TIDUF05 August 2022
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- 5
- 1System Description
- 2System Overview
- 3Hardware, Testing Requirements, and Test Results
- 4Design and Documentation Support
- 5Documentation Support
- 6Support Resources
- 7Trademarks
4.1.3.2 PMIC Layout Recommendations
The PMIC portion of the layout requires careful consideration to minimize both PCB area and noise. As EMI is a critical concern in automotive systems, the TPS650330-Q1 device includes a spread spectrum feature to reduce conducted and radiated emissions, allowing more flexibility with placement and layout for space-constrained applications. However, it is still recommended to follow as many best practices as possible. This includes minimizing the area traveled by switching currents between buck regulator input capacitor, inductor, and output capacitor with tight component placement and minimal return path to the PMIC thermal pad. Figure 4-1 shows an example of this for buck 1 and buck 3.
For the LDO, separation of input and output capacitor ground planes will reduce noise coupling from the switching rails to the sensitive 2.8-V analog rail. To further reduce noise coupling, the dedicated AGND pin of the PMIC is connected to the ground plane on an internal layer with a via, rather than directly to the noisier thermal pad on the top layer.
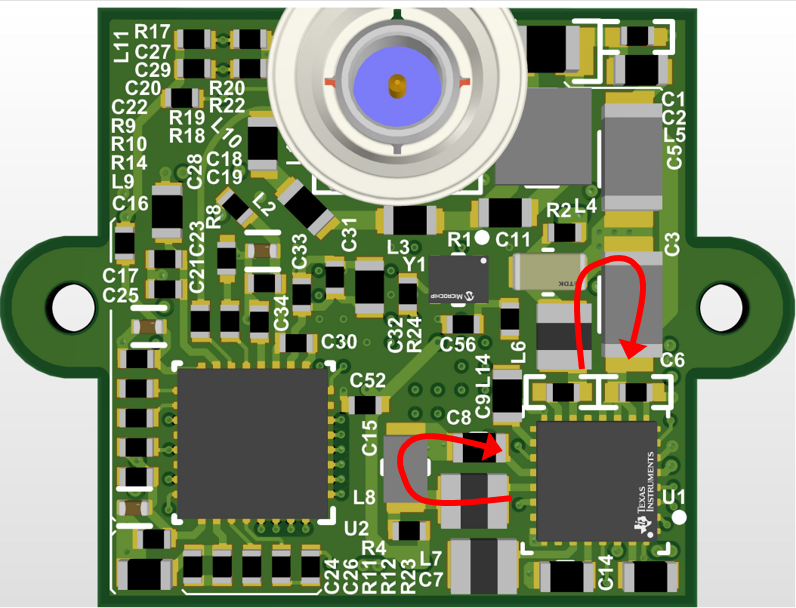 Figure 4-1 PMIC PCB Layout
Figure 4-1 PMIC PCB Layout