TIDUET0A November 2019 – July 2020
1 System Description
In the ECall application, when the main battery voltage is high, all of the related circuits in the ECall is supplied by the main battery through a buck converter. When the main battery voltage drops to a low level, the buck converter browns out, the back-up battery starts working, it supplies the equipment through a boost converter. Figure 1-1 shows a traditional ECall block diagram. Besides a high-voltage buck converter, it uses two boost converters and one charger and because of the two boost converters, this is redundant and reduces efficiency.
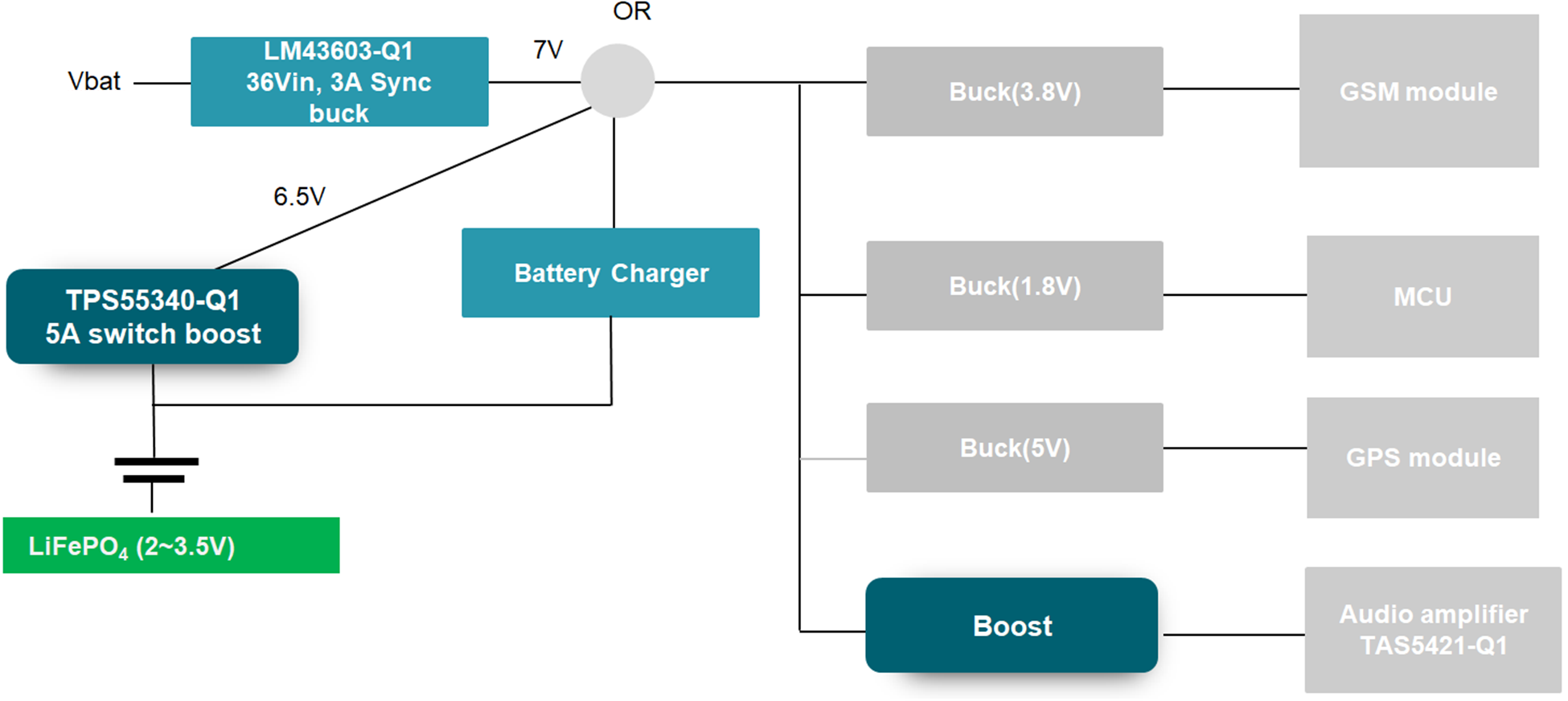 Figure 1-1 Traditional ECall Block
Diagram
Figure 1-1 Traditional ECall Block
DiagramThe TIDA-050031 takes into consideration cost and the size while avoiding the redundancy of a traditional ECall block diagram in Figure 1. This reference design delivers a simple and low cost backup power circuit for the automotive ECall application. The structure is very simple. Only one boost converter is used in the circuit. The boost converter TPS61088-Q1 can output 8 V/1.6A with high efficiency at 2 V input voltage. So the minimum backup battery voltage can be down to 2 V. Besides extending the lifetime of the backup battery, the TIDA-050031 is also flexible and less redundancy.