TIDUF18A October 2022 – February 2024
- 1
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- 6
- 1 CLLLC System Description
- 2 CLLLC System Overview
- 3 Totem Pole PFC System Description
- 4 Highlighted Products
-
5 Hardware, Software, Testing Requirements, and Test Results
- 5.1 Required Hardware and Software
- 5.2
Testing and Results
- 5.2.1 Test Setup (Initial)
- 5.2.2
CLLLC Test Procedure
- 5.2.2.1 Lab 1. Primary to Secondary Power Flow, Open Loop Check PWM Driver
- 5.2.2.2
Lab 2. Primary to Secondary Power Flow, Open Loop CheckPWM
Driver and ADC with Protection, Resistive Load Connected on Secondary
- 5.2.2.2.1 Setting Software Options for Lab 2
- 5.2.2.2.2 Building and Loading the Project and Setting up Debug Environment
- 5.2.2.2.3 Using Real-time Emulation
- 5.2.2.2.4 Running the Code
- 5.2.2.2.5 Measure SFRA Plant for Voltage Loop
- 5.2.2.2.6 Verify Active Synchronous Rectification
- 5.2.2.2.7 Measure SFRA Plant for Current Loop
- 5.2.2.3 Lab 3. Primary to Secondary Power Flow, Closed Voltage Loop Check, With Resistive Load Connected on Secondary
- 5.2.2.4 Lab 4. Primary to Secondary Power Flow, Closed Current Loop Check, With Resistive Load Connected on Secondary
- 5.2.2.5 Lab 5. Primary to Secondary Power Flow, Closed Current Loop Check, With Resistive Load Connected on Secondary in Parallel to a Voltage Source to Emulate a Battery Connection on Secondary Side
- 5.2.3 TTPLPFC Test procedure
- 5.2.4 Test Results
- 6 Design Files
- 7 Software Files
- 8 Related Documentation
- 9 Terminology
- 10About the Author
- 11Revision History
2.2 Design Considerations and System Design Theory
LLC converters are widely popular due to their ability to achieve ZVS at the primary side, and ZCS on the secondary side. A typical LLC Series Resonant Converter (SRC) is shown in Figure 2-2. The primary side of this converter is half bridge; thus, the transformer utilization from a Volt-sec perspective is half. In addition, the current rating for the switches is twice of what is needed, compared to when a full-bridge structure is used.
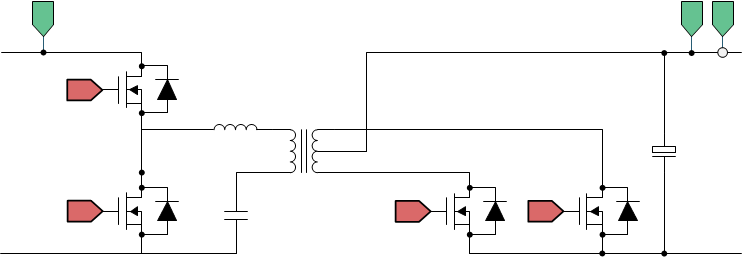 Figure 2-2 LLC Half-Bridge SRC
Figure 2-2 LLC Half-Bridge SRCAlthough half-bridge LLC SRCs are attractive at lower power for cost reasons, for high-power and high-density applications, a full-bridge LLC SRC is desired for the following reasons:
- A full-bridge LLC converter better utilizes the magnetic core of the transformer on both the secondary side and primary side; therefore, it is able to offer better power density.
- A full-bridge LLC converter reduces current rating; and therefore, reduces the cost of copper in wires. The converter also enables higher power (compared to half-bridge SRCs) to be achieved with the same copper wires.
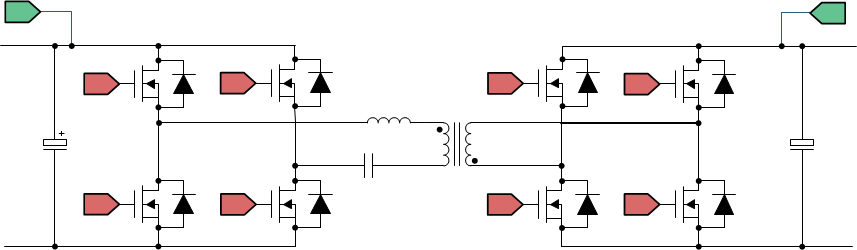 Figure 2-3 Full-Bridge LLC Converter
Figure 2-3 Full-Bridge LLC ConverterA full-bridge LLC converter, as shown in Figure 2-3, falls under the broad category of Dual Active Bridge (DAB) converters. Under DAB converters, the converter can be classified on the basis of model or operation:
- A phase-shifted DAB converter is one of the most popular converters historically.
- Resonant DAB converters have different variants on resonant tanks (LC, LLC, CLLC, CLLLC, and so forth).
Resonant DAB converters are of interest because high efficiency, high power, and high density are achievable with such converters. CLLLC, with its symmetric tank, is capable of bidirectional operation. The problem with using an LLC structure for bidirectional use is that the switching frequency, when operating in the reverse power flow mode, is governed by the transformer winding capacitance and the leakage inductance. This offers little or no control on the gain of the power stage and the switching frequency. Therefore, the CLLLC type of structure is preferred as it offers much better control on the switching frequency and an additional degree of freedom on the gain.