TIDT377 December 2023
2.3.1.2 Bode Plot With Battery at Constant Battery Voltage
Figure 2-4 shows where the battery reached the charge voltage set point; in this case the SEPIC converter runs in constant-voltage mode. VIN was set to 24 V, VOUT to 26 V (on the charger) and the charge current is 0.8 A
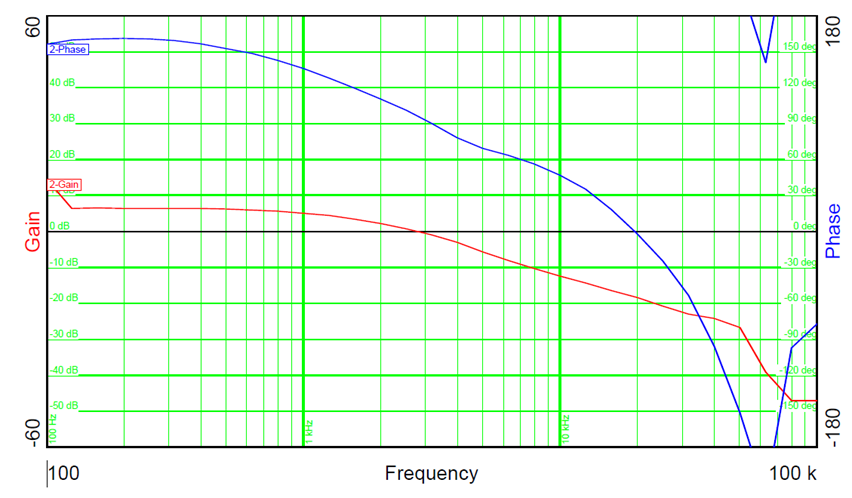 Figure 2-4 Bode Plot With Battery at
Constant Battery Voltage
Figure 2-4 Bode Plot With Battery at
Constant Battery Voltage