TIDUEY8 March 2023
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- 5
- 1System Description
-
2System Overview
- 2.1 Design Block Diagram
- 2.2 Highlighted Products
- 2.3
Design Steps
- 2.3.1 Multiple JESD204B Synchronization Requirements
- 2.3.2 Clock Tree Design
- 2.3.3 Power Management
- 3Getting Started Hardware and Software
- 4Testing and Results
- 5Design and Documentation Support
- 6About the Authors
3.2.4 TSW14J57EVM Evaluation Programming Sequence
The HSDC Pro software interfaces with the TSW14J57EVM to capture and analyze the digital data from the ADC12DJ3200-SP in SNR measurement and skew measurement.
To operate the TSW14J57EVM tools in primary and secondary mode for skew measurement, follow the README note available in the HSDC TIDA01019x GUI software folder. Next, include the updated firmware, .ini files, and other settings in HSDC Pro GUI folder.
Follow the TSW14J57 JESD204B High-Speed Data Capture and Pattern Generator Card user’s guide for HSDC Pro setup and to capture and analyze the data. The following steps show how to configure the HSDC Pro GUI for capturing the data and operating in primary and secondary mode.
- Select ADC12DJxx00_JMODE3_F&K_1_32_sysref.ini to interface with the ADC12DJ3200EVM-CVAL GUI for JMODE3
- Set the ADC sampling frequency to 3.2 GHz
- Set the ADC input target frequency
- For SNR measurement, click on the Capture tab and the data is captured on the screen
- For skew measurement, configure one HSDC Pro in primary mode (Test Options) and another in secondary mode.
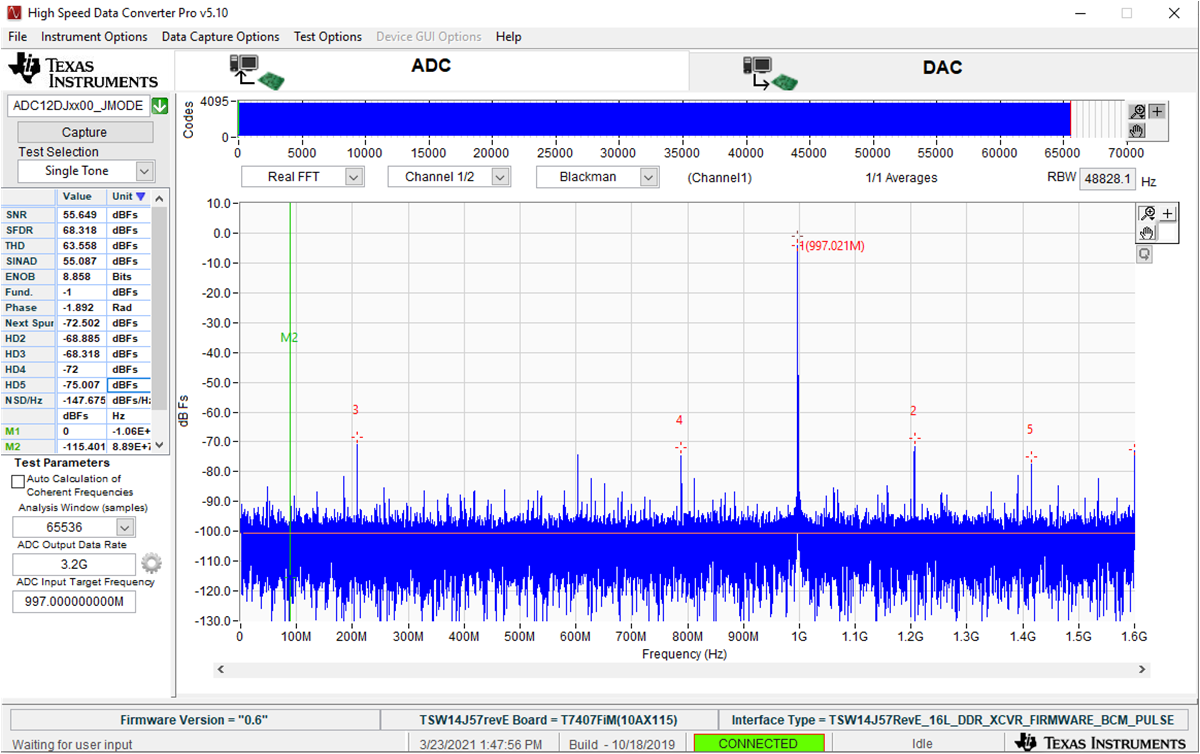 Figure 3-7 First Test of the Setup by
Capturing a Spectrum
Figure 3-7 First Test of the Setup by
Capturing a Spectrum