TIDUF67 April 2024
- 1
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- 6
- 1System Description
- 2System Overview
- 3System Design Theory
-
4Hardware, Software, Testing Requirements,
and Test Results
- 4.1 Hardware Requirements
- 4.2 Software Requirements
- 4.3 Test Setup
- 4.4 Test Results
- 4.5 Adding Additional Functionality to Motor Control Project
- 4.6 Building a Custom Board
- 5General Texas Instruments High Voltage Evaluation (TI HV EVM) User Safety Guidelines
- 6Design and Documentation Support
- 7About the Author
4.6.1.2.4 Configuring the PWM Module
The SysConfig file configures the PWM channels. The base addresses of the PWM channels that are used for the motor controller PWM inputs are defined in the hal.h file, and the base addresses are assigned to the PWM handles in the hal.c file. The connection diagram for the PWM signals between the LP-AM263 and BOOSTXL-3PHGANINV is shown in Figure 4-47.
 Figure 4-47 PWM Connection Diagram
Figure 4-47 PWM Connection DiagramThe code to configure the PWM signals is shown in the following, taken from the .syscfg, hal.h and hal.c files.
The base addresses of the PWM modules are defined in the hal.h file as shown in the following.
#define MTR1_PWM_U_BASE CONFIG_EPWM13_BASE_ADDR #define MTR1_PWM_V_BASE CONFIG_EPWM3_BASE_ADDR #define MTR1_PWM_W_BASE CONFIG_EPWM9_BASE_ADDRThe GPIOs are set up as PWM outputs in the .syscfg file.
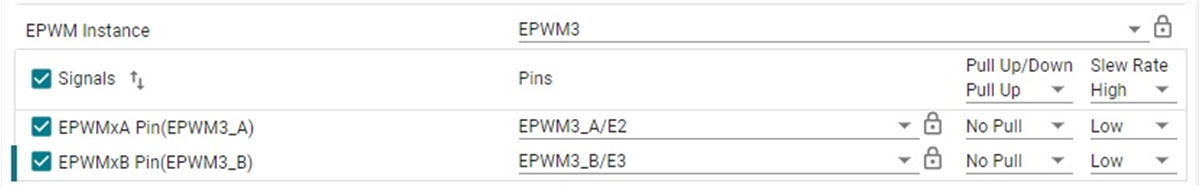 Figure 4-48 GPIO Configuration for
PWM Modules
Figure 4-48 GPIO Configuration for
PWM Modules- The following code assigns the corresponding base
addresses of the PWM modules to the PWM handle in the HAL_MTR1_init() function
that is located in the hal.c file. The following code does not need to be
changed when adapting the code to a new board or TI MCU, the following code
block shows how the PWM handle is initialized in the
code.
// initialize PWM handles for Motor 1 obj->pwmHandle[0] = MTR1_PWM_U_BASE; //!< the PWM handle obj->pwmHandle[1] = MTR1_PWM_V_BASE; //!< the PWM handle obj->pwmHandle[2] = MTR1_PWM_W_BASE; //!< the PWM handle - Figure 4-49 shows the EPWM time base configuration. Sync out pulse for phase A is used as
sync in pulse source for other PWMs.
 Figure 4-49 EPWM Time Base
Configuration
Figure 4-49 EPWM Time Base
ConfigurationEPWM Action Qualifier Configurationshows the EPWM action qualifier output event configuration forLP-AM263 and BOOSTXL-3PHGANINV combination. PWM action qualifier outputs need to be set up based on the hardware board.
 Figure 4-50 EPWM Action Qualifier
Configuration
Figure 4-50 EPWM Action Qualifier
ConfigurationFigure 4-51 shows the EPWM dead-band configuration for LP-AM263 . Swap output is checked for EPWMxA-B to match the high side and low side PWMs in LaunchPad™ and Booster Pack™.
 Figure 4-51 EPWM Dead-Band
Configuration
Figure 4-51 EPWM Dead-Band
Configuration