TIDUED6B august 2018 – april 2023
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- Design Images
- 1System Description
- 2System Overview
- 3Hardware, Software, Testing Requirements, and Test Results
- 4Design Files
- 5Software Files
- 6Related Documentation
- 7Trademarks
- 8About the Author
- 9Revision History
2.2.1.1 mmWave Sensor People Counting
The implementation of the people-counting application example in the signal-processing chain consists of the following blocks, implemented as DSP code executing on the C674x core in the IWR6843. The tracking module runs on the ARM® Cortex®-R4F processor.
- Range Processing:
- For each antenna, 1D windowing, and 1D fast Fourier transform (FFT)
- Range processing is interleaved with the active chirp time of the frame
- Capon beam forming:
- Static clutter removal
- Co-variance matrix generation, inverse-angle spectrum generation, and integration is performed
- Outputs range-angle heat map
- CFAR detection algorithm:
- Two-pass, constant false-alarm rate
- First pass cell averaging smallest of CFAR-CASO in the range domain, confirmed by second pass cell averaging smallest of CFAR-CASO in the angle domain, to find detection points.
- Doppler estimation:
- For each detected [range, azimuth] pair from the detection module, estimate the Doppler by filtering the range bin using Capon beam-weights, and then run a peak search over the FFT of the filtered range bin.
- Tracking:
- Perform target localization, and report the results.
- Output of the tracker is a set of trackable objects with certain properties like position, velocity, physical dimensions, and point density
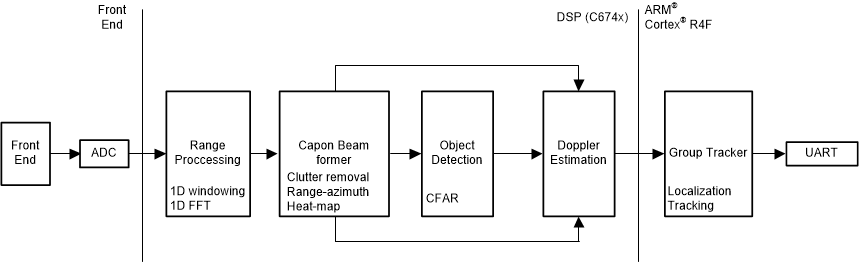 Figure 2-2 People-Counting Application Block Diagram
Figure 2-2 People-Counting Application Block Diagram