TIDUF60 December 2023
- 1
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- 6
- 1System Description
-
2System Overview
- 2.1 Block Diagram
- 2.2 Design Considerations
- 2.3 Highlighted Products
- 2.4 System Design Theory
-
3Hardware, Software, Testing Requirements, and Test Results
- 3.1 Getting Started Hardware
- 3.2 Getting Started GUI
- 3.3
Getting Started C2000 Firmware
- 3.3.1 Download and Install Software Required for Board Test
- 3.3.2 Opening Project Inside CCS
- 3.3.3 Project Structure
- 3.3.4 Test Procedure
- 3.4 Test Results
- 3.5 Migrate Firmware to a New Hardware Board
- 3.6 Getting Started MSPM0 Firmware
- 4Design and Documentation Support
- 5About the Author
2.4.2.4.1.2 Single-Shunt Current Sensing
The single-shunt current-sensing technique measures the DC-link bus current, with knowledge of the power FET switching states and reconstructs the three-phase current of the motor. The detailed description of the single shunt technique is described in the Sensorless-FOC for PMSM With Single DC-Link Shunt application note.
On this reference board, implement the single-shunt current-sensing technique by removing two shunts and shorting the connection of the U, V, W ground of the power module as shown in Figure 2-32.
- On the motherboard, remove current shunt resistors R81, and R82, just keep only shunt resistor R80 to sense the DC-Link current.
- On TMS320F2800137 daughterboard, remove C86 to increase U2A bandwidth for single-shunt sampling.
- On the MSPM0G1507 daughterboard, remove C29 to increase the bandwidth for single-shunt sampling.
- Use a thick wire to connect the NU, NV, and NW pins together.

 Figure 2-32 Single-Shunt Current-Sensing Circuit for TMS320F2800137
Figure 2-32 Single-Shunt Current-Sensing Circuit for TMS320F2800137Figure 2-33 shows the single-shunt current-sensing circuit for the MSPM0G1507 daughterboard.
 Figure 2-33 MSPM0G1507 Single-Shunt Current-Sensing Circuit
Figure 2-33 MSPM0G1507 Single-Shunt Current-Sensing CircuitBy default, the board has three shunt resistors, Figure 2-34 shows the layout of the shunt resistors. To run with a single-shunt resistor, remove R81 and R82 while keeping R80, solder NU, NV and NW (pin 2 of R80, R81, and R82) together, then all three phase currents flow through only R80.
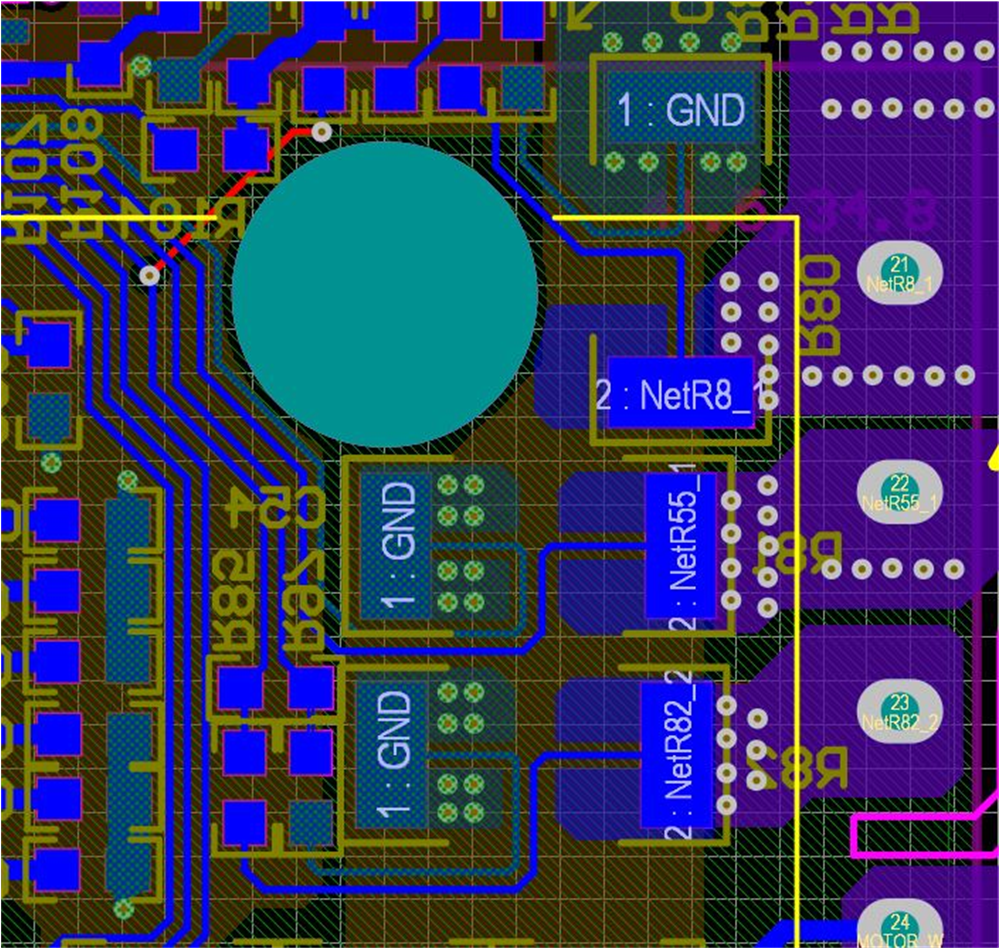 Figure 2-34 Shunt Resistors Layout
Figure 2-34 Shunt Resistors LayoutThe DC-Link current is a unidirectional signal, so the DC current offset can be set to a minimum or maximum value to improve the ADC sampling range for the DC-Link current as Figure 2-35 shows. On the TMS320F2800137 daughterboard, change R7 from 10 kΩ to 1 kΩ/1% resistor for the reference voltage to have 0.3-V offset for DC current sensing.
 Figure 2-35 DC Offset Reference for Single Shunt of TMS320F2800137 Daughterboard
Figure 2-35 DC Offset Reference for Single Shunt of TMS320F2800137 DaughterboardThe transfer function of this current sampling circuit and the calculation for single shunt are the same as the three shunts.
For the MSPM0 daughterboard, offset for single-shunt current sensing can also be reduced to 0.3 V by reducing R31 from 20 kΩ to 2 kΩ, as shown in Figure 2-33.