TIDUEZ1 March 2021
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- 5
- 1System Description
-
2System Overview
- 2.1 Block Diagram
- 2.2
Design Considerations
- 2.2.1 Multichannel SSR with Independent Isolation Between SSR Channels
- 2.2.2 Design Challenge With Single Isolation
- 2.2.3 Multichannel SSR Drive With Single Isolation Multichannel Digital Isolator
- 2.2.4 Need of High-Impedance Voltage Translator
- 2.2.5 Design to Minimize Cross-Coupling and MOSFET Gate Pick up Due to Other SSR Switching
- 2.2.6 Schematic: Design of Gate-Drive Circuit
- 2.2.7 Schematic: Digital Isolator Circuit
- 2.2.8 Schematic: 3.3 V to 10V_ISO, 5V_ISO Power Supply
- 2.3 Highlighted Products
- 3Hardware, Software, Testing Requirements, and Test Results
- 4Design and Documentation Support
- 5About the Author
2.2.8 Schematic: 3.3 V to 10V_ISO, 5V_ISO Power Supply
Figure 2-12 shows the open-loop flyback power supply. Figure 2-13 shows the TIMER circuit to generate the pulse-width modulation (PWM) signal. The power supply does not have a closed loop to control the output voltage. The output voltage will be decided based on the output load. The output load will be minimum when all the SSRs are off and maximum when all the SSRs are OFF. The flyback is designed to ensure that the output voltage variation is within 7–10 V during the load change. Table 2-2 shows the design specification of the flyback power supply.
| Parameter | Minimum | Typical | Maximum | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flyback Input Voltage | 3.2 V | 3.3 V | 3.4 V | Assuming 2% tolerance |
| Output Voltage | 6.5 V | 8.5 V | 10 V | |
| Output Current | 5.5 mA | 10.2 mA | 15 mA | Typ value when half of the SSR are ON |
The flyback transformer used in the reference design board is the coupled inductor 744889030330 (Wurth). The coupled inductor has a turns ratio of 1:3 and primary inductance of 33 µH. The PWM frequency used is 250 kHz with a 34% duty cycle. An alternate part for the flyback transformer could be LPR4012-223DMR (Coil Craft) having 1:3 turns ratio and 22-µH primary inductance. With the couple inductor LPR4012-223DMR, the frequency used should be around 400 kHz. MOSFET Q1 is a logic FET to enable switching with a 3.3-V supply. The selected coupled inductor should provide sufficient function isolation voltage for the 24-VAC supply operation.
The TLC555 timer is configured to create a PWM frequency of 250 kHz at a 34% duty cycle. The designer can also generate a PWM from the MCU and connect to pin 9 of connector J3. If the PWM from the timer is used, then populate R15 and do not populate R26. If PWM from the MCU is used, then populate R26 and do not populate R15. The diodes D7 and D6 in the TIMER circuit are used to generate PWM frequency less than 50%. The resistors R16, R17, and capacitor C14 are tuned to get the desired frequency and duty cycle. See the TLC555 LinCMOS™ Timer Data Sheet for detailed design. The PWM from the timer or MCU is connected to the input of the buffer U6 (SN74LV1T34DCKR) and the gate resistor used is 100 Ω. Make sure that the resistor R12 is not populated. The MOSFET Q1 can be driven directly from the MCU as well (with a minimum 4- to 6-mA drive capacity from the MCU), and in that case remove U6 and populate R12 with a 0-Ω resistor. The gate resistance R7 should be increased to limit the MCU pin current.
The linear regulator TLV76050 generates 5V_ISO from the 10V_ISO. The 5V_ISO is used as secondary side supply for ISO7760 and ISO7740 digital isolators. The 10V_ISO (In schematic Figure 2-12, the 10V_ISO node is marked as 12V_ISO) is used as the power supply for the gate-driver circuit of SSR MOSFET (by connecting R8 and removing R9). The secondary side of the digital isolator can be powered with 3.3 V as well and in that case a 3.3-V output regulator can be used. The TLV70433 is a recommended 3.3-V regulator option in case an ultra-low quiescent current is required.
The resistor R5 is used at the output of the flyback to ensure the minimum load to ensure no load voltage regulation within control. The Zener diode D2 is used as a voltage clamp for overvoltage protection. IN1 – IN10 are the relay on and relay off control signal from the MCU for the SSR channels 1 to 10, in order. The VGD_ISO is the supply to the gate-drive PNP transistor. The VGD_ISO is connected to the 10-V supply by populating R8. The resistor R9 is not populated. The reference design uses 3.3-V voltage at the input of the isolated power supply by keeping R2 populated and R4 not populated.
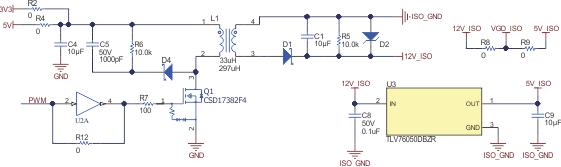 Figure 2-12 Open-Loop Flyback Power Supply
Figure 2-12 Open-Loop Flyback Power Supply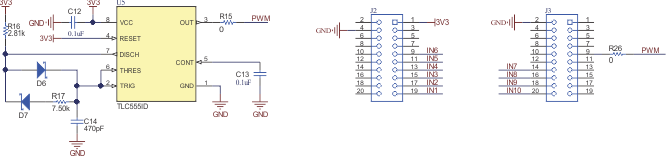 Figure 2-13 TIMER to Generate PWM Signal and
Interface Connector
Figure 2-13 TIMER to Generate PWM Signal and
Interface Connector