TIDUF13 November 2022 ADS117L11 , ADS127L11
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- 5
- 1System Description
- 2System Overview
- 3System Design Theory
- 4Hardware, Software, Testing, and Test Results
- 5Design and Documentation Support
- 6About the Author
3.1.1.2 Excitation, Output Bias Voltage, and Output Impedance
As previously mentioned, the output voltage of the IEPE sensor can be as large as ±10 V. To avoid the requirement of a dual supply, the AC output of the IEPE sensor is shifted with a certain constant voltage called output bias voltage, which is typically in the range of 9 V to 12 V. Having the AC signal superimposed on the DC output bias voltage dictates a minimum compliance voltage from the current source supplying the sensor not to have signal clipping. This compliance voltage is also called excitation voltage. Excitation voltage is simply the maximum possible output bias voltage added to the maximum AC voltage output.
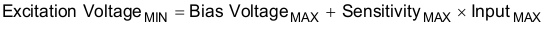
A value of 18 V to 22 V is typical for excitation voltage. An upper maximum also exists for the excitation voltage that must not be exceeded to avoid damaging the sensor electronics.
Output impedance is the effective AC output impedance seen by the interface circuit. Typical values are 300 Ω down to below 100 Ω. A lower impedance means less error in measurement when considering the finite input impedance of the interface circuit.