TIDUF18A October 2022 – February 2024
- 1
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- 6
- 1 CLLLC System Description
- 2 CLLLC System Overview
- 3 Totem Pole PFC System Description
- 4 Highlighted Products
-
5 Hardware, Software, Testing Requirements, and Test Results
- 5.1 Required Hardware and Software
- 5.2
Testing and Results
- 5.2.1 Test Setup (Initial)
- 5.2.2
CLLLC Test Procedure
- 5.2.2.1 Lab 1. Primary to Secondary Power Flow, Open Loop Check PWM Driver
- 5.2.2.2
Lab 2. Primary to Secondary Power Flow, Open Loop CheckPWM
Driver and ADC with Protection, Resistive Load Connected on Secondary
- 5.2.2.2.1 Setting Software Options for Lab 2
- 5.2.2.2.2 Building and Loading the Project and Setting up Debug Environment
- 5.2.2.2.3 Using Real-time Emulation
- 5.2.2.2.4 Running the Code
- 5.2.2.2.5 Measure SFRA Plant for Voltage Loop
- 5.2.2.2.6 Verify Active Synchronous Rectification
- 5.2.2.2.7 Measure SFRA Plant for Current Loop
- 5.2.2.3 Lab 3. Primary to Secondary Power Flow, Closed Voltage Loop Check, With Resistive Load Connected on Secondary
- 5.2.2.4 Lab 4. Primary to Secondary Power Flow, Closed Current Loop Check, With Resistive Load Connected on Secondary
- 5.2.2.5 Lab 5. Primary to Secondary Power Flow, Closed Current Loop Check, With Resistive Load Connected on Secondary in Parallel to a Voltage Source to Emulate a Battery Connection on Secondary Side
- 5.2.3 TTPLPFC Test procedure
- 5.2.4 Test Results
- 6 Design Files
- 7 Software Files
- 8 Related Documentation
- 9 Terminology
- 10About the Author
- 11Revision History
5.2.2.4.1 Setting Software Options for Lab 4
- Open <install Directory>\C2000Ware_DigitalPower_SDK_<version>\libraries\sfra\gui\CompDesigner.exe
- The compensation designer will then launch and prompt the user to select a valid SFRA data file. Import the SFRA data from the run in Lab 1 for the current loop, into the compensation designer to design a two-pole, two-zero compensator. It is good to keep more margins during this iteration of the design to ensure that when the loop is closed, the system is stable. Plant data from different runs of the SFRA can be checked to get a stable system under all conditions.
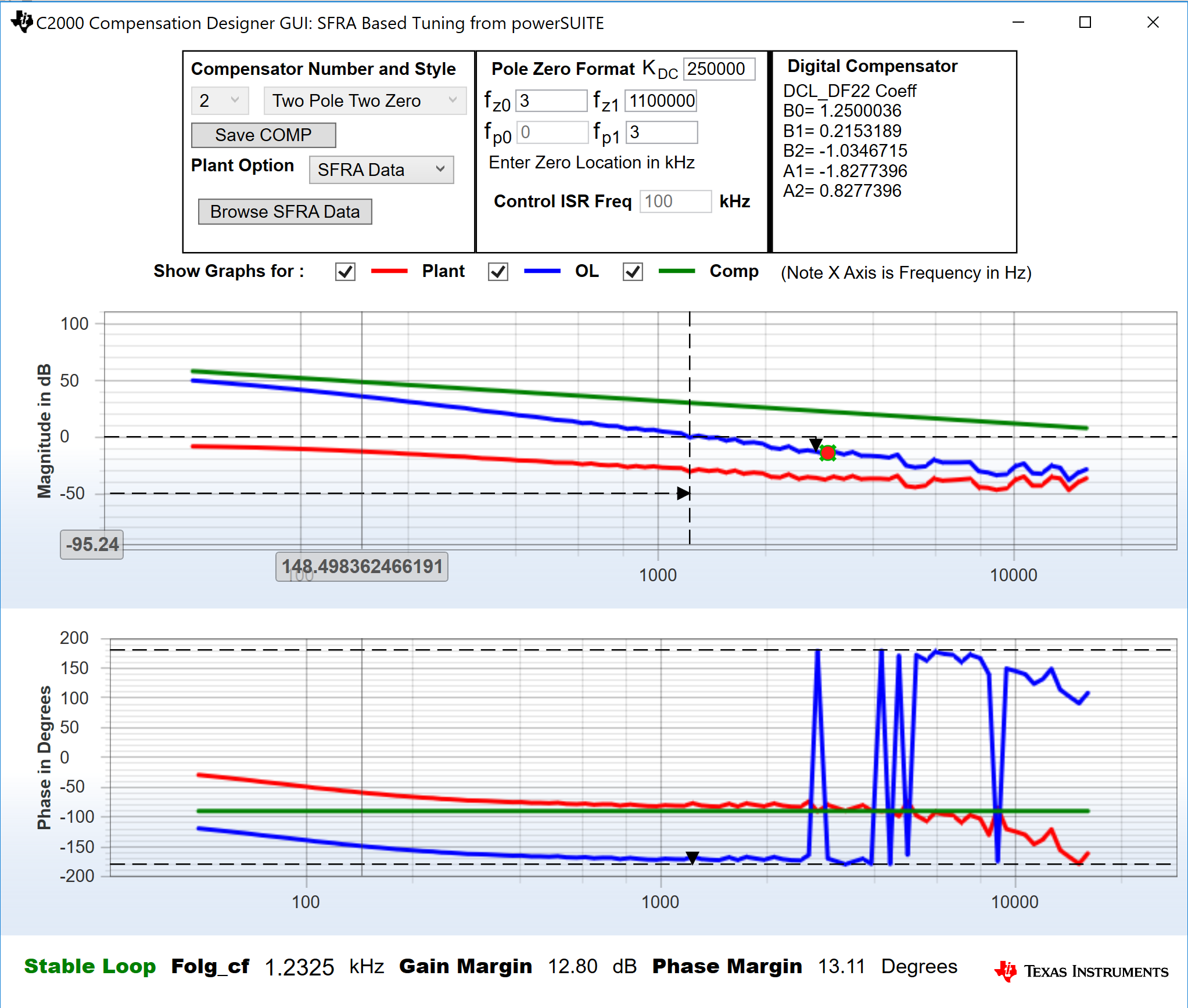 Figure 5-24 Compensator Design With SFRA Based Plant Measurement for the Current Loop, Lab 4Note:
Figure 5-24 Compensator Design With SFRA Based Plant Measurement for the Current Loop, Lab 4Note:The tuning is carried out in DF22 fashion; however, we run the DF13 in the software. This is done because soft-starting the DF13 is easier, whereas not possible with the DF22 structure. The coefficients in both cases remain the same. At the writing of this document, the DF12 structure is not available in DCL.
- Once satisfied with the compensator design, The compensator values can be updated in the CLLLC_settings.h file.
- Close the compensation designer
- The following defines are set in the
settings.h file for this build.
#if CLLLC_LAB == 4 #define CLLLC_CONTROL_RUNNING_ON CLA_CORE #define CLLLC_POWER_FLOW CLLLC_POWER_FLOW_PRIM_SEC #define CLLLC_INCR_BUILD CLLLC_CLOSED_LOOP_BUILD #define CLLLC_CONTROL_MODE CLLLC_CURRENT_MODE #define CLLLC_TEST_SETUP CLLLC_TEST_SETUP_RES_LOAD #define CLLLC_PROTECTION CLLLC_PROTECTION_ENABLED #if CLLLC_SFRA_ALLOWED == 1 #define CLLLC_SFRA_TYPE CLLLC_SFRA_CURRENT #else #define CLLLC_SFRA_TYPE CLLLC_SFRA_DISABLED #endif #define CLLLC_SFRA_AMPLITUDE (float32_t)CLLLC_SFRA_INJECTION_AMPLITUDE_LEVEL1 #endif