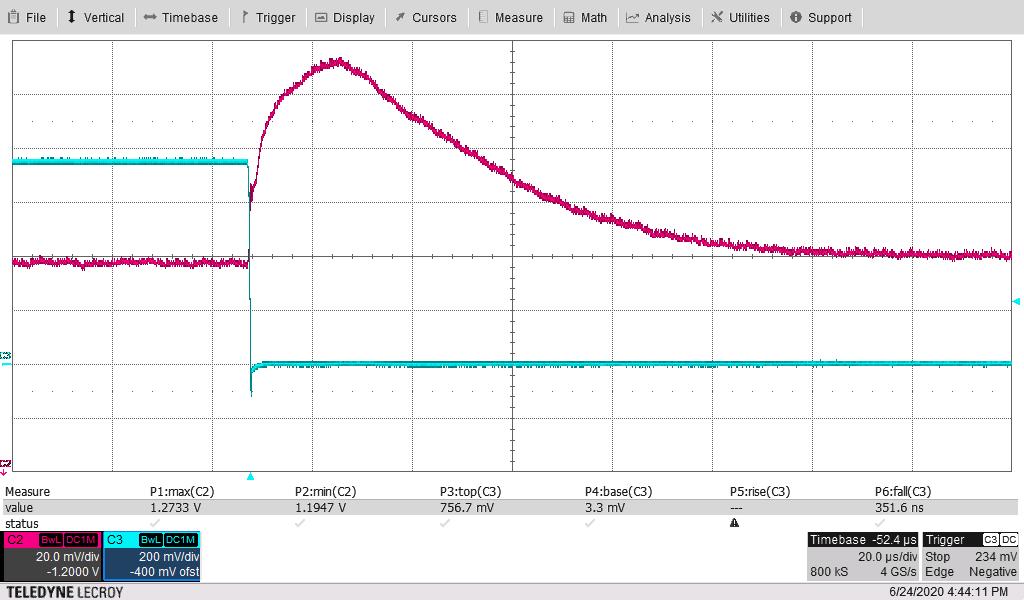
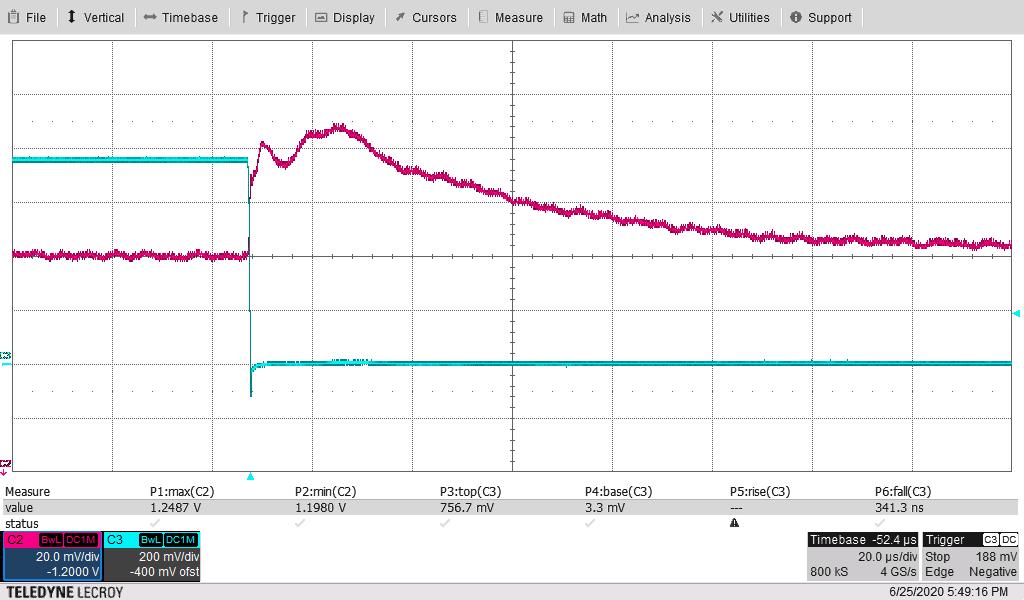
Figure 4-7 shows the 1.2-V output voltage when the load current is stepped between 125 A and 200 A. An external static load of 125 A was used along with onboard dynamic load for 75-A pulses. The other parameters follow:
- VIN = 12 V, rise 11.85 A/μs, fall 12.5 A/μs (10 mV/DIV, 10 A/DIV, 200 μs/DIV)
The dynamic load response measured at VOUT is measured on the bottom side of the board using a coaxial connection: see Test Setup.
The measured maximum overshoot of 20.4 mV above nominal 1 V or 2.04% above nominal. The measured maximum undershoot of 23.9 mV below nominal 1 V or 2.39% below nominal.
- The current-sense waveform below is across a 10-mΩ resistor to ground on the dynamic load.
- Blue trace J500 on board
Hence, the “top” of this pulse of 750 mV above the base divided by 10 mΩ, corresponds to a 75-A pulse.
- dI/dT of rise is 80% of this 75 A (as rise time is defined for “10% to 90%” or 80%”) or 60 A divided by the rise time of 481 ns; or 60/0.48 or 125 A/μs. Rise time readings were 454–481 ns, 481 ns is used to estimate the dI/dT.
- dI/dT of fall is 80% of this 20 A (as fall time is defined for “90% to 10%” or 80%”) or 60 A divided by the fall time of 360 ns; or 60/0.36 or –165 A/μs. Fall time readings were 340 ns–360 ns, 360 ns is used to estimate the dI/dT.
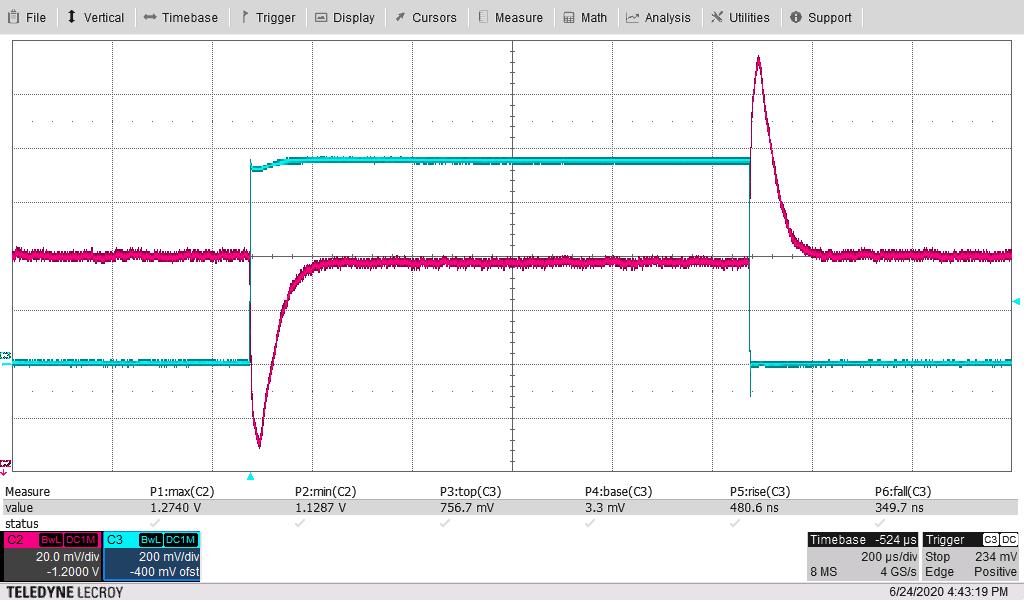
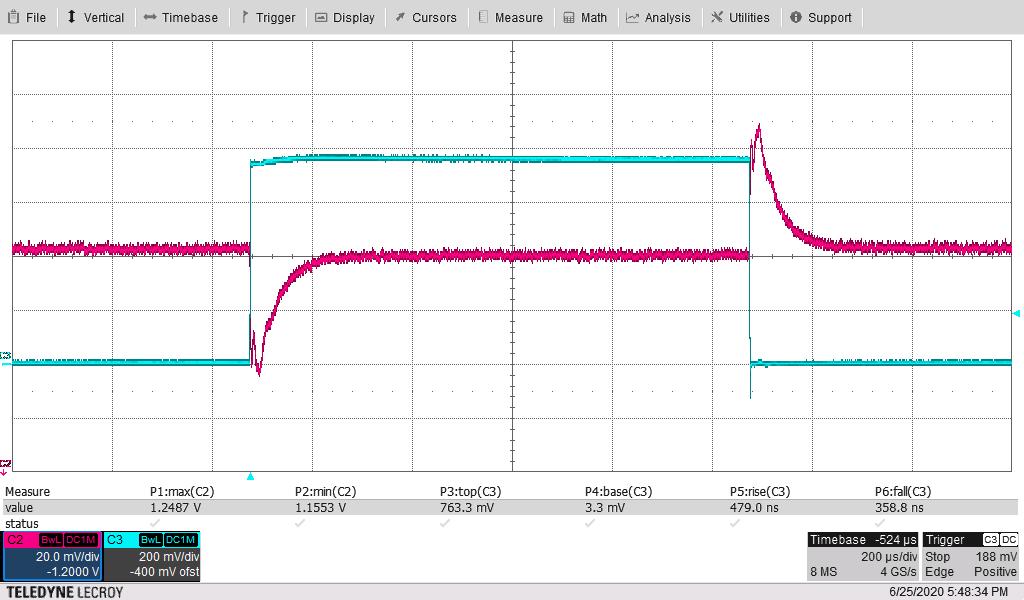
Figure 4-9 through Figure 4-12 are the same pair of waveforms, adjusting the time scale to highlight the load step and load-dump responses.