TIDT350 October 2023
- 1
- Description
- Features
- Applications
- 1Test Prerequisites
- 2Testing and Results
- 3Waveforms
2.3 Bode Plots With Dynamic Voltage Scaling
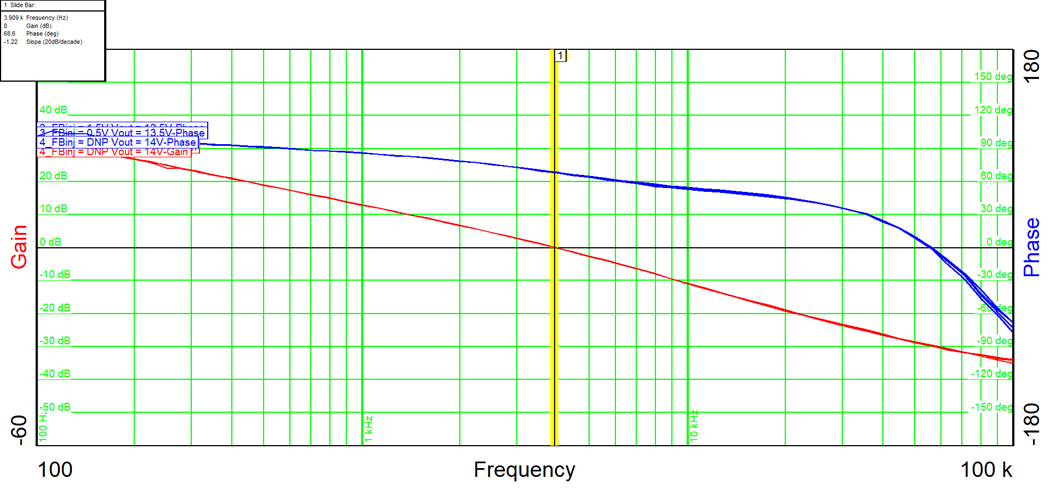 Figure 2-14 Bode Plot
Figure 2-14 Bode PlotTable 2-2 Summary of Measurement 1
| Measurement 1 | |
|---|---|
| Injection voltage TP8 | open |
| Input voltage | 5 V |
| Output voltage | 14 V |
| Load current | full load |
| Bandwidth | 3.9 kHz |
| Phase margin | 68° |
| Gain margin | 29 dB |
Table 2-3 Summary of Measurement 2
| Measurement 2 | |
|---|---|
| Injection voltage TP8 | 3.3 V |
| Input voltage | 5 V |
| Output voltage | 11 V |
| Load current | full load |
| Bandwidth | 3.9 kHz |
| Phase margin | 69° |
| Gain margin | 29 dB |