TIDUBF0 January 2022
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- 5
- 1System Description
- 2System Overview
- 3Hardware, Testing Requirements, and Test Results
- 4Design and Documentation Support
- 5Tools and Software
- 6Documentation Support
- 7Support Resources
- 8Trademarks
3.3.3 Power Supply Voltage Ripple
To achieve a quality output video stream, the output voltage ripple on the OX01F10 and DS90UB933-Q1 supplies must be low so that it does not affect the integrity of the high-speed data and internal PLL clocks. Measurements for 3.8-V, 3.3-V, 1.8-V, and 1.1-V rails are shown in Figure 3-6, Figure 3-7, and Figure 3-8, respectively. The rails that impact imager performance are the 3.3-V and 1.1-V rails as they are responsible for providing a clean analog rail and digital supply. The 3.8-V rail powers the entire system and also has excellent ripple performance of 0.4%. As measured, the 3.3-V and 1.1-V rails have a ripple performance of 0.1% and 0.7%, respectively. The 1.8-V rail is significant to the serializer, because it supplies the VDD and VDD_PLL rails. The 1.8-V rail has great voltage ripple performance at 0.5%. The voltage ripple on all rails is low enough for video output to be successfully transmitted.
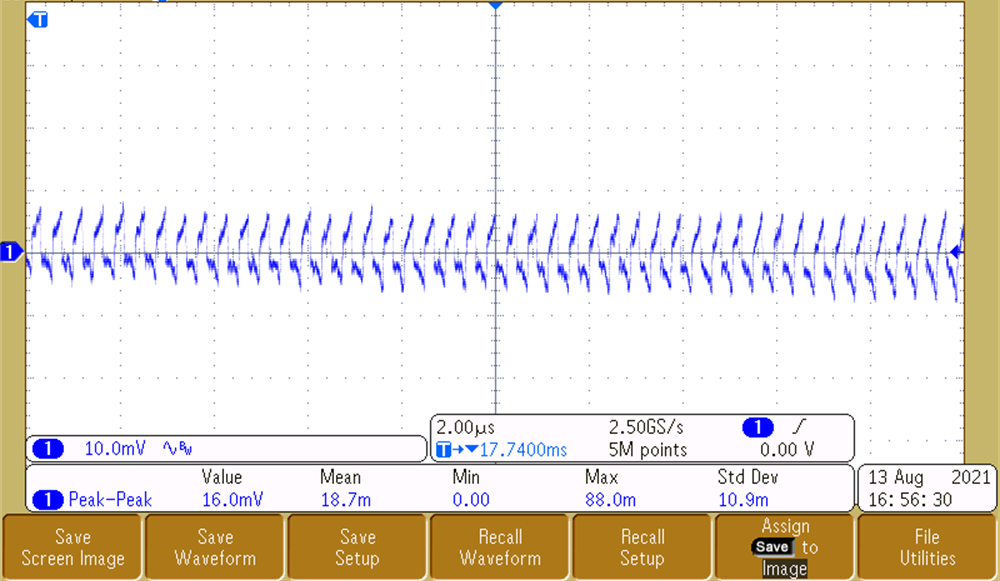 Figure 3-6 Output Voltage Ripple - 3.8 V
Figure 3-6 Output Voltage Ripple - 3.8 V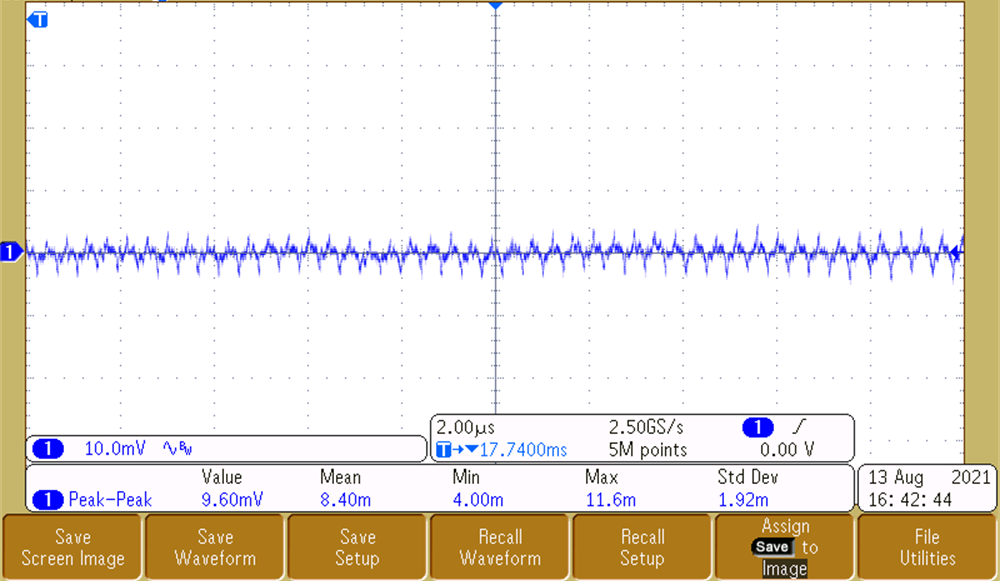 Figure 3-8 Output Voltage Ripple - 1.8 V
Figure 3-8 Output Voltage Ripple - 1.8 V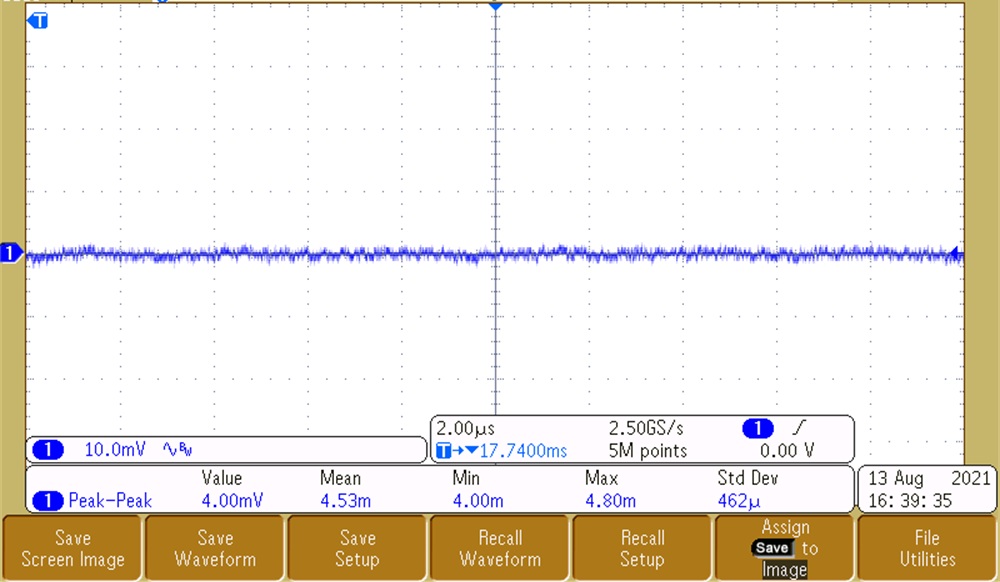 Figure 3-7 Output Voltage Ripple - 3.3 V
Figure 3-7 Output Voltage Ripple - 3.3 V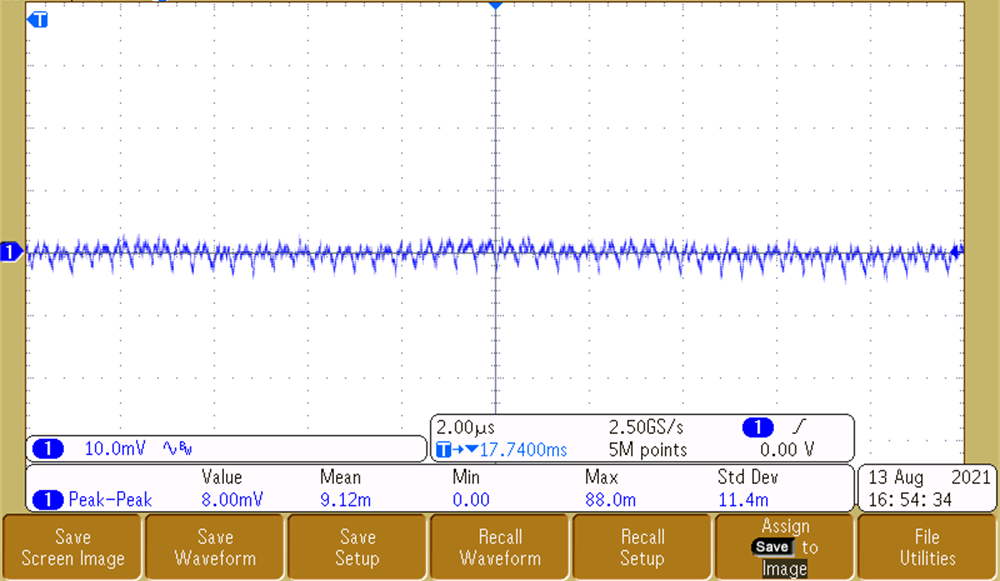 Figure 3-9 Output Voltage Ripple - 1.1 V
Figure 3-9 Output Voltage Ripple - 1.1 V