TIDUEJ6A January 2019 – July 2022
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- 5
- 1System Description
- 2System Overview
- 3Hardware, Software, Testing Requirements, and Test Results
- 4Design and Documentation Support
- 5About the Authors
- 6Revision History
2.2.1 Flow Measurement
The ultrasonic gas-flow meter design is based on the principle of ToF measurement. This measurement refers to the time it takes a signal to travel from a transmitting transducer to a receiving transducer.
Figure 3-2 shows a flow pipe.
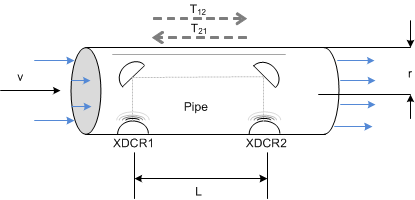 Figure 3-2 ToF in Flow Meter
Figure 3-2 ToF in Flow MeterThe propagation time of a signal traveling from the first transducer (XDR1) to the second transducer (XDR2) is given by T12. T21 represents the propagation time in the opposite direction. Calculate these timings according to the following equations as a function of the velocity of the ultrasound in gas and the velocity of gas flow. Because this length is much larger than the radius of the pipe, r, the propagation length of the wave that is perpendicular to the flow is considered to be negligible in the following analysis.
where
- c is the velocity of the ultrasound in the medium.
- v is the velocity of gas flow.
- L is the propagation length of the pipe along the flow of gas.
Use Equation 1 through Equation 3 to derive the velocity of gas flow (v), which is possible even without knowing the velocity of the ultrasound in the medium (c).
This reference design calculates gas flow assuming that the velocity of the ultrasound is unknown. In this case, derive Equation 4 from Equation 1 and Equation 2 by eliminating c .
Using Equation 4, calculate the actual propagation times, T12 and T21, in the two directions along the cross section of the pipe.