TIDUEZ6 December 2021 TPS62912 , TPS62913
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- 5
- 1System Overview
- 2Hardware, Software, Testing Requirements, and Test Results
- 3Design and Documentation Support
- 4About the Author
- 5Acknowledgement
1.4.2 Clock Jitter and System SNR
The ADC SNR degrades due to external clock jitter and internal ADC aperture jitter. SNR of the ADC, limited by the total jitter, is calculated as in Equation 1:
SNR of the ADC is also affected by the quantization noise of the ADC, thermal noise, and jitter. The effective SNR of ADC that includes all of these artifacts can be represented using Equation 2:
Figure 1-5 shows the effective SNR of a 14-bit ADC from Texas Instruments. The external clock jitter depends on the clock generator section and should be designed in such a way that it is not limiting the ADC SNR performance.
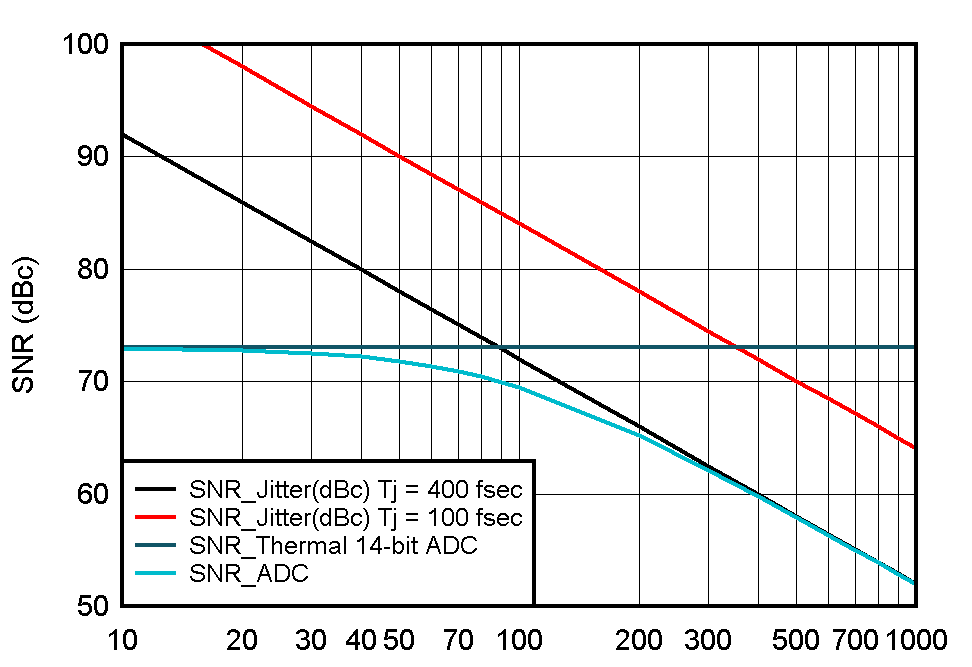 Figure 1-5 SNR Performance vs Input
Frequency
Figure 1-5 SNR Performance vs Input
Frequency