TIDUEY9 April 2021
2 System Overview
TI’s radar mmWave integrated chips (ICs) include hardware and firmware elements to enable monitoring of its mmWave, analog and digital sections. Most of digital elements of device have built in diagnostic capability.
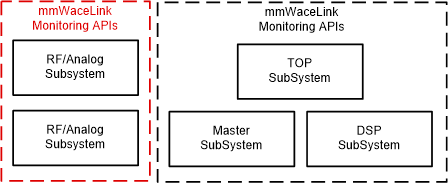 Figure 2-1 mmWave Sensor Monitor &
Diagnostic
Figure 2-1 mmWave Sensor Monitor &
DiagnosticAnalog Subsystem contains the RF and Analog functionality of the device. It has two/three transmitters and four Receiver chains along with the Clock oscillator and FMCW signal generation circuitry (Cleanup APLL, Synthesizer, frequency multipliers etc.). Radar Subsystem is responsible for initializing and calibrating the Analog/RF modules. Also it periodically monitors the Analog/RF functionality to ensure all the Analog/RF modules work in their defined limits. This functionality can be configured through mmwavelink Monitoring APIs by MSS/DSS application with various mode and reporting options.
TOP, Master, and DSP subsystem contain various memory and digital components which have safety diagnostic features. These features can be configured and verified using Safety Diagnostic Library to manage both systematic and random faults of the device.
Figure 2-2 shows all the safety components of mmwave sensor device, which might differ for different device variants.
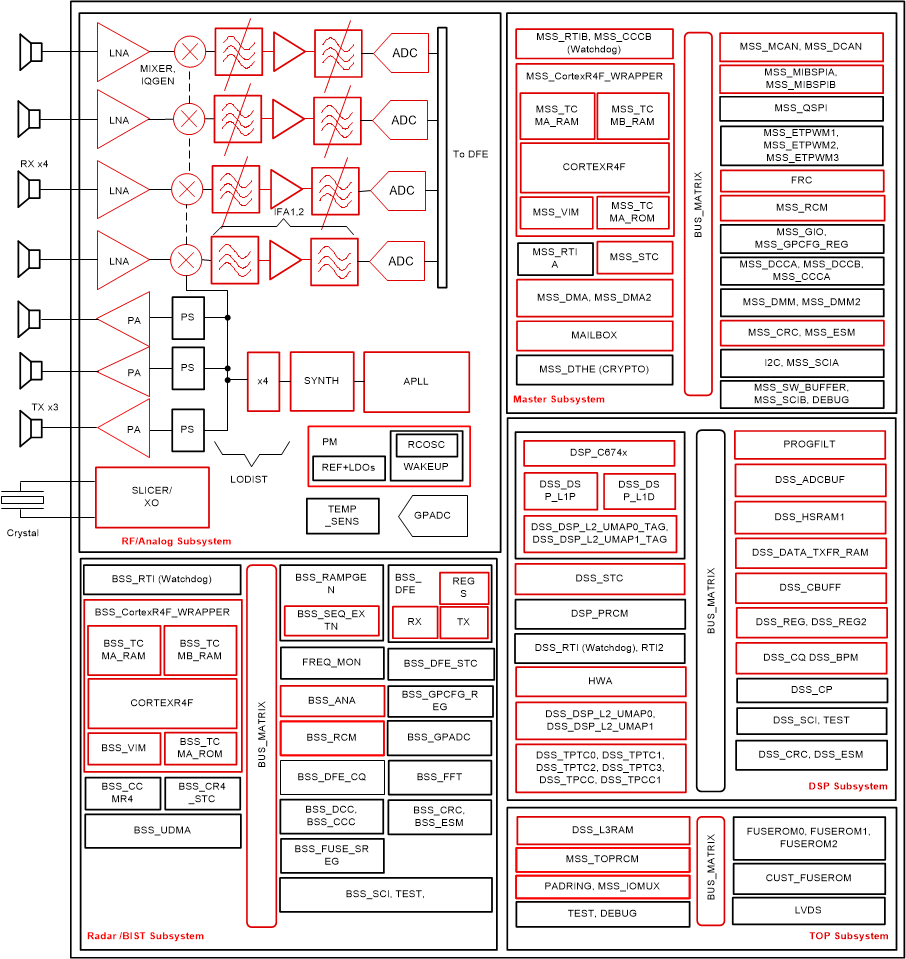 Figure 2-2 mmWave Safety
Components
Figure 2-2 mmWave Safety
Components