TIDUFA8 November 2024
- 1
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- 6
- 1System Description
- 2System Overview
- 3System Design Theory
- 4Link Budget
- 5Hardware, Software, Testing Requirements and Test Results
- 6Design and Documentation Support
- 7About the Authors
2.4 IWRL6432 Reference Design Architecture
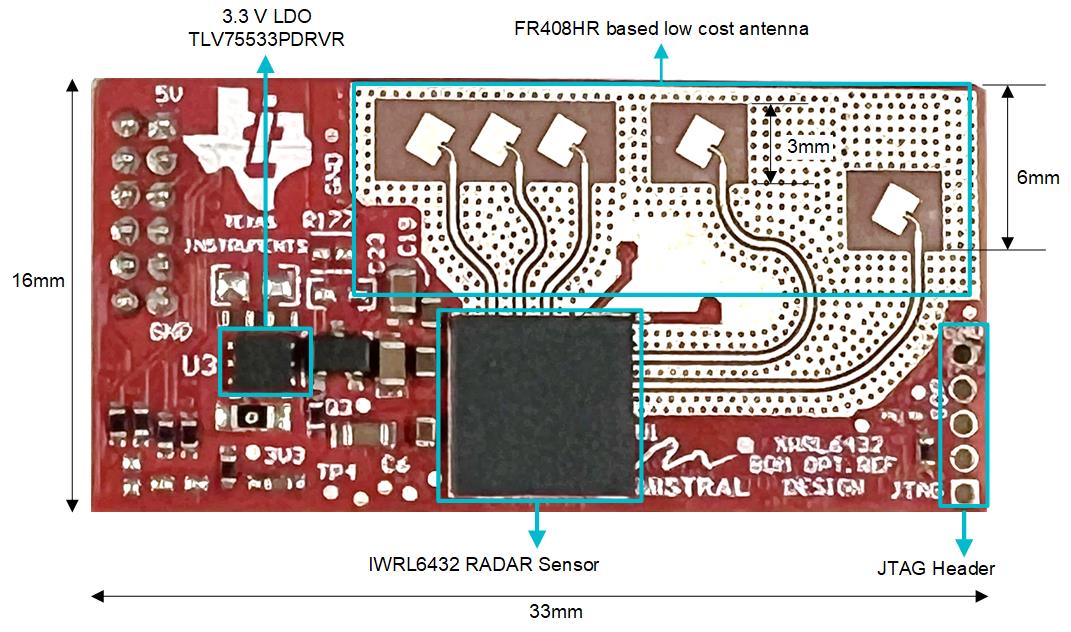
Figure 2-2 Board Labeling Front View: 2D Antenna
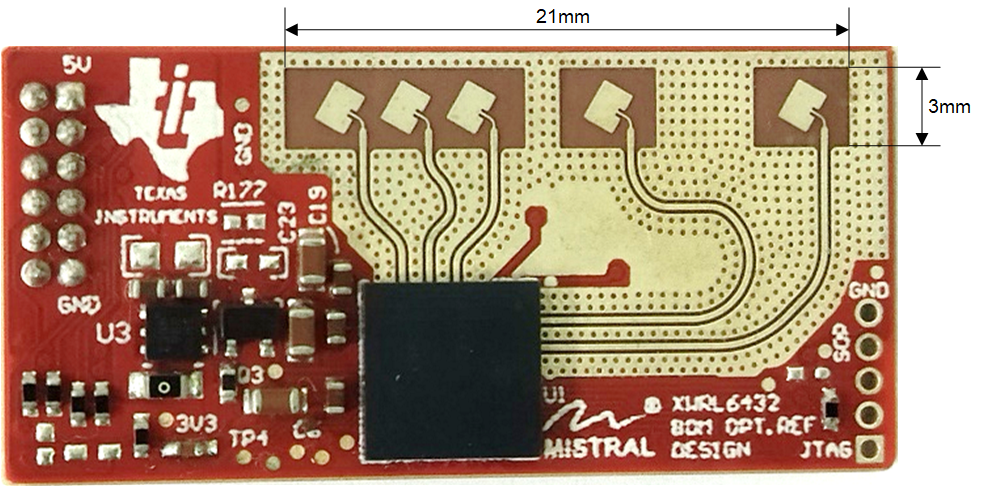
Figure 2-3 Board Labeling Front View: 1D Antenna
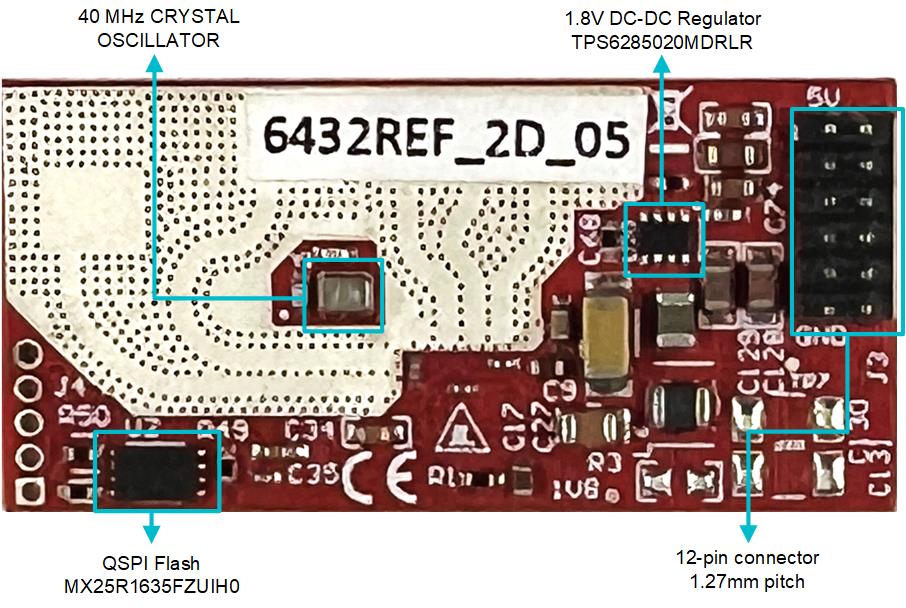
Figure 2-4 Board Labeling Back View

Figure 2-5 12-Pin Connector Details
Primary radar SOC: IWRL6432.
Additional FLASH memory: MX25R1635F.
Power distribution network: TPS6285020M (1.8V supply), TLV75533P (3.3V supply)
Connector: 1.27mm pitch 12-pin male header. Figure 2-5 provides details about the connector.
Interface options: UART (RS232), SPI and I2C with 2 GPIOs and 1 optional JTAG interface.
Note: If JTAG needs to be used, SOP0 is not recommended to be
directly connected to power lines (VIO or GND). In that case a pull-up pull-down
network can be used. For more details on SOP circuits, please refer to the IWRL6432BOOST EVM design files.
This section explains the design architecture in terms of the on-board and on-chip power distribution network and the component selection. This discussion includes several cost reduction techniques that have been followed to optimize the BOM of the reference design.