TIDUD61E October 2020 – April 2021
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- 5
- 1System Description
- 2System Overview
-
3Hardware, Software, Testing Requirements, and Test Results
- 3.1
Required Hardware and Software
- 3.1.1 Hardware
- 3.1.2
Software
- 3.1.2.1 Opening Project Inside CCS
- 3.1.2.2 Project Structure
- 3.1.2.3 Using CLA on C2000 MCU to Alleviate CPU Burden
- 3.1.2.4 CPU and CLA Utilization and Memory Allocation
- 3.1.2.5
Running the Project
- 3.1.2.5.1 Lab 1: Open Loop, DC (PFC Mode)
- 3.1.2.5.2 Lab 2: Closed Current Loop DC (PFC)
- 3.1.2.5.3 Lab 3: Closed Current Loop, AC (PFC)
- 3.1.2.5.4 Lab 4: Closed Voltage and Current Loop (PFC)
- 3.1.2.5.5 Lab 5: Open loop, DC (Inverter)
- 3.1.2.5.6 Lab 6: Open loop, AC (Inverter)
- 3.1.2.5.7 Lab 7: Closed Current Loop, DC (Inverter with resistive load)
- 3.1.2.5.8 Lab 8: Closed Current Loop, AC (Inverter with resistive load)
- 3.1.2.5.9 Lab 9: Closed Current Loop (Grid Connected Inverter)
- 3.1.2.6 Running Code on CLA
- 3.1.2.7
Advanced Options
- 3.1.2.7.1 Input Cap Compensation for PF Improvement Under Light Load
- 3.1.2.7.2 83
- 3.1.2.7.3 Adaptive Dead Time for Efficiency Improvements
- 3.1.2.7.4 Phase Shedding for Efficiency Improvements
- 3.1.2.7.5 Non-Linear Voltage Loop for Transient Reduction
- 3.1.2.7.6 Software Phase Locked Loop Methods: SOGI - FLL
- 3.2 Testing and Results
- 3.1
Required Hardware and Software
- 4Design Files
- 5Software Files
- 6Related Documentation
- 7About the Author
- 8Revision History
3.1.2.5.3.3 Running Code
- The project is programmed to wait for input voltage to exceed approximately 70Vrms to drive the in rush relay, and clear the trip.
- Run the project by clicking
 .
. - Now apply an input voltage of approximately 120 V, the board comes out of the undervoltage condition and inrush relay is driven. The trip clears, and a small amount of current of approximately 0.55-A RMS is drawn. The watch window looks similar to Figure 3-22. The bus voltage is close to 180 V.
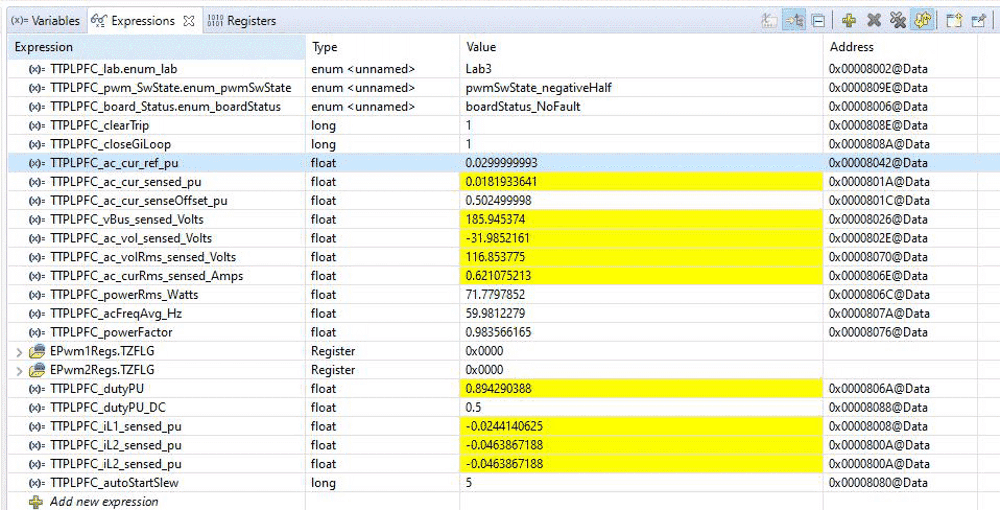 Figure 3-22 Watch Expression, Lab 3, AC After Closed Current Loop Operation Begins
Figure 3-22 Watch Expression, Lab 3, AC After Closed Current Loop Operation Begins - Now slowly increase TTPLPFC_ac_cur_ref_pu to 0.14, that is, 2.4-A input, and the bus voltage rises to 380 V. The voltage and current waveform are shown in Figure 3-23.
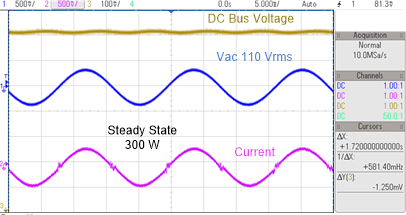 Figure 3-23 Input AC input, Current and Output DC Voltage Waveform
Figure 3-23 Input AC input, Current and Output DC Voltage Waveform - SFRA is integrated in the software of this build to verify the designed compensator provides enough gain and phase margin by measuring on hardware. To run the SFRA keep the project running, and from the cfg page, click on the SFRA icon. SFRA GUI appears.
- Select the options for the device on the SFRA GUI. For example, for F28377D select floating point. Click on Setup Connection. On the pop-up window uncheck the boot on connect option, and select an appropriate COM port. Click OK. Return to the SFRA GUI, and click Connect.
- The SFRA GUI connects to the device. A SFRA sweep can now be started by clicking Start Sweep. The complete SFRA sweep takes a few minutes to finish. Activity can be monitored by seeing the progress bar on the SFRA GUI and also checking the flashing of blue LED on the back on the control card that indicates UART activity. Once complete, a graph with the open loop plot appears, Figure 3-24. This is similar to the plot seen under DC conditions; however, some additional noise is visible due to AC harmonic frequencies close to the measured frequencies. The BW, PM, and GM numbers are very similar to the DC case. Note the graph shown in Figure 3-24 was taken with direct grid AC input. When using AC source interaction of the AC source output, impedance can be observed, which can affect the control margins.
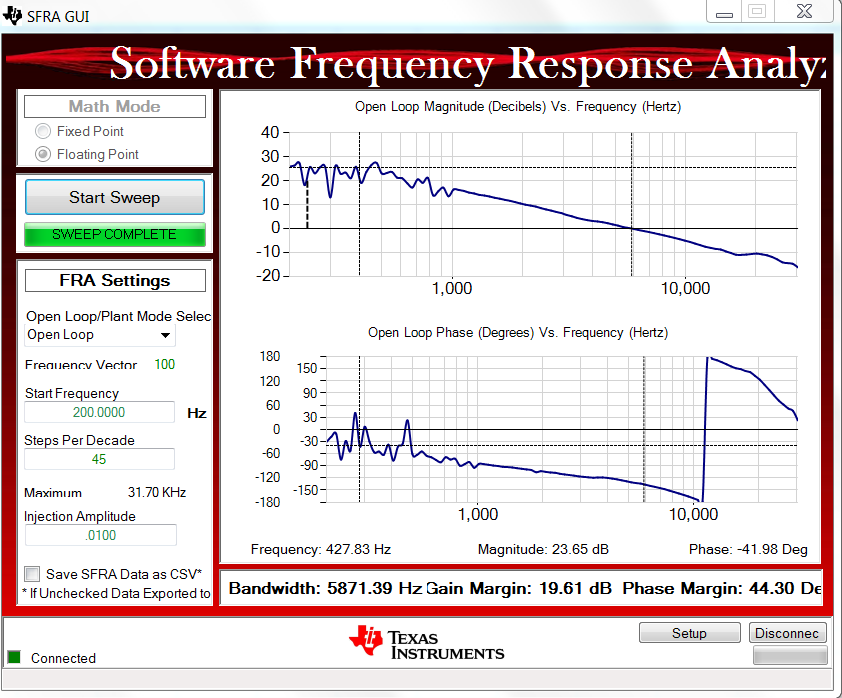 Figure 3-24 SFRA Run, Closed Current Loop, Open Loop Gain
Figure 3-24 SFRA Run, Closed Current Loop, Open Loop Gain - To bring the system to a safe stop, switch off the output from the AC power supply thus bring the input AC voltage down to zero, observe the TTPLPFC_vBus_sensed_Volts comes down to zero as well.
- Fully halting the MCU when in real-time mode is a two-step process. First halt the processor by using the Halt button on the toolbar (
 ) or by using Target → Halt. Then take the MCU out of real-time mode by clicking on
) or by using Target → Halt. Then take the MCU out of real-time mode by clicking on  . Finally, reset the MCU (
. Finally, reset the MCU ( ) .
) . - Close the CCS debug session by clicking on Terminate Debug Session (Target → Terminate all).
