TIDUFA8 November 2024
- 1
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- 6
- 1System Description
- 2System Overview
- 3System Design Theory
- 4Link Budget
- 5Hardware, Software, Testing Requirements and Test Results
- 6Design and Documentation Support
- 7About the Authors
3.5.2.2 Ground Return Path
The recommendation is to follow this design practice for all the on-chip LDO outputs to maintain shortest forward path.
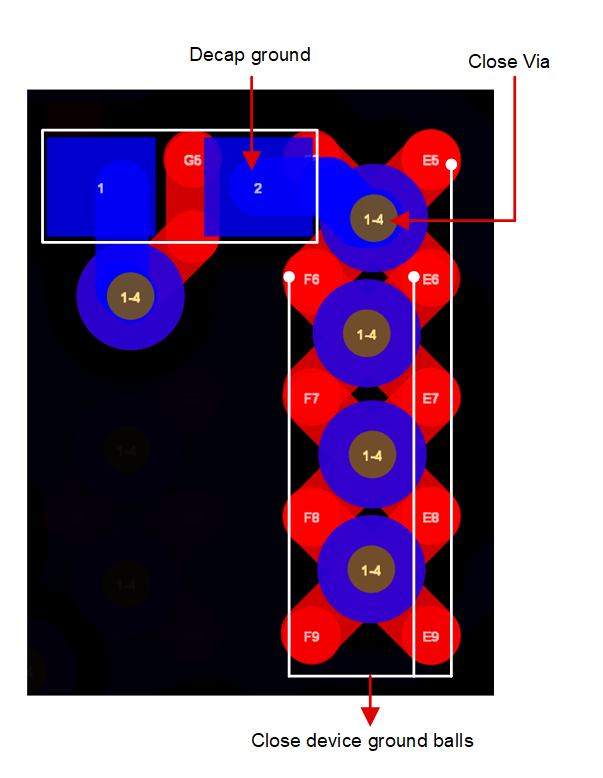
Figure 3-31 Ground Return Path
An output path that can potentially act as a source of out-of-spec parasitic values consists of two elements:
- The forward path, that connects the BGA balls to the capacitor lead
- the ground return path that connects the capacitor ground to the device ground to close the loop. Figure 3-31 is a good example of ground return path.
As we can see in Figure 3-31, the decap ground is connected to a via which is placed very close to the ground lead of the capacitor. Further, the device ground is also very close to the via. This provides the shortest ground return path for the signal.