TIDUEY8 March 2023
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- 5
- 1System Description
-
2System Overview
- 2.1 Design Block Diagram
- 2.2 Highlighted Products
- 2.3
Design Steps
- 2.3.1 Multiple JESD204B Synchronization Requirements
- 2.3.2 Clock Tree Design
- 2.3.3 Power Management
- 3Getting Started Hardware and Software
- 4Testing and Results
- 5Design and Documentation Support
- 6About the Authors
4.2.1 Phase Noise Measurement Results
TIDA-010191 clocking board LMX2615-SP devices show almost the same results since both are identical on the board. Table 4-1 shows the measured phase noise performance of the LMX2615-SP at various clock frequencies in the clock board. Measured phase noise plots are shown in Figure 4-5 through Figure 4-7.
Table 4-1 Measured Phase Noise
| OUTPUT FREQUENCY (GHz) | CONDITION | LMX2615-SP DATA SHEET PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz) | TIDA-010191 MEASURED PHASE NOISE (dBc/Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3.5 | 10-kHz offset | –111.5 | –112.2 |
| 100-kHz offset | –115.3 | –114.4 | |
| 1-MHz offset | –121.9 | –120.6 | |
| 10-MHz offset | –146.3 | –146.7 | |
| 40-MHz offset | –150.9 | –151.5 | |
| 9.0 | 10-kHz offset | –104.9 | –110 |
| 100-kHz offset | –111.4 | –111.8 | |
| 1-MHz offset | –121.9 | –122.3 | |
| 10-MHz offset | –146 | –147 | |
| 40-MHz offset | –153 | –154 | |
| 15.0 | 10-kHz offset | –100.8 | –106.1 |
| 100-kHz offset | –107.2 | –107.7 | |
| 1-MHz offset | –114.3 | –114 | |
| 10-MHz offset | –140.4 | –140.8 | |
| 40-MHz offset | –151 | –149 |
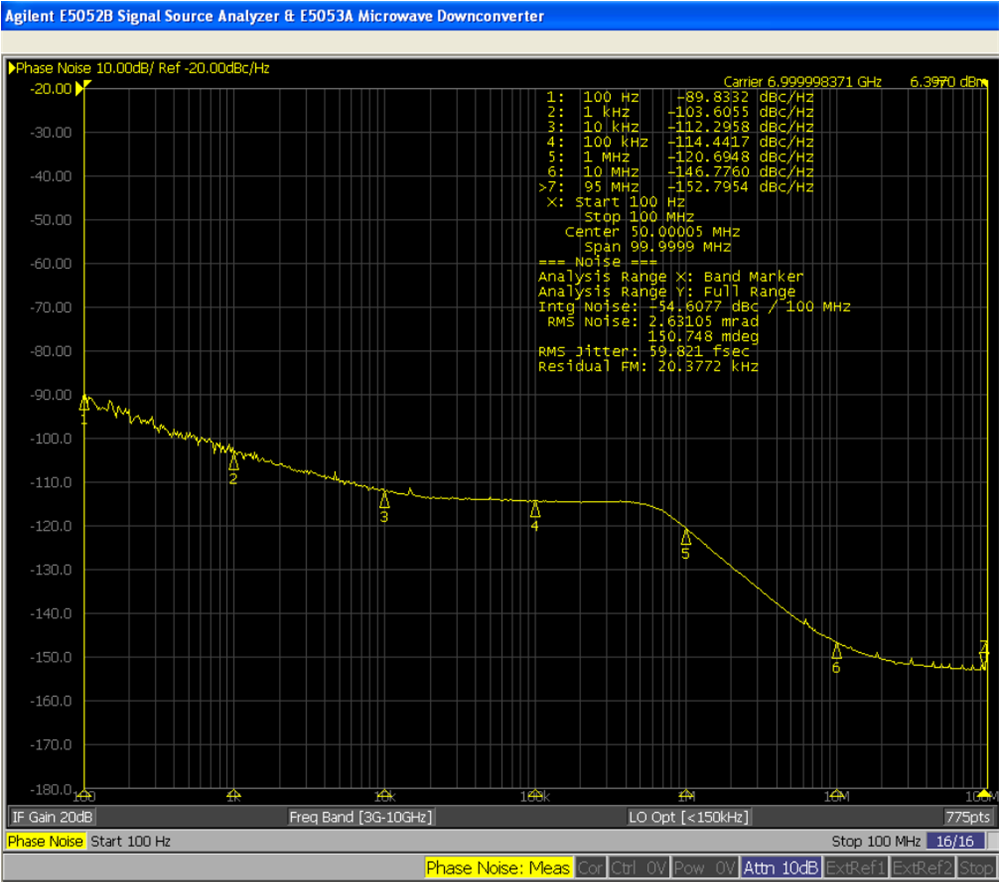 Figure 4-5 Phase Noise at 7-GHz Carrier Frequency
Figure 4-5 Phase Noise at 7-GHz Carrier Frequency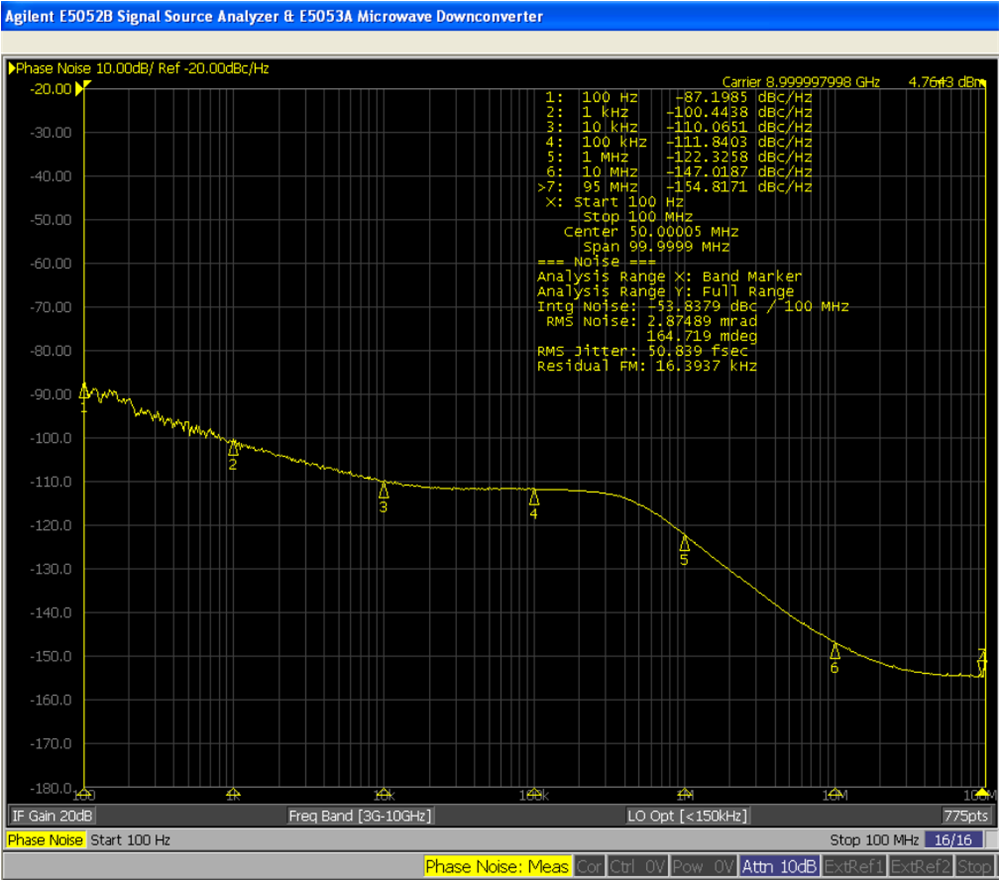 Figure 4-6 Phase Noise at 9-GHz Carrier Frequency
Figure 4-6 Phase Noise at 9-GHz Carrier Frequency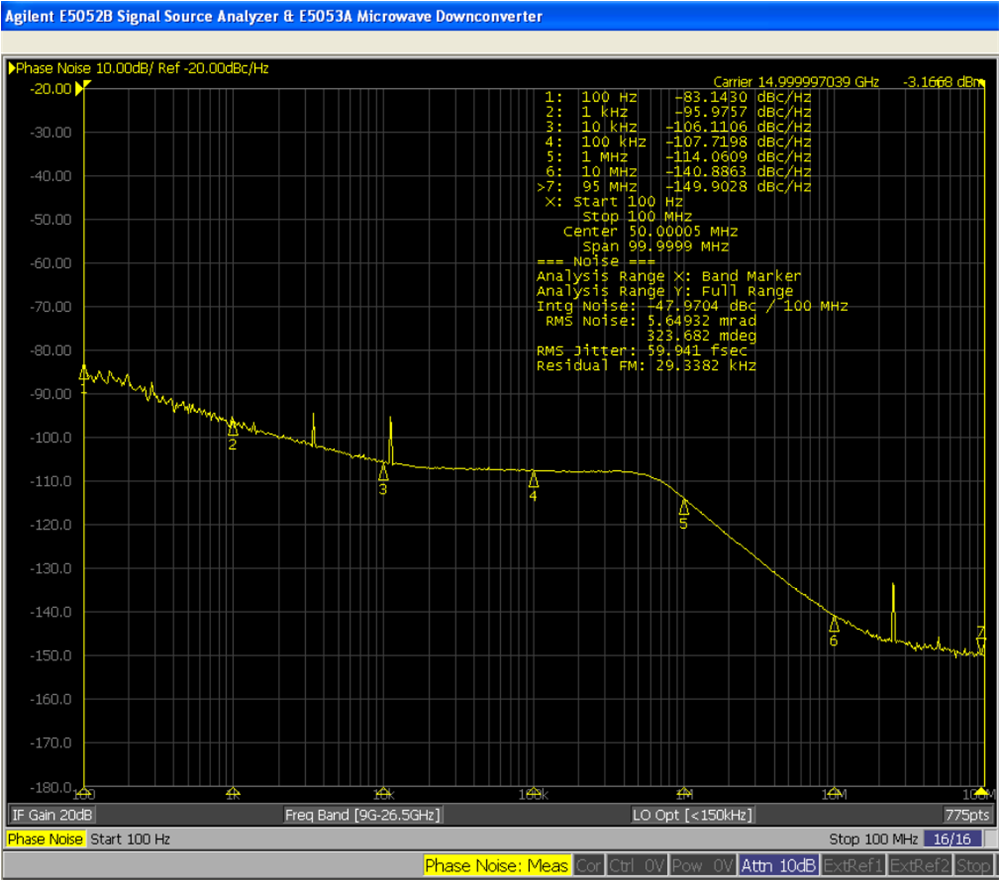 Figure 4-7 Phase Noise at 15-GHz Carrier
Frequency
Figure 4-7 Phase Noise at 15-GHz Carrier
Frequency