TIDT356 October 2023
- 1
- Description
- Features
- Applications
- 1Test Prerequisites
- 2Testing and Results
- 3Waveforms
2.1.2.2 PCB Bottom Side
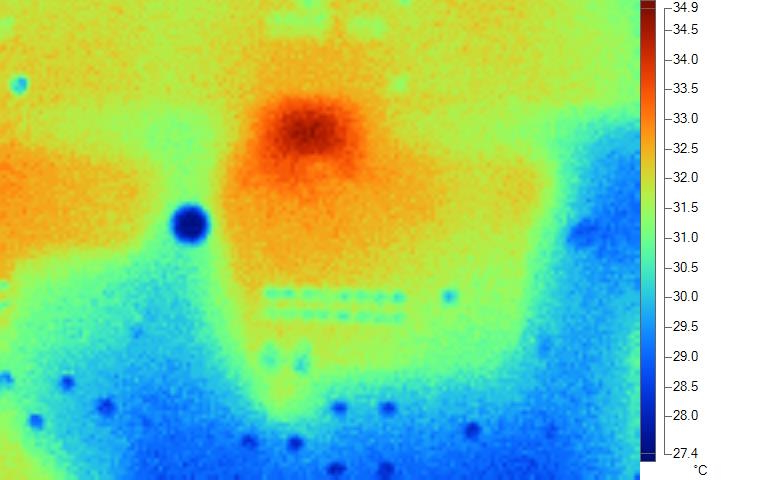 Figure 2-4 PCB Bottom IR Photo for 80%
Duty Cycle Switching
Figure 2-4 PCB Bottom IR Photo for 80%
Duty Cycle SwitchingOn the bottom side of the PCB the area with the largest temperature rise is underneath the IC (U2), where the gate drive signals connect to their respective polygons.