TIDT286 June 2022
2.5.4 2-A Output Current
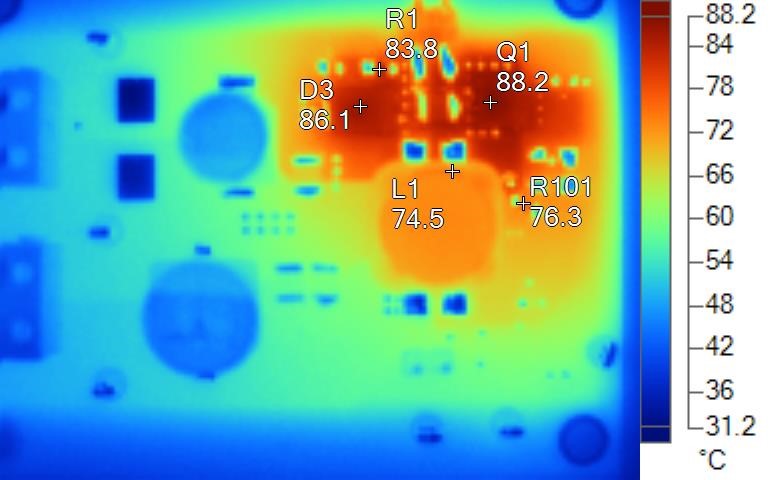 Figure 2-9 IR Photo With 2-A Maximum
Output Current
Figure 2-9 IR Photo With 2-A Maximum
Output CurrentNote:
The thermal measurements show that the power stage itself is able to withstand a continuous load higher than 1 A.
At custom pulsed load, the temperature rise of the power stage is around dT = +20K.