TIDUEX5 October 2020
- Description
- Resources
- Applications
- Features
- 5
- 1System Description
- 2System Overview
-
3Hardware, Software, Testing Requirements, and
Test Results
- 3.1
Hardware Requirements
- 3.1.1 Getting Started
- 3.1.2 Testing and Results
- 3.1
Hardware Requirements
- 4Design and Documentation Support
3.1.2.2 Over-Voltage Protection Clamping-Mode
Over voltage clamping mode is implemented by shorting together the j 1 connector. By doing so the OV pin will be connected to the resistor divider which is connected to the source of the HGATE driven MOSFETs.
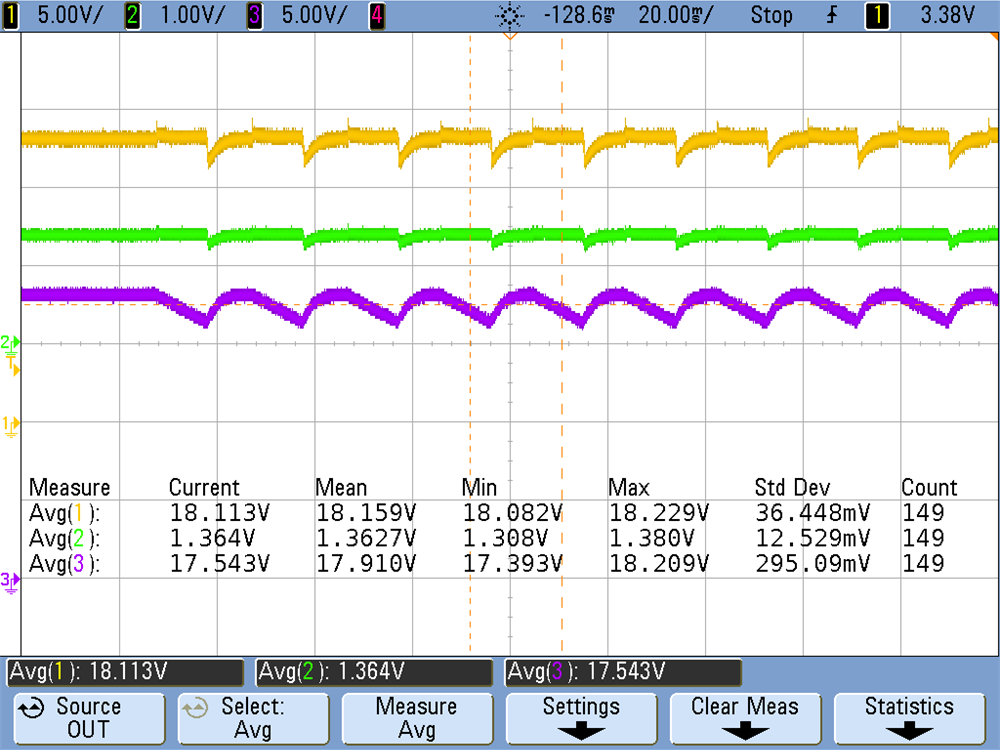 Figure 3-2 Over-Voltage Protection
Clamping Mode
Figure 3-2 Over-Voltage Protection
Clamping ModeFigure 3-2 shows over-voltage clamping with the HGATE MOSFETs switching to regulate the output. By having the OV pin connected to the resistor divider at the source of the HGATE driven MOSFETs, the MOSFETs will switch on and off clamping the voltage at the output.