TIDT374 March 2024
2.4 Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Measurement
The graph below shows the conducted emission EMI noise and the EN55022 Class-B Quasi-Peak limits (measurement from the worst-case line). The measurement is not certified. The board was connected to a line impedance stabilization network (LISN) and an isolation transformer; the loads were power resistors. The receiver was set to quasi-peak detector, 10kHz bandwidth. The negative terminal of the converter was connected to the ground of the LISN.
| Input voltage | = 230VAC | |
| Output 1 | = 8V at 1A | |
| Output 2 | = 18V at 0.25A | |
| Output 3 | = 24V at 1.2A |
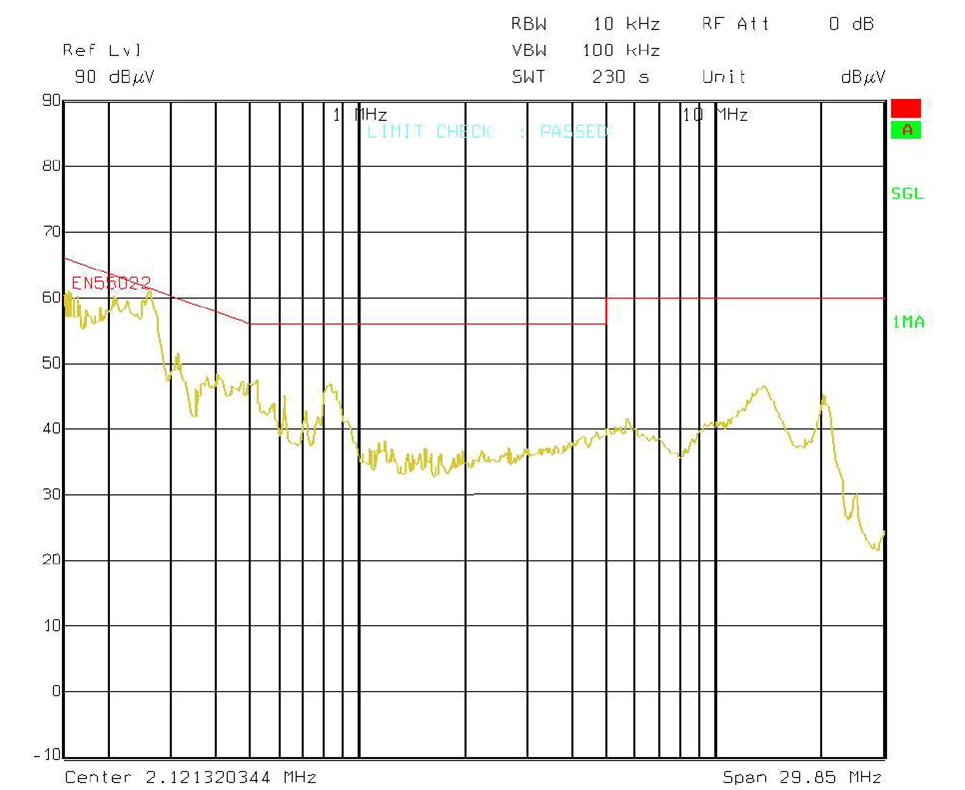 Figure 2-7 EMI
Figure 2-7 EMI