TIDT226 April 2021
4.3 Output Voltage Ripple
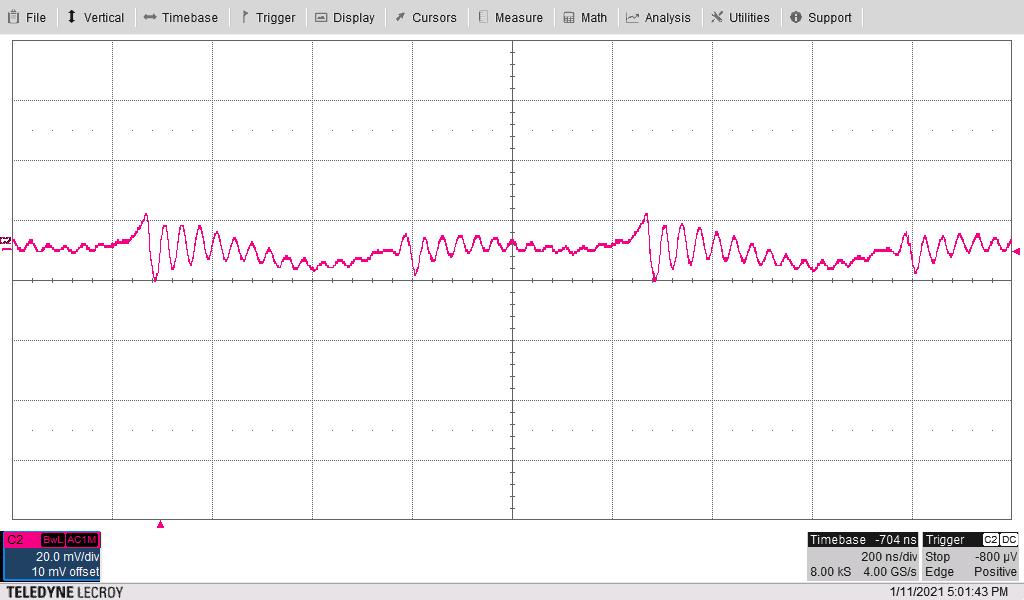
The following waveform shows the 20-V output ripple voltage (AC coupled) measured across C4. The input voltage is 24 V and the 20-V and –4-V outputs are loaded to 100 mA each.
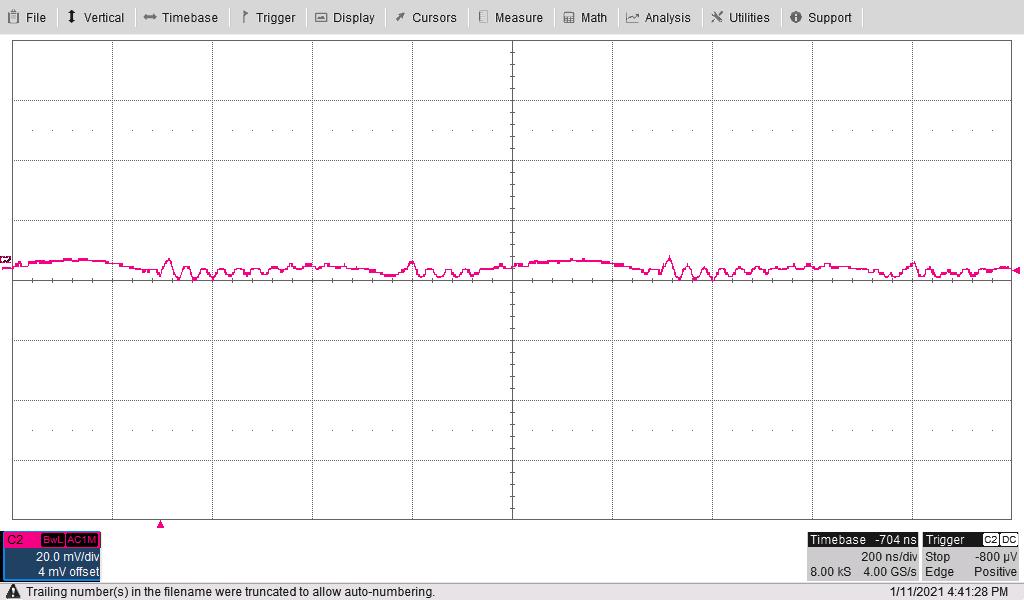
The following waveform shows the 20-V output ripple voltage (AC coupled) measured across C4. The input voltage is 24 V and the 20-V and –4-V outputs are loaded to 300 mA each.
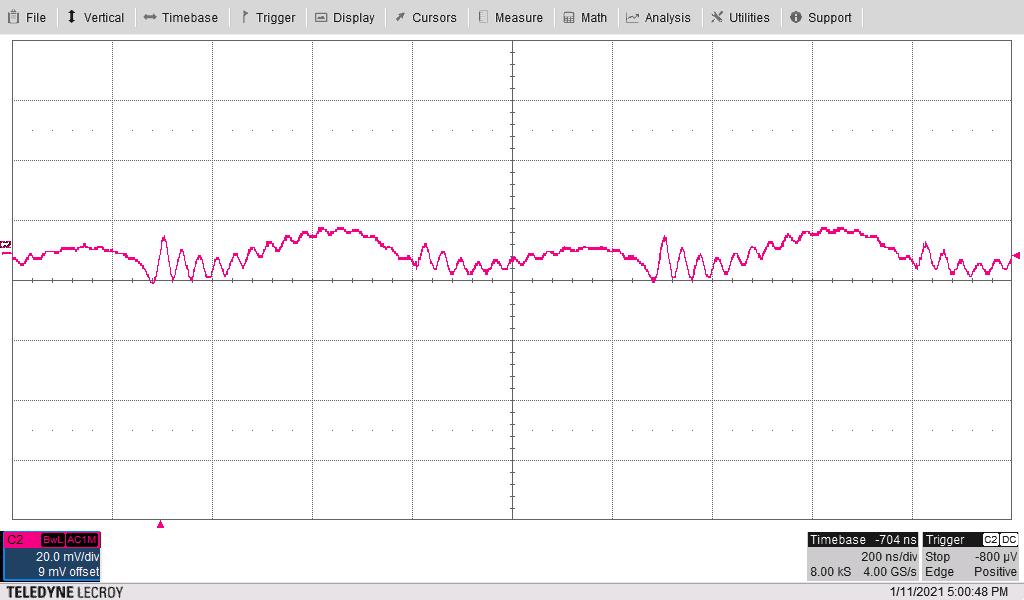
The following waveform shows the –4-V output ripple voltage (AC coupled) measured across C5. The input voltage is 24 V and the 20-V and –4-V outputs are loaded to 100 mA each.
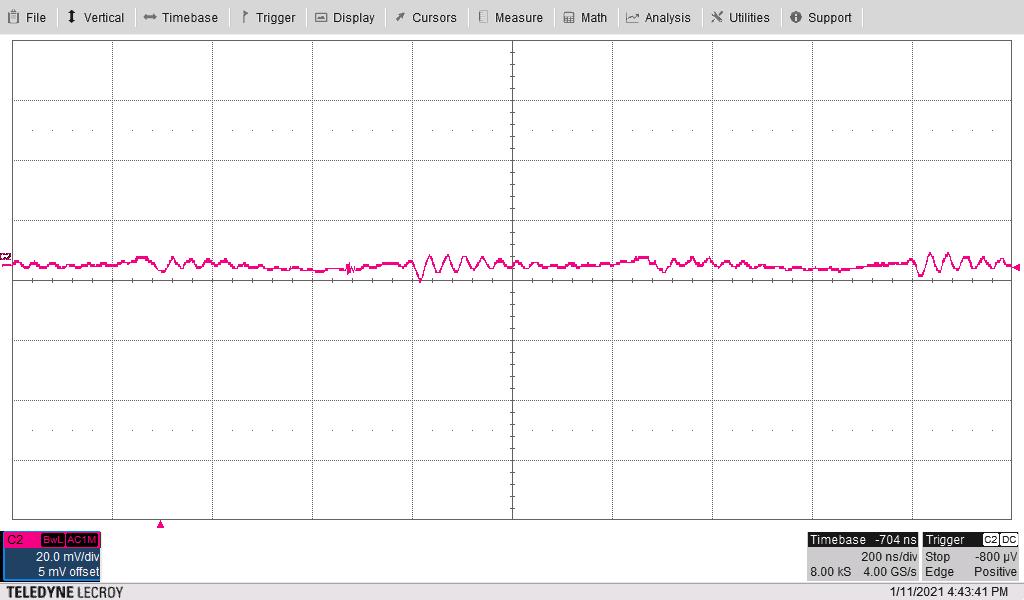
The following waveform shows the –4-V output ripple voltage (AC coupled) measured across C5. The input voltage is 24 V and the 20-V and –4-V outputs are loaded to 300 mA each.