TIDUEK9E November 2018 – April 2020
3.2.2 Test Results
Before running the navigation demo, close all of the ROS terminal consoles for both the AM572x EVM and the Ubuntu Linux box. Then, follow the steps below to run the demo.
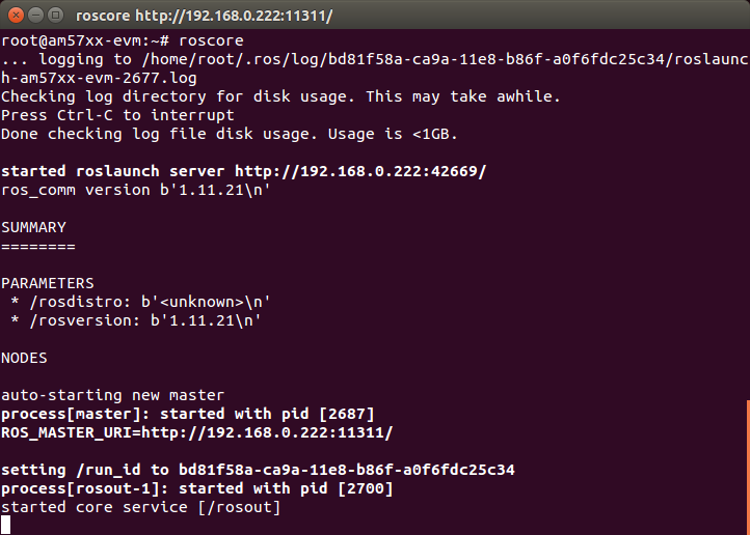
- Open the first SSH terminal to the AM572x EVM and run roscore (see Figure 7).
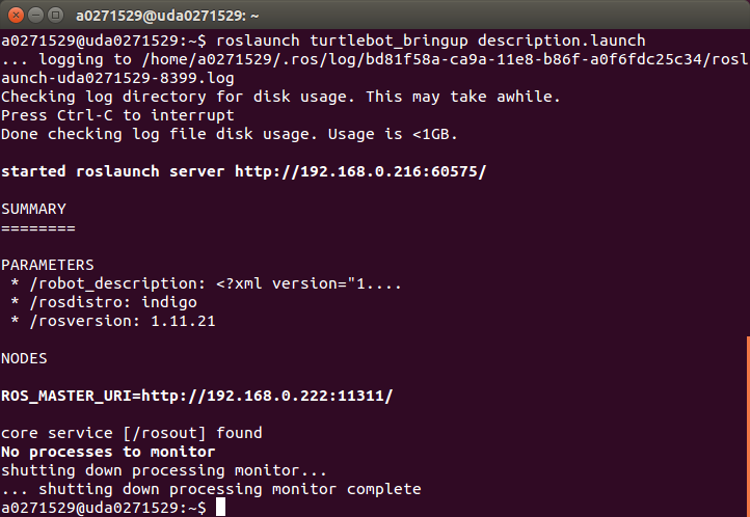
- Open a terminal console on the Ubuntu Linux box, and launch the robot description (see Figure 8).
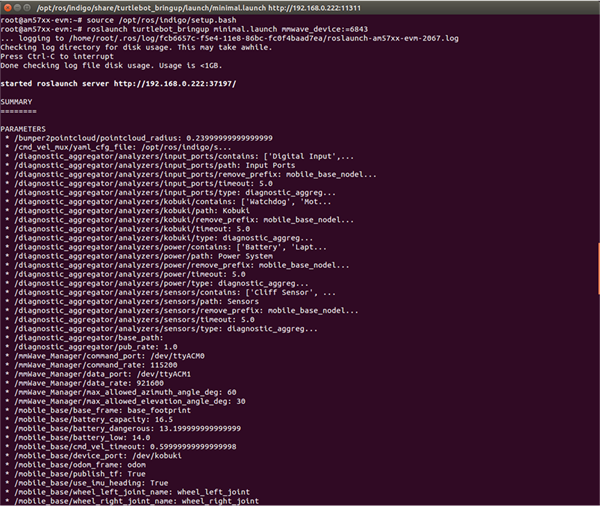
- Open the second SSH terminal to the AM572x EVM. Run the minimal.launch of turtlebot_bringup to set up the mmWave sensor and the Kobuki. Set the mmwave_device to "6843" at the end of this command. Section 3.2.2 shows the beginning of running minimal.launch, and Figure 10 shows the end of minimal.launch.
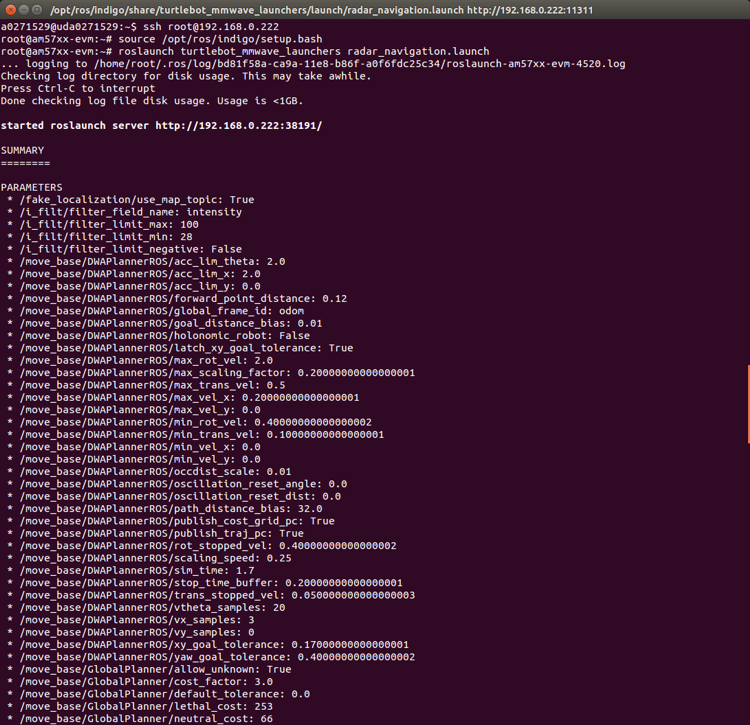
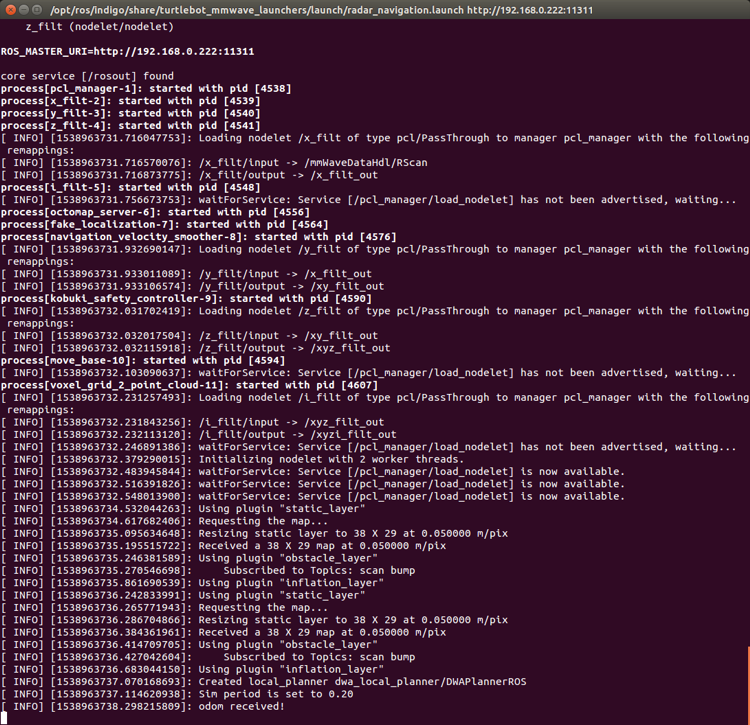
- Open the third SSH terminal to the AM572x EVM, and launch the radar navigation with the mmWave sensor. Figure 11 shows the beginning of running radar_navigation.launch, and Figure 12 shows the end of radar_navigation.launch.
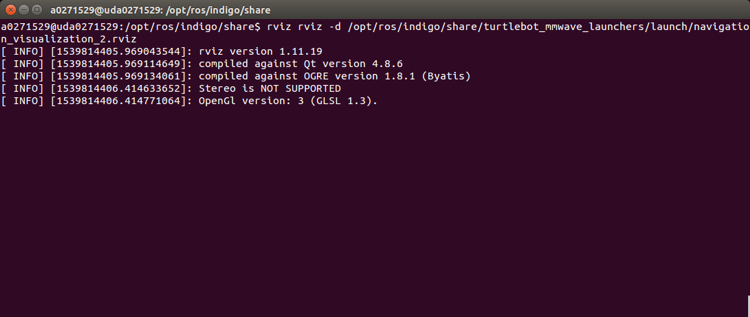
- Open a terminal console on the Ubuntu Linux box, and launch the Rviz (navigation_visualization_2.rviz) for real-time visualization of the navigation. Figure 13 shows the console output and Figure 14 shows the Rviz display.
- Start navigation on the AM572x EVM by setting the initial position and the goal to be reached
source /opt/ros/indigo/setup.bash
roscore
roslaunch turtlebot_bringup description.launch
NOTE
For other compatible mmWave sensors, this step will differ. Refer to Section 3.2.2.1.2 for additional steps required to enable support for other mmWave EVMs.
source /opt/ros/indigo/setup.bash
roslaunch turtlebot_bringup minimal.launch mmwave_device:=6843
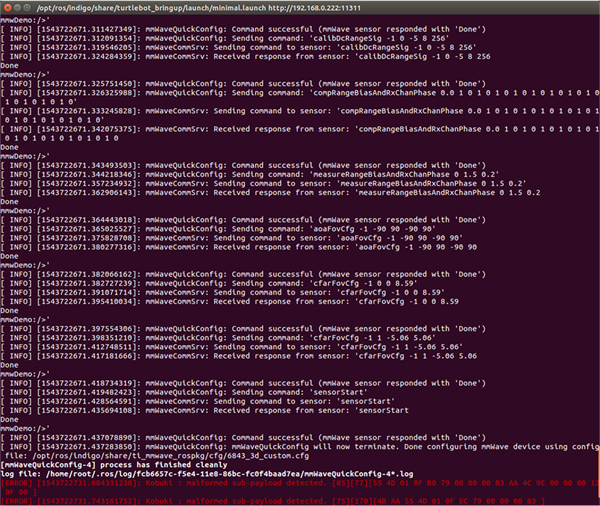
After the Kobuki and the mmWave sensor are configured, you might see this periodic “Kobuki : malformed subpayload detected” error message. These error messages come from the Kobuki driver and do not affect the operation of the demo.
source /opt/ros/indigo/setup.bash
roslaunch turtlebot_mmwave_launchers radar_navigation.launch
rosrun rviz rviz -d
/opt/ros/indigo/share/turtlebot_mmwave_launchers/launch/navigation_v
isualization_2.rviz
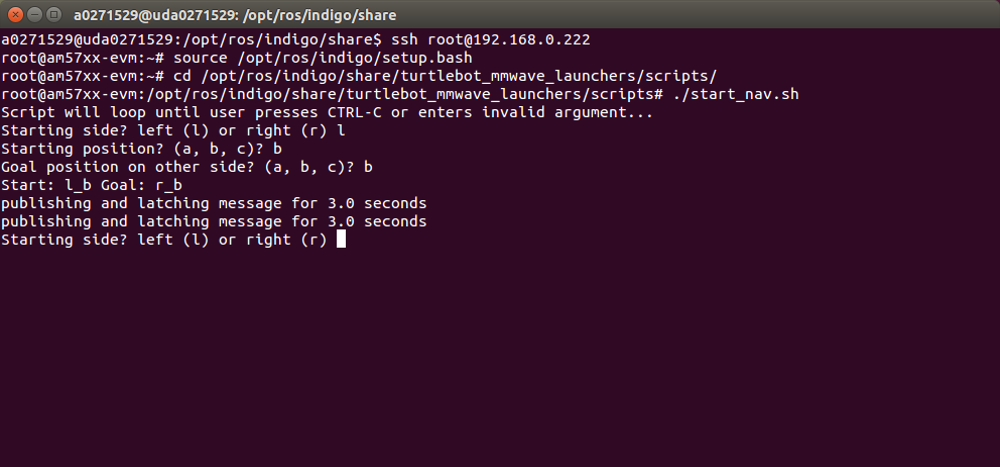
The demo uses a pre-defined size 4-by-6 feet map file, with three locations (a, b, and c for top, middle, and bottom, respectively) on each side (left and right).Open the fourth SSH terminal to the AM572x EVM, and set the initial position with the side (left or right) and the location (a, b, or c), and then, set the location (a, b, or c) on the other side as the goal, by running the scripts below (see Figure 15):
source /opt/ros/indigo/setup.bash
cd /opt/ros/indigo/share/turtlebot_mmwave_launchers/scripts/
./start_nav.sh
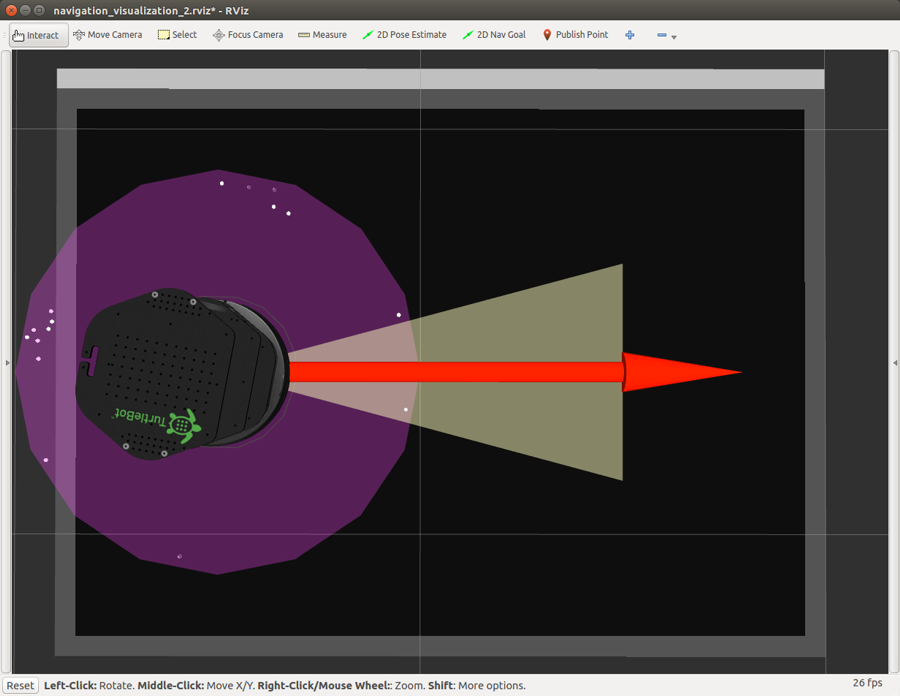
First, the Kobuki has the initial left-side middle-point B position set (see Figure 16).
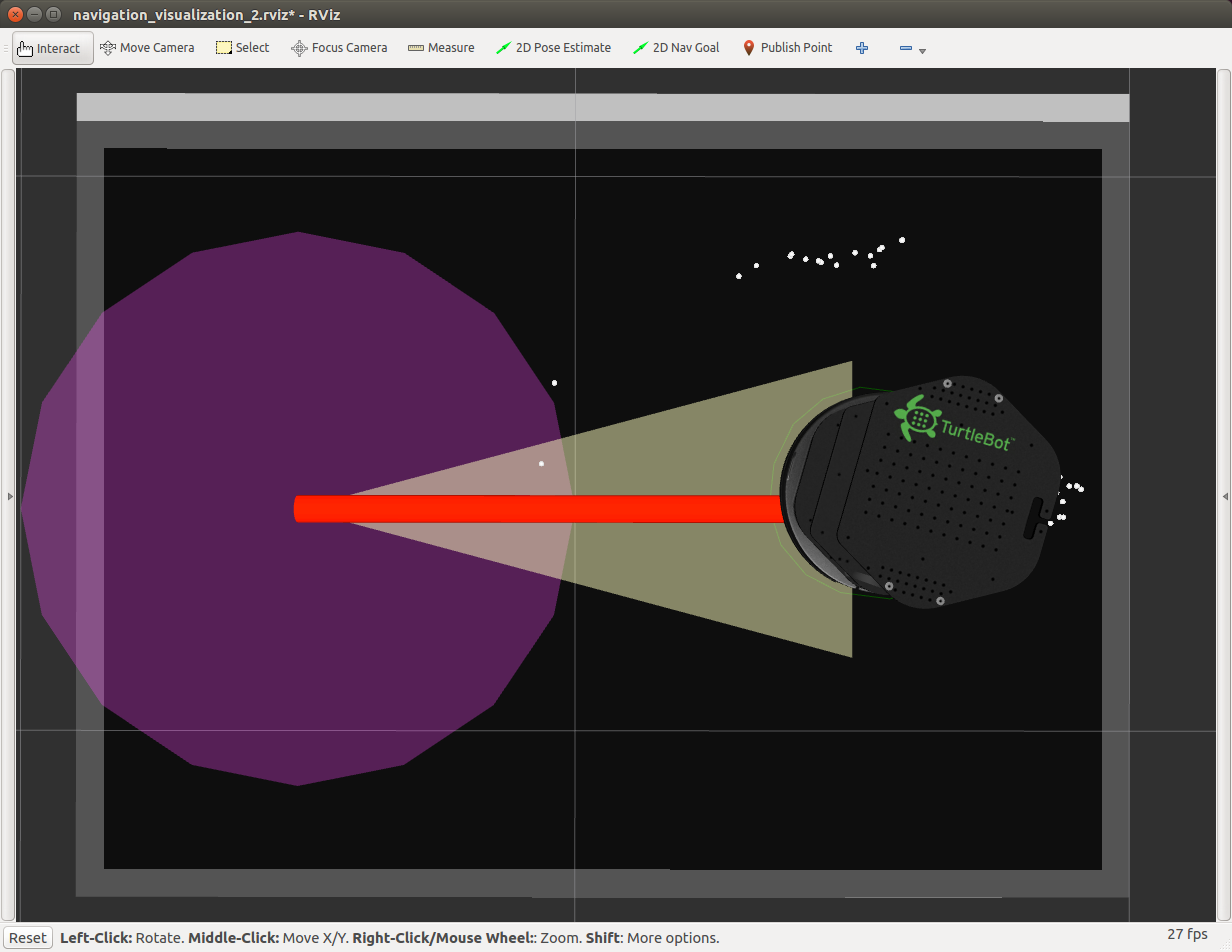
Then, the Kobuki navigates to the right-side middle-point B goal (see Figure 17), following the shortest path available. After it reaches the goal, the Kobuki rotates and faces toward the initial position.
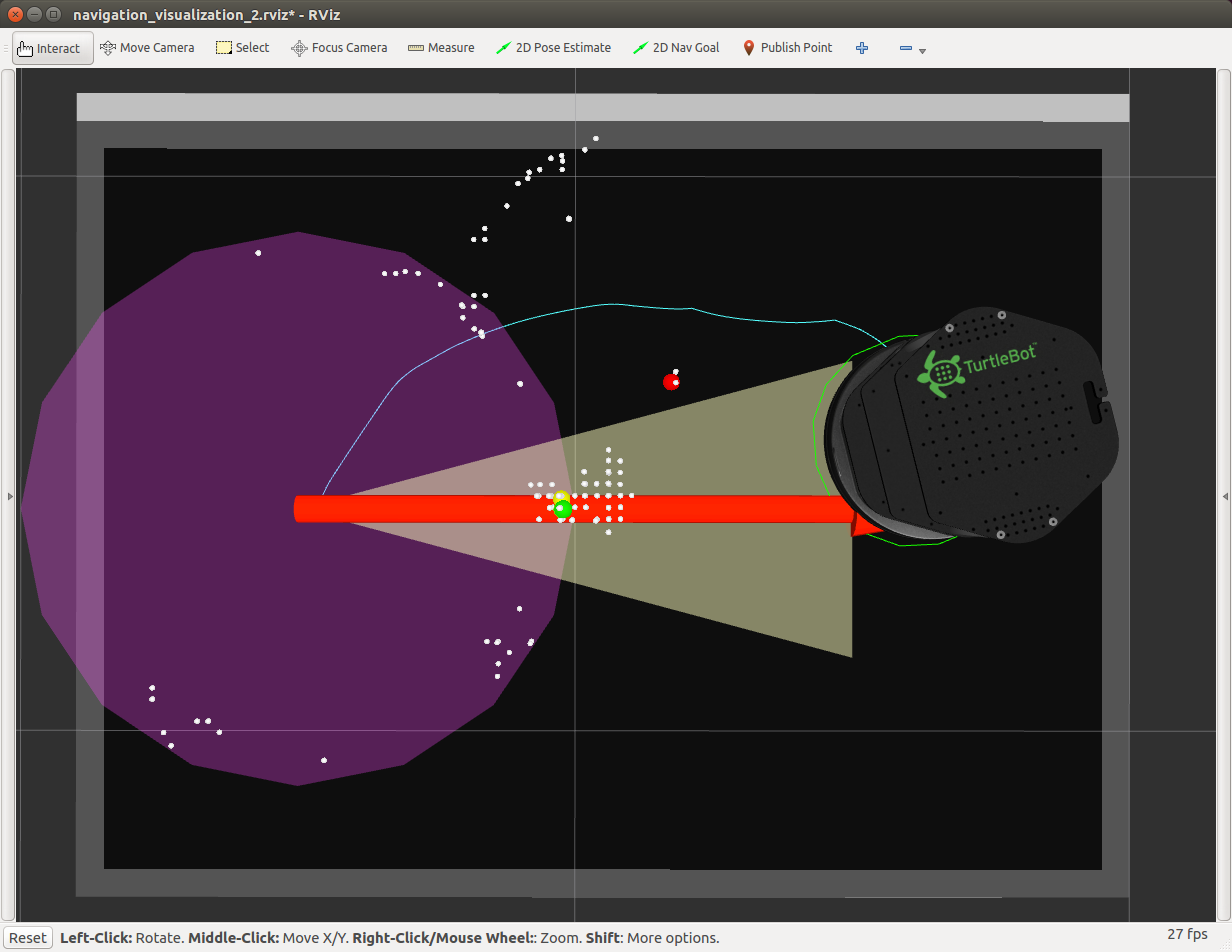
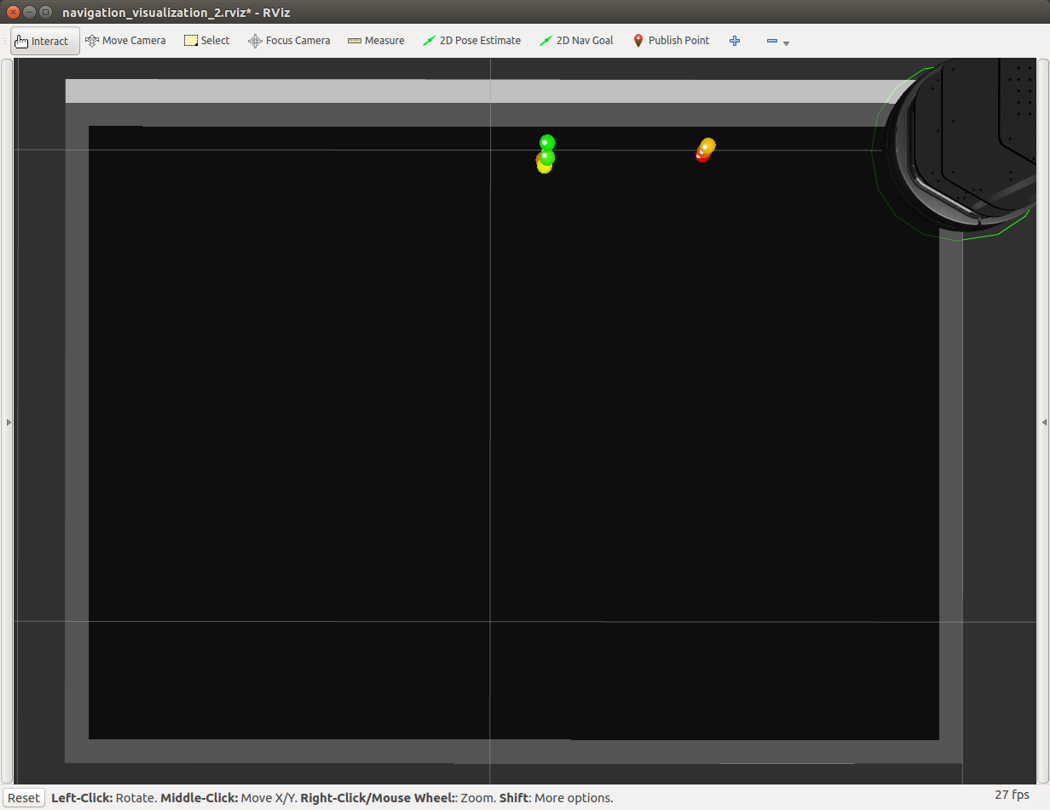
If there are objects between the initial position and the goal, the mmWave sensor detects them (shown as red/yellow/green circles in Rviz as in Figure 18). With the radar sensing data, a new path (the thin blue line connecting the initial position and the goal) is found in real-time to avoid the obstacles, demonstrating the "sense and avoid" capability of the autonomous navigation in this reference design (see Figure 18).
To re-run the navigation demo, simply specify the starting side/position and the goal position from the console of "./start_nav.sh"(see Figure 15).